1.Spectral extension简介
Spectral extension是通过低频的transform coefficients合成高频transform coefficients的过程。
spectral extension的实现与channel coupling类似,但是由于只需要transmit一些用于合成高频transform coefficients的metadat,因此比coupling更能减少datarate。
而且spectral extension能用于mono signal,而coupling至少需要2个channel.
spectral extension的核心部分是band structure, spectral extension band接近于critical band. spectral extension基于band来计算energy ratio和band border.
原始信号的频谱如下图:
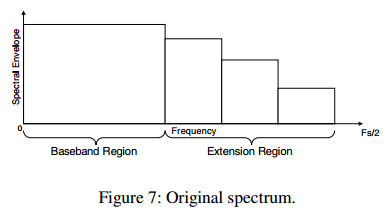
信号的频谱分为两个部分:baseband region和extension region. extension region基于band structure分为多个band,对于每一个band计算一个energy ratio.对于整个extension region,通过measure extension region的noise-like character得到一个noise blending parameter.计算出这些parameter后,原始信号的extension region的transform coefficient被discard.
接下来进行translation,其过程如下图:
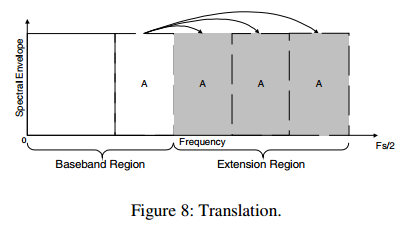
translation将baseband region的transform coefficient copy到extension region.
baseband region中被copy的部分称为copy region.通常copy region会比extension region小,因此会将copy region进行多次copy来fill extension region,这种过程称为wrapping,在Figure 8中copy region被wrap了两次。wrap会导致translation过程中边界处频谱的不连续。由于每个band对应一个scale factor,如果wrapping发生在一个band内,scale factor并不能减少这种不连续。如果wrapping只发生在band border,紧邻的两个bandd的scale factor可以减少不连续。因此translation确保wrapping发生在band之间。
简单的从baseband region copy到extension region不能产生natural sound signal.因为大部分signal在随着频率增大会更像noise.因此translated transform coefficients需要和noise spectrum根据noise-blending function 进行blend.
由于大部分signal在高频部分更像noise ,因此noise-blending function在高频权重更大。noise-blending function是线性的,其slope依赖于原始信号的bandwidth,其intercept依赖于noise blending parameter.
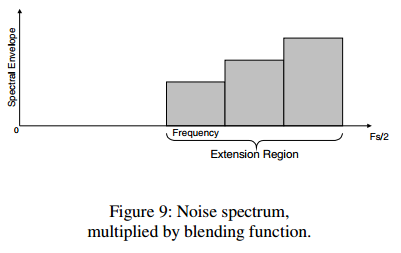
产生的noise spectrum的band energy和translated band相同,noise spectrum乘以noise-blending function得到的信号如下:
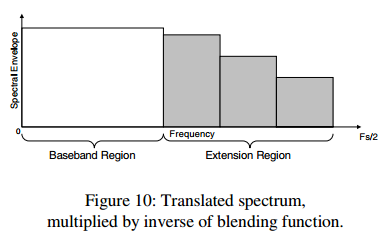
translated spectrum和inverse noise-blending function相乘的结果如下:
乘以了 noise-blending function后的translatged spectrum和noise spectrum进行blending如下图,注意每个blended band的energy和figure 8中的translated band的energy相等。
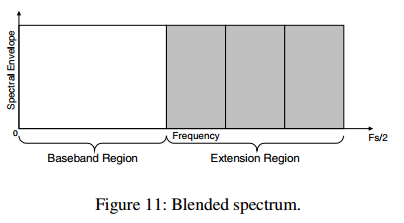
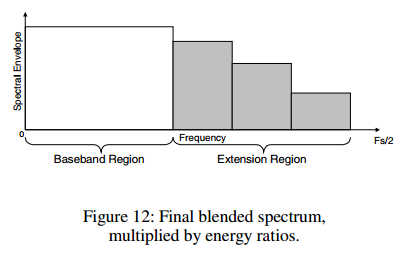
blending后的translated spectrum使用energy ratio进行scale后的spectrum与原始信号的banded envelop match:
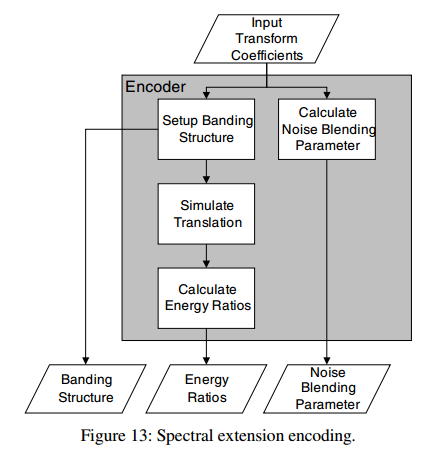
2. Encoder Operation
Encoder分析extension region计算出noise-blending parameter,决定band structure,并simulates decoder translation来计算出energy ratio.
