定义接口和目标对象
/** * 参考人员接口 * * @author Silence * */ public interface Candidate { /** * 答题 */ public void answerTheQuestions(); }
/** * 懒学生 * * @author Silence * */ public class LazyStudent implements Candidate { private String name; public LazyStudent(String name) { super(); this.name = name; } @Override public void answerTheQuestions() { // 懒学生只能写出自己的名字不会答题 System.out.println("姓名:" + name); } }
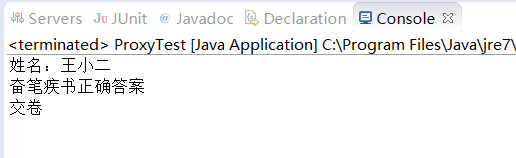
静态代理
/** * 静态代理,也要实现接口,不利于代码维护 * * @author Silence * */ public class Gunman implements Candidate { private Candidate target; // 被代理对象 public Gunman(Candidate target) { this.target = target; } @Override public void answerTheQuestions() { // 枪手要写上代考的学生的姓名 target.answerTheQuestions(); // 枪手要帮助懒学生答题并交卷 System.out.println("奋笔疾书正确答案"); System.out.println("交卷"); } }
@Test public void ProxTest1() { Candidate candidate = new Gunman(new LazyStudent("王小二")); candidate.answerTheQuestions(); }
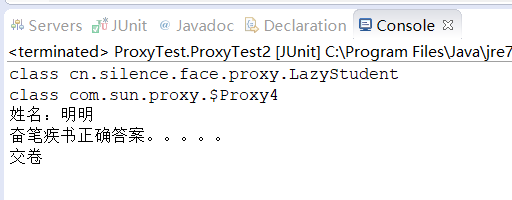
动态代理---不需要实现接口,推荐使用
public class ProxyFactory { private Candidate target; public ProxyFactory(Candidate target) { this.target = target; } public Object getProxyInstance() { return Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { // 执行目标对象的方法 Object retVal = method.invoke(target, args); System.out.println("奋笔疾书正确答案。。。。。"); System.out.println("交卷"); return retVal; } }); } }
@Test public void ProxyTest2(){ // 目标 对象 Candidate target = new LazyStudent("明明"); // 原始的类型 System.out.println(target.getClass()); // 给目标对象创建代理对象 Candidate proxy = (Candidate) new ProxyFactory(target).getProxyInstance(); // 内存中动态生成的代理对象 System.out.println(proxy.getClass()); // 执行方法 【代理对象】 proxy.answerTheQuestions(); } }