Student文档如下:
|
{ “name”: “zhangsan”, “score”: { “English”: 69, “Math”: 86, “Computer”: 77 } } { “name”: “lisi”, “score”: { “English”: 55, “Math”: 100, “Computer”: 88 } } |
1.根据上面给出的文档,完成如下操作:
(1)用MongoDB Shell设计出student集合;
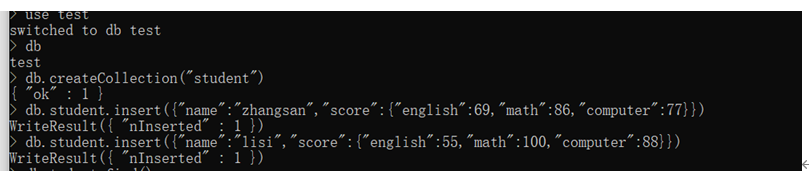
(2)用find()方法输出两个学生的信息;

(1) 用find()方法查询zhangsan的所有成绩(只显示score列);

(4)修改lisi的Math成绩,改为95。

2.根据上面已经设计出的Student集合,用MongoDB的Java客户端编程,实现如下操作:
(1)添加数据:English:45 Math:89 Computer:100
与上述数据对应的文档形式如下:
|
{ “name”: “scofield”, “score”: { “English”: 45, “Math”: 89, “Computer”: 100 } } |

MongoClient mongoClient = new MongoClient("127.0.0.1", 27017);
DB db = mongoClient.getDB("test");
DBCollection collection = db.getCollection("student");
DBObject doc = new BasicDBObject();
doc.put("name", "scofield");
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("english","45");
map.put("math","89");
map.put("computer","100");
doc.put("score",map);
db.getCollection("student").insert(doc);
(2)获取scofield的所有成绩成绩信息(只显示score列)

MongoClient mongoClient = new MongoClient("127.0.0.1", 27017);
DB db = mongoClient.getDB("test");
DBCollection collection = db.getCollection("student");
DBObject doc = new BasicDBObject();
doc.put("name","scofield");
DBCursor cursor = collection.find(doc);
try{
while(cursor.hasNext()){
System.out.println("student集合所拥有的name为--[" + cursor.next().get("name") + "]");
}
}finally{
cursor.close();
}
System.out.println("student集合中的记录数为----------->" + cursor.count());
System.out.println("student集合数据格式化后的JSON串为-->" + JSON.serialize(cursor));