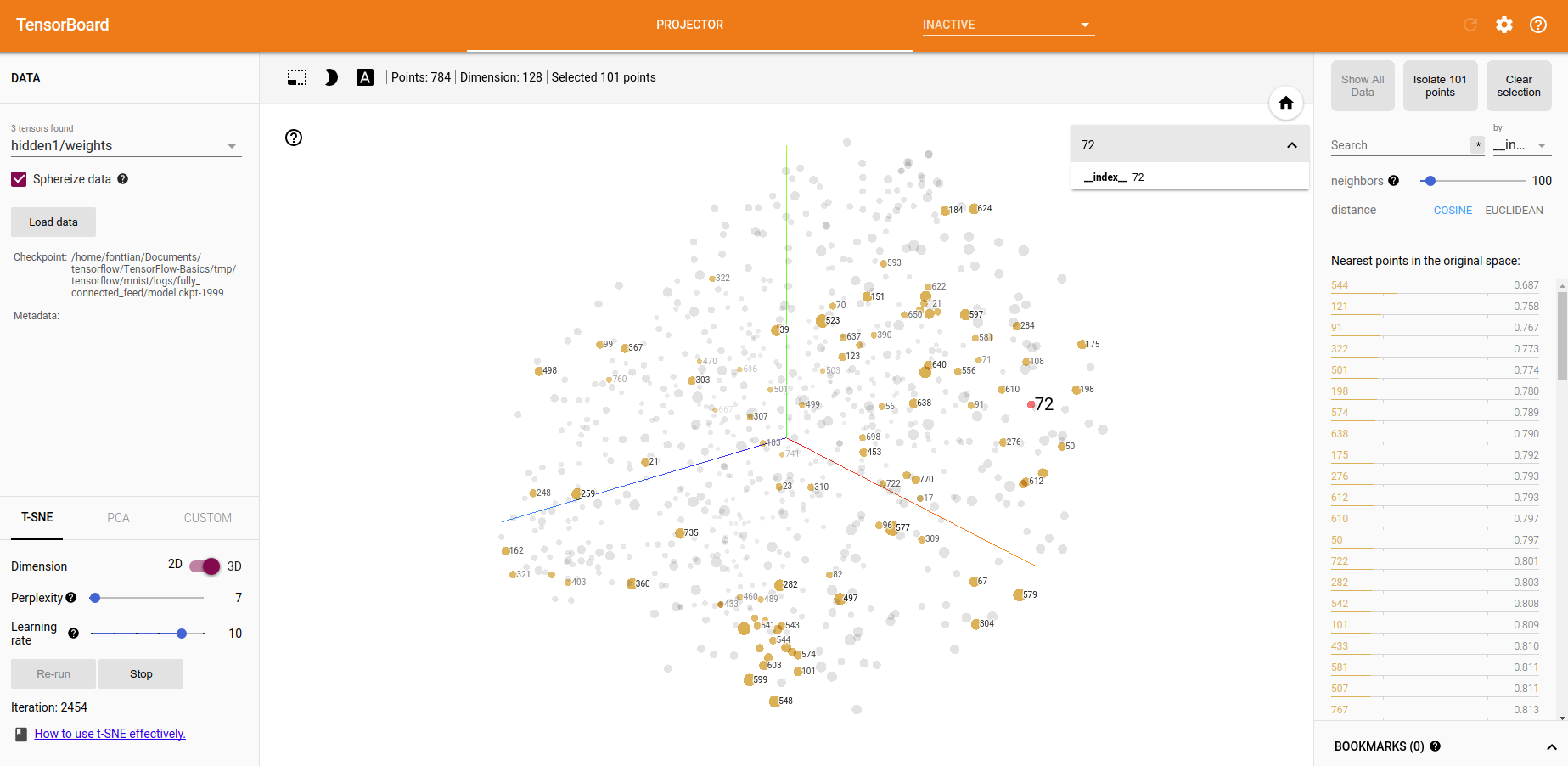
简介
这部分代码来自tensorflow的源码,代码中的注释相当的详细,假如对于9.2 你已经比较详细,那么我建议您运行这份源码示例.他会给你很好的帮助.
