using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Navigation;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
using System.IO;
namespace 老陈Wpf
{
/// <summary>
/// MainWindow.xaml 的交互逻辑
/// </summary>
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
public static int Count = 0;
public static int right = 0;
int m = 0;
private void luti_Click_1(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
StreamWriter n1 = File.AppendText("C:\n1.txt");
n1.WriteLine(textBox1.Text);
n1.Close();
StreamWriter n2 = File.AppendText("C:\n2.txt");
n2.WriteLine(textBox2.Text);
n2.Close();
StreamWriter n3 = File.AppendText("C:\n3.txt");
n3.WriteLine(textBox3.Text);
n3.Close();
MessageBox.Show("录题成功");
textBox1.Text = "";
textBox2.Text = "";
textBox3.Text = "";
}
//开始按钮
private void start_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
//出题
string[] n1 = new string[100];
n1 = File.ReadAllLines("C:\n1.txt");
textBox1.Text = n1[m];
string[] n2 = new string[100];
n2 = File.ReadAllLines("C:\n2.txt");
textBox2.Text = n2[m];
string[] n3 = new string[100];
n3 = File.ReadAllLines("C:\n3.txt");
textBox3.Text = n3[m];
m++;
}
//结束
private void end_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
textBox5.Text = MainWindow.Count.ToString();//题目总数
textBox6.Text = MainWindow.right.ToString();
textBox7.Text = ((MainWindow.right / (double)(MainWindow.Count)) * 100).ToString() + "%";//正确率
}
//运算结果的触发事件
private void textBox4_KeyDown(object sender, KeyEventArgs e)
{
wpf.Class1.yunsuanfu yunsuanfu = null;
double a = Convert.ToDouble(textBox1.Text);//第一个数赋值
double b = Convert.ToDouble(textBox3.Text);//第二个数赋值
string c= textBox2.Text;//运算符号
switch (c)
{ case"+":
yunsuanfu = new wpf.Class1.yunsuanfu(new wpf.Class1.Add());//调用策略模式
break;
case "-":
yunsuanfu = new wpf.Class1.yunsuanfu(new wpf.Class1.Sub());
break;
case "*":
yunsuanfu = new wpf.Class1.yunsuanfu(new wpf.Class1.Mul());
break;
default:
break;
}
if(e.Key == Key.Enter)
{
string result = yunsuanfu.Cal(a, b,c).ToString();
if(textBox4.Text==result.ToString())
{
MessageBox.Show("回答正确!下一题请按开始按钮!");
right++;
Count++;
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("回答错误!下一题请按开始按钮!");
Count++;
}
textBox4.Clear();
}
}
}
}
策略模式的代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace wpf
{
class Class1
{//定义一个接口
public interface Calculator
{
double Cal(double a, double b);//定义一个方法用于计算
}
public class Add : Calculator
{
public double Cal(double a, double b)
{
double result;
result = a + b;
return result;
}
}
public class Sub : Calculator
{
public double Cal(double a, double b)
{
double result;
result = a - b;
return result;
}
}
public class Mul : Calculator
{
public double Cal(double a, double b)
{
double result;
result = a * b;
return result;
}
}
public class yunsuanfu
{
private Calculator calculate;
public yunsuanfu(Calculator calculate)
{
this.calculate = calculate;
}
public double Cal(double a, double b, string m)//返回运算结果
{
return this.calculate.Cal(a, b);
}
}
}
}
运行后的界面 
PSP消耗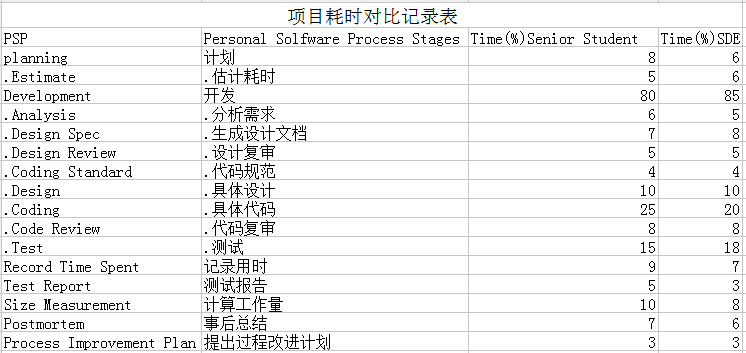
总结:对于这次的策略模式的实现,我觉得在实现的过程中很难,由于我基础比较差,以前根本对策略模式没什么了解,所以对于策略模式的实现,我请教了我们班学霸级的同学把我教会,我才开始做这次的作业,在测试代码的过程中遇到了很多困难,不过在我的小伙伴的帮助下解决了。对于上次博客老师评论的“控件命名要表意”,我觉得很对,控件表意后再看很快找到了,这次代码关于命名控件上我做了一些修改。PSP耗时分析我第一次写,可能会不太好,我是在老师建议后去看了闫同学的博客后写的,觉得很佩服别的同学能学以致用,以后应该向她学习。