转自: http://blog.51cto.com/linhongyu/1615895
一、前言
近期一项目A需实现数据同步到另一项目B数据库中,在不改变B项目的情况下,只好选择项目A中切换数据源,直接把数据写入项目B的数据库中。这种需求,在数据同步与定时任务中经常需要。
那么问题来了,该如何解决多数据源问题呢?不光是要配置多个数据源,还得能灵活动态的切换数据源。以spring+hibernate框架项目为例(引用:http://blog.csdn.net/wangpeng047/article/details/8866239博客的图片):

单个数据源绑定给sessionFactory,再在Dao层操作,若多个数据源的话,那不是就成了下图:

可见,sessionFactory都写死在了Dao层,若我再添加个数据源的话,则又得添加一个sessionFactory。所以比较好的做法应该是下图:
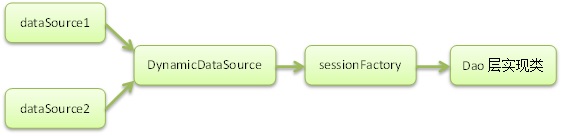
接下来就为大家讲解下如何用spring来整合这些数据源,同样以spring+hibernate配置为例。
二、实现原理
1、扩展Spring的AbstractRoutingDataSource抽象类(该类充当了DataSource的路由中介, 能有在运行时, 根据某种key值来动态切换到真正的DataSource上。)
从AbstractRoutingDataSource的源码中:
1 public abstract class AbstractRoutingDataSource extends AbstractDataSource implements InitializingBean
我们可以看到,它继承了AbstractDataSource,而AbstractDataSource不就是javax.sql.DataSource的子类,So我们可以分析下它的getConnection方法:
获取连接的方法中,重点是determineTargetDataSource()方法,看源码:
上面这段源码的重点在于determineCurrentLookupKey()方法,这是AbstractRoutingDataSource类中的一个抽象方法,而它的返回值是你所要用的数据源dataSource的key值,有了这个key值,resolvedDataSource(这是个map,由配置文件中设置好后存入的)就从中取出对应的DataSource,如果找不到,就用配置默认的数据源。
看完源码,应该有点启发了吧,没错!你要扩展AbstractRoutingDataSource类,并重写其中的determineCurrentLookupKey()方法,来实现数据源的切换:
DataSourceHolder这个类则是我们自己封装的对数据源进行操作的类:
2、有人就要问,那你setDataSource这方法是要在什么时候执行呢?当然是在你需要切换数据源的时候执行啦。手动在代码中调用写死吗?这是多蠢的方法,当然要让它动态咯。所以我们可以应用spring aop来设置,把配置的数据源类型都设置成为注解标签,在service层中需要切换数据源的方法上,写上注解标签,调用相应方法切换数据源咯(就跟你设置事务一样):
当然,注解标签的用法可能很少人用到,但它可是个好东西哦,大大的帮助了我们开发:
1 package com.datasource.test.util.database; 2 3 import java.lang.annotation.*; 4 5 @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE}) 6 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 7 @Documented 8 public @interface DataSource { 9 String name() default DataSource.master; 10 11 public static String master = "dataSource1"; 12 13 public static String slave1 = "dataSource2"; 14 15 public static String slave2 = "dataSource3"; 16 17 }
三、配置文件
为了精简篇幅,省略了无关本内容主题的配置。
项目中单独分离出application-database.xml,关于数据源配置的文件。
四、疑问
多数据源切换是成功了,但牵涉到事务呢?单数据源事务是ok的,但如果多数据源需要同时使用一个事务呢?这个问题有点头大,网络上有人提出用atomikos开源项目实现JTA分布式事务处理。你怎么看?
五、dataSourceExchange 是怎样写的?
dataSourceExchange对应的类可以实现接口org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor的invoke方法|@|@Override|@|public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {|@| DataSource dataSource = invocation.getMethod().getAnnotation(DataSource.class); |@| DataSourceHolder.setDataSource(dataSource.name());|@| try {|@| invocation.proceed();|@| } catch (Exception ex) { |@| }|@| return null;|@|}|@|pointcut的expression也可以写成@annotation(com.xxx.DataSource)|@|使用的时候,只需要在方法上加上注解@DataSource就行了|@|@DataSource(name = DataSource.slave1)|@|public void insert(String name) {|@|}