首先我们给出大小端的定义:
小端:较高的有效字节存放在较高的的存储器地址,较低的有效字节存放在较低的存储器地址。
大端:较高的有效字节存放在较低的存储器地址,较低的有效字节存放在较高的存储器地址。
将0x12345678写入到以1000h开始的内存中,这里0x12346578中0x12~0x78的地址是从高到低
如果,我们的机器是小端存储的话,结果为:
数据 地址
0x78 1000H
0x56 1001H
0x34 1002H
0x12 1003H
如果我们的机器是大端存储的话,结果为:
数据 地址
0x12 1000H
0x34 1001H
0x56 1002H
0x78 1003H
写到这里,读者大概明白,大小端是怎么存储在内存中,然后我们给出判断大小端的方法.
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstdlib> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #include<string> 6 #include<queue> 7 #include<algorithm> 8 #include<map> 9 #include<iomanip> 10 #include<stdlib.h> 11 #define INF 99999999 12 using namespace std; 13 14 int panduan_1(){ 15 int a = 0x12345678; 16 char *c = (char*)&a; 17 for(int i = 0;i<4;i++){ 18 printf("%x ",c[i]); 19 } 20 return ((c[0]==0x78)&&(c[1]==0x56)&&(c[2]==0x34)&&(c[3]==0x12)); 21 } 22 union p{ 23 int a; 24 char b; 25 }; 26 int panduan_2(){ 27 p p1; 28 p1.a = 1; 29 return p1.a==p1.b; 30 } 31 int main(){ 32 33 if(panduan_1()){ 34 cout<<"little duan"<<endl; 35 }else{ 36 cout<<"big duan"<<endl; 37 } 38 if(panduan_2()){ 39 cout<<"little duan"<<endl; 40 }else{ 41 cout<<"big duan"<<endl; 42 } 43 system("pause"); 44 return 0; 45 }
结果:

方法1:是利用定义,在地址上判断存的是否是高低位的数据,来解决问题.
方法2:在union中所有的数据成员共用一个空间,同一时间只能储存其中一个数据成员,所有的数据成员具有相同
的起始地址。即上述的union虽然定义了两个成员,但其实这个union只占用了4个字节(32位机器中),往a成员
赋值,然后读取b就相读取a成员的低位第一个字节的值。如果机器使用大端模式,则u.a=1那a的最高字节值为1;
如果机器使用小段模式,则u.a=1则a的最低位字节为1。上述可知b和a有相同的起始位,所以读取b如果等于1,
则为小端模式,b为0则为大端模式
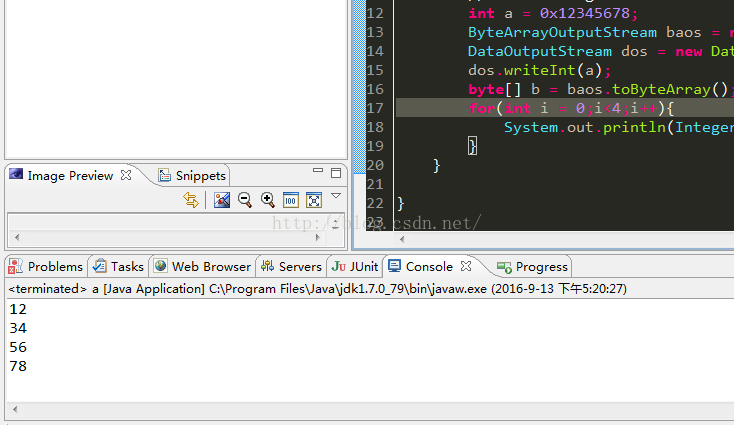
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; public class demo { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int a = 0x12345678; ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(baos); dos.writeInt(a); byte[] b = baos.toByteArray(); for(int i = 0;i<4;i++){ System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(b[i])); } } }
结果:
JVM中,实际是以大端存储的.
这样,我们通过两种语言来解决大小端问题.