这份代码主要展示了projector模块(当然你也可以结合9.2 进行扩展),其中的T-SNE以及PCA都是官方提供的可视化方案,很有意思.
关键点
- argparse : python的一个类库python中的argparse模块
- fill_feed_dict: tensorflow中的一种数据类型,其实就是tf版本的字典
代码
# - * - coding: utf - 8 -*-
# 作者:田丰(FontTian)
# 创建时间:'2017/8/7'
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
"""Trains and Evaluates the MNIST network using a feed dictionary."""
# pylint: disable=missing-docstring
import argparse
import os.path
import sys
import time
from six.moves import xrange # pylint: disable=redefined-builtin
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import mnist
# Basic model parameters as external flags.
FLAGS = None
def placeholder_inputs(batch_size):
"""Generate placeholder variables to represent the input tensors.
These placeholders are used as inputs by the rest of the model building
code and will be fed from the downloaded data in the .run() loop, below.
Args:
batch_size: The batch size will be baked into both placeholders.
Returns:
images_placeholder: Images placeholder.
labels_placeholder: Labels placeholder.
"""
# Note that the shapes of the placeholders match the shapes of the full
# image and label tensors, except the first dimension is now batch_size
# rather than the full size of the train or test data sets.
images_placeholder = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(batch_size,
mnist.IMAGE_PIXELS))
labels_placeholder = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=(batch_size))
return images_placeholder, labels_placeholder
def fill_feed_dict(data_set, images_pl, labels_pl):
"""Fills the feed_dict for training the given step.
A feed_dict takes the form of:
feed_dict = {
<placeholder>: <tensor of values to be passed for placeholder>,
....
}
Args:
data_set: The set of images and labels, from input_data.read_data_sets()
images_pl: The images placeholder, from placeholder_inputs().
labels_pl: The labels placeholder, from placeholder_inputs().
Returns:
feed_dict: The feed dictionary mapping from placeholders to values.
"""
# Create the feed_dict for the placeholders filled with the next
# `batch size` examples.
images_feed, labels_feed = data_set.next_batch(FLAGS.batch_size,
FLAGS.fake_data)
feed_dict = {
images_pl: images_feed,
labels_pl: labels_feed,
}
return feed_dict
def do_eval(sess,
eval_correct,
images_placeholder,
labels_placeholder,
data_set):
"""Runs one evaluation against the full epoch of data.
Args:
sess: The session in which the model has been trained.
eval_correct: The Tensor that returns the number of correct predictions.
images_placeholder: The images placeholder.
labels_placeholder: The labels placeholder.
data_set: The set of images and labels to evaluate, from
input_data.read_data_sets().
"""
# And run one epoch of eval.
true_count = 0 # Counts the number of correct predictions.
steps_per_epoch = data_set.num_examples // FLAGS.batch_size
num_examples = steps_per_epoch * FLAGS.batch_size
for step in xrange(steps_per_epoch):
feed_dict = fill_feed_dict(data_set,
images_placeholder,
labels_placeholder)
true_count += sess.run(eval_correct, feed_dict=feed_dict)
precision = float(true_count) / num_examples
print(' Num examples: %d Num correct: %d Precision @ 1: %0.04f' %
(num_examples, true_count, precision))
def run_training():
"""Train MNIST for a number of steps."""
# Get the sets of images and labels for training, validation, and
# test on MNIST.
data_sets = input_data.read_data_sets(FLAGS.input_data_dir, FLAGS.fake_data)
# Tell TensorFlow that the model will be built into the default Graph.
with tf.Graph().as_default():
# Generate placeholders for the images and labels.
images_placeholder, labels_placeholder = placeholder_inputs(
FLAGS.batch_size)
# Build a Graph that computes predictions from the inference model.
logits = mnist.inference(images_placeholder,
FLAGS.hidden1,
FLAGS.hidden2)
# Add to the Graph the Ops for loss calculation.
loss = mnist.loss(logits, labels_placeholder)
# Add to the Graph the Ops that calculate and apply gradients.
train_op = mnist.training(loss, FLAGS.learning_rate)
# Add the Op to compare the logits to the labels during evaluation.
eval_correct = mnist.evaluation(logits, labels_placeholder)
# Build the summary Tensor based on the TF collection of Summaries.
summary = tf.summary.merge_all()
# Add the variable initializer Op.
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# Create a saver for writing training checkpoints.
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# Create a session for running Ops on the Graph.
sess = tf.Session()
# Instantiate a SummaryWriter to output summaries and the Graph.
summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(FLAGS.log_dir, sess.graph)
# And then after everything is built:
# Run the Op to initialize the variables.
sess.run(init)
# Start the training loop.
for step in xrange(FLAGS.max_steps):
start_time = time.time()
# Fill a feed dictionary with the actual set of images and labels
# for this particular training step.
feed_dict = fill_feed_dict(data_sets.train,
images_placeholder,
labels_placeholder)
# Run one step of the model. The return values are the activations
# from the `train_op` (which is discarded) and the `loss` Op. To
# inspect the values of your Ops or variables, you may include them
# in the list passed to sess.run() and the value tensors will be
# returned in the tuple from the call.
_, loss_value = sess.run([train_op, loss],
feed_dict=feed_dict)
duration = time.time() - start_time
# Write the summaries and print an overview fairly often.
if step % 100 == 0:
# Print status to stdout.
print('Step %d: loss = %.2f (%.3f sec)' % (step, loss_value, duration))
# Update the events file.
summary_str = sess.run(summary, feed_dict=feed_dict)
summary_writer.add_summary(summary_str, step)
summary_writer.flush()
# Save a checkpoint and evaluate the model periodically.
if (step + 1) % 1000 == 0 or (step + 1) == FLAGS.max_steps:
checkpoint_file = os.path.join(FLAGS.log_dir, 'model.ckpt')
print('***********************')
print('checkpoint_file : ',checkpoint_file)
print('***********************')
saver.save(sess, checkpoint_file, global_step=step)
# Evaluate against the training set.
print('Training Data Eval:')
do_eval(sess,
eval_correct,
images_placeholder,
labels_placeholder,
data_sets.train)
# Evaluate against the validation set.
print('Validation Data Eval:')
do_eval(sess,
eval_correct,
images_placeholder,
labels_placeholder,
data_sets.validation)
# Evaluate against the test set.
print('Test Data Eval:')
do_eval(sess,
eval_correct,
images_placeholder,
labels_placeholder,
data_sets.test)
def main(_):
if tf.gfile.Exists(FLAGS.log_dir):
tf.gfile.DeleteRecursively(FLAGS.log_dir)
tf.gfile.MakeDirs(FLAGS.log_dir)
run_training()
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
'--learning_rate',
type=float,
default=0.01,
help='Initial learning rate.'
)
parser.add_argument(
'--max_steps',
type=int,
default=2000,
help='Number of steps to run trainer.'
)
parser.add_argument(
'--hidden1',
type=int,
default=128,
help='Number of units in hidden layer 1.'
)
parser.add_argument(
'--hidden2',
type=int,
default=32,
help='Number of units in hidden layer 2.'
)
parser.add_argument(
'--batch_size',
type=int,
default=100,
help='Batch size. Must divide evenly into the dataset sizes.'
)
parser.add_argument(
'--input_data_dir',
type=str,
default='/home/fonttian/Data/MNIST_data/',
help='Directory to put the input data.'
)
parser.add_argument(
'--log_dir',
type=str,
default='tmp/tensorflow/mnist/logs/fully_connected_feed',
help='Directory to put the log data.'
)
parser.add_argument(
'--fake_data',
default=False,
help='If true, uses fake data for unit testing.',
action='store_true'
)
FLAGS, unparsed = parser.parse_known_args()
tf.app.run(main=main, argv=[sys.argv[0]] + unparsed)