在encoder分析extension region的spectral envelop的两个条件:时间上angle precession的变化和magnitute 的变化。如果angle or magnitute变化不连续,原始信号的spectrum更像noise,所以在translation后会blending更多noise,否则则blending较少noise.在bitstream中, noise-blending parameter quantize为5 bit。
banding structure的一个band包含多个subband,每个subband包含12个transform coefficient. default banding structure接近于auditory critical band.
接下来计算energy ratio:
首先计算extension region的banded energy:
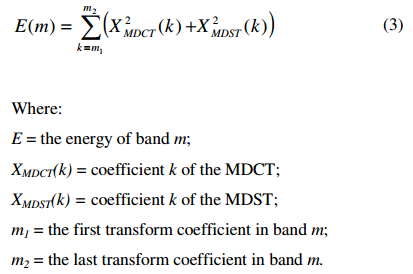
在encoder端,simulate translation过程,计算synthesized extension region的banded energy.
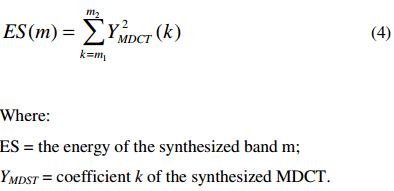
计算energy ratio:
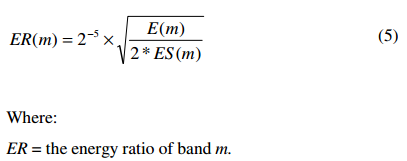
3.Decoder Operation
Decoder基于baseband transform coefficients和encoder 传送的metadata合成高频部分的transform coefficients.
Spectral extension decoding 过程如下:
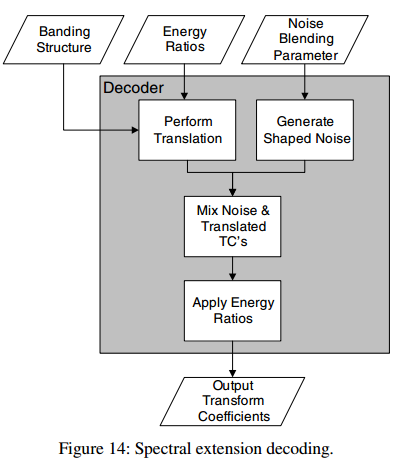
在decoder首先进行translation,将baseband copy region的transform coefficients copy到extension region。
接下来generate noise spectrum来与translated transform coefficients进行blending. noise spectrum 使用zero-mean, unity-variance pseudo-random noise generator来产生。
每个band的noise-blending factors由noise-blending parameter 得到:
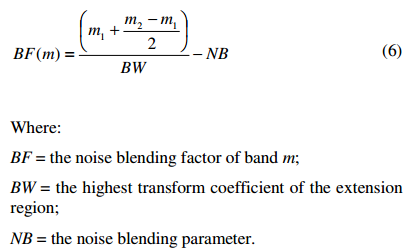
通过noise-blending factors计算mixing coefficients.
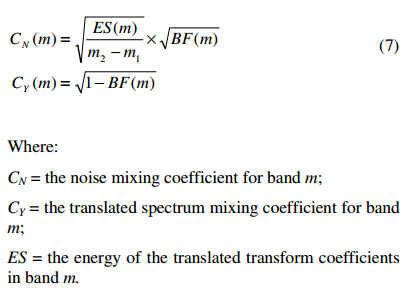
接下来将translated transform coefficients 和noise spectrum 进行blending:
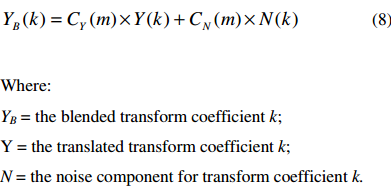
与noise spectrum blending后的transform coefficients乘以energy ratio得到高频部分的transform coefficients:
