1.介绍及注意事项
链表由Josh Bloch书写,属于Java集合框架中的一种,LinkedList实现的是双链表,实现了所有的链表操作,可能够实现所有元素(包括)的基本操作。
链表是非线程同步的,多线程情况下需要使用外部同步。
使用迭代器遍历此类时具有快速失败的特性(遍历过程中移除节点会报错)
/**
* Doubly-linked list implementation of the {@code List} and {@code Deque}
* interfaces. Implements all optional list operations, and permits all
* elements (including {@code null}).
*
* <p>All of the operations perform as could be expected for a doubly-linked
* list. Operations that index into the list will traverse the list from
* the beginning or the end, whichever is closer to the specified index.
*
* <p><strong>Note that this implementation is not synchronized.</strong>
* If multiple threads access a linked list concurrently, and at least
* one of the threads modifies the list structurally, it <i>must</i> be
* synchronized externally. (A structural modification is any operation
* that adds or deletes one or more elements; merely setting the value of
* an element is not a structural modification.) This is typically
* accomplished by synchronizing on some object that naturally
* encapsulates the list.
*
* If no such object exists, the list should be "wrapped" using the
* {@link Collections#synchronizedList Collections.synchronizedList}
* method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental
* unsynchronized access to the list:<pre>
* List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList(...));</pre>
*
* <p>The iterators returned by this class's {@code iterator} and
* {@code listIterator} methods are <i>fail-fast</i>: if the list is
* structurally modified at any time after the iterator is created, in
* any way except through the Iterator's own {@code remove} or
* {@code add} methods, the iterator will throw a {@link
* ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of concurrent
* modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather than
* risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined
* time in the future.
*
* <p>Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed
* as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the
* presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators
* throw {@code ConcurrentModificationException} on a best-effort basis.
* Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this
* exception for its correctness: <i>the fail-fast behavior of iterators
* should be used only to detect bugs.</i>
*
* <p>This class is a member of the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html">
* Java Collections Framework</a>.
*
* @author Josh Bloch
* @see List
* @see ArrayList
* @since 1.2
* @param <E> the type of elements held in this collection
*/
2.整体结构
LinkedList封装在Java.util包内,继承于AbstractSequentialList<E>抽象类(抽象类中定义了接口的基本方法,在子类中需要全部实现)
实现的接口有List<E>(List的基本方法), Deque<E>(队列的方法), Cloneable(用于对象的复制), java.io.Serializable(对象序列化,可用以对象的深复制)。
LinkedList继承结构如下:
java.lang.Object java.util.AbstractCollection<E> java.util.AbstractList<E> java.util.AbstractSequentialList<E> java.util.LinkedList<E>
LinkedList整体包含的整体功能如下:

linkedList维护的是双向链表,双向链表结构图如图所示
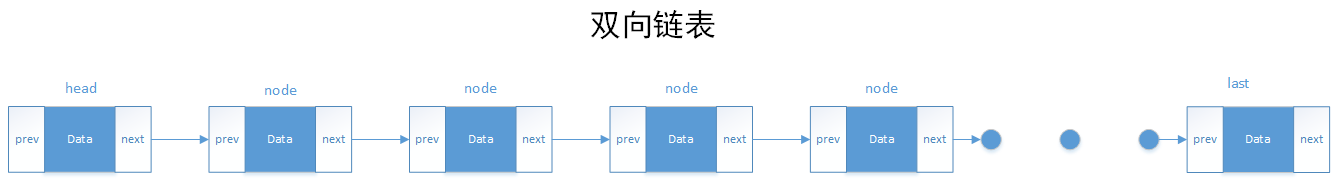
可以看出,源码内包含了三个成员变量,size,first,last和serialVersionUID,其中size用以维护链表大小,first和last用以维护链表的头尾节点,serialVersionUID是一个是根据类名、接口名、成员方法及属性等来生成一个64位的哈希字段,用来Java运行时判断类的一致性。
源码包含了三个类,Node类实现链表的节点,ListItr类实现了迭代器接口,在利用迭代器遍历链表的时候使用,DescendingIterator 是降序迭代器,能够返回一个逆序的迭代器列表。
Node类的源码如下:
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
可以看出,双向链表的单个节点需要维护两个指针和一个存储的值,prev需要指向前一个变量,如果是首节点则为null,next需要指向后一个变量,如果是尾节点则为null。Node<E>使用了泛型,泛型是Java SE 1.5的新特性,泛型的本质是参数化类型,也就是说所操作的数据类型被指定为一个参数,能够在实现参数“”。
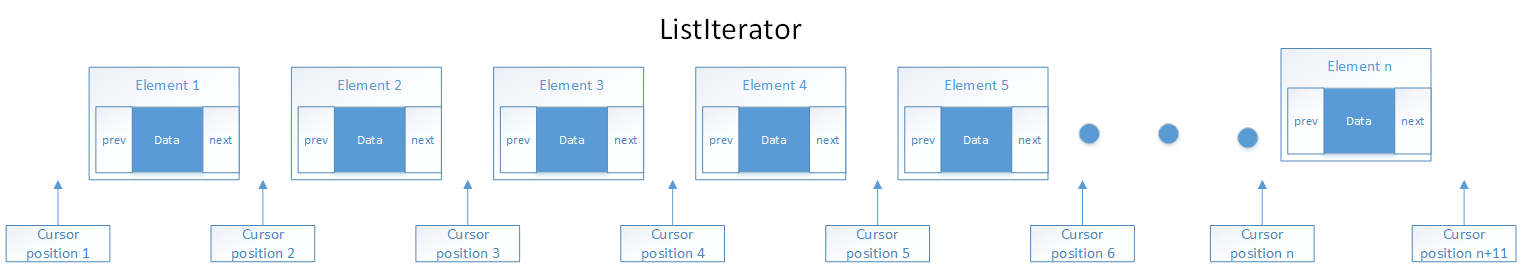
ListItr实现的是ListIterator接口,ListIterator接口继承的是Iterator接口,能够实现向前或向后任意方向遍历的列表迭代器,在迭代过程中可以修改元素(不能够增加删除,增删会导致快速失败“fail-fast”),该接口相当于维护了一个游标,能够获取当前位置,或者指向前一个或者后一个,游标标示的是节点中间的位置(相当于链表的链),因此对于有n个元素的迭代器,游标位置可以有n+1个,下图表示了这种情况。
ListIterator接口的方法API如下所示:
void add(E e) //添加一个元素(可选操作) boolean hasNext() //检查列表中是否还有下一个元素 boolean hasPrevoius() //检查列表中是否还有上一个元素 E next() //返回游标后的元素,并移动到下一个位置 int nextIndex() //返回游标后一个元素索引 E previous() //返回游标前的元素,并移动到前一个位置 int prevoiusIndex()//返回游标前一个元素索引 void remove() //移除被next()或previous()返回的元素(可选操作) void set() //修改被next()或previous()返回的元素(可选操作)
ListItr类的源码注释如下:
1 private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> { 2 private Node<E> lastReturned = null; //最后一个返回的节点 3 private Node<E> next;//下一个节点 4 private int nextIndex;//下一个指针 5 private int expectedModCount = modCount;//用以判定迭代对象是否被修改 6 7 ListItr(int index) { 8 // assert isPositionIndex(index); 9 next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);//判断是否是末尾的位置 10 nextIndex = index; 11 } 12 13 public boolean hasNext() { 14 return nextIndex < size; 15 } 16 17 public E next() { 18 checkForComodification();//首先检查迭代对象是否被修改 19 if (!hasNext())//检查是否存在下一个节点 20 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 21 //下面代码表示返回游标后的对象,并将游标后移一位 22 lastReturned = next; 23 next = next.next; 24 nextIndex++; 25 return lastReturned.item; 26 } 27 28 public boolean hasPrevious() { 29 return nextIndex > 0; 30 } 31 32 public E previous() { 33 checkForComodification();//检查对象是否被修改 34 if (!hasPrevious())//检测对象是否存在 35 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 36 //返回游标前一个节点,并将游标前移一位 37 lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev; 38 nextIndex--; 39 return lastReturned.item; 40 } 41 42 public int nextIndex() { 43 return nextIndex; 44 } 45 46 public int previousIndex() { 47 return nextIndex - 1; 48 } 49 50 public void remove() { 51 checkForComodification();//检测对象是否修改 52 if (lastReturned == null)//检测对象是否存在 53 throw new IllegalStateException(); 54 55 Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next;//先将移除的代码后的节点信息保留下来 56 unlink(lastReturned);//移除该节点 57 if (next == lastReturned)//如果next指向的节点被删除了,需要指向下一个节点 58 next = lastNext; 59 else 60 nextIndex--; 61 lastReturned = null;//返回节点为空 62 expectedModCount++; 63 } 64 65 public void set(E e) { 66 if (lastReturned == null) 67 throw new IllegalStateException(); 68 checkForComodification();////检查是否被修改 69 lastReturned.item = e; 70 } 71 72 public void add(E e) { 73 checkForComodification(); 74 lastReturned = null; 75 //在当前位置添加节点,并将指针后移 76 if (next == null) 77 linkLast(e); 78 else 79 linkBefore(e, next); 80 nextIndex++; 81 expectedModCount++; 82 } 83 84 final void checkForComodification() { 85 if (modCount != expectedModCount)//检查修改的次数是否一致 86 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 87 } 88 }
在ListItr中,重要的的功能有从index开始遍历ListItr(index),移动到下一个元素next(),移动到前一个元素previous(),移除对象remove(),设置set(E e),添加对象add(E e),检查是否改动checkForComodification()等。
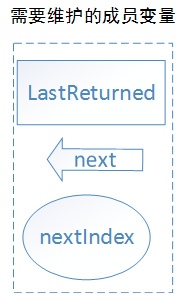
对于迭代器,首先需要维护的变量如下
源码如下:
1 private Node<E> lastReturned = null; //最后一个返回的节点 2 private Node<E> next;//下一个节点 3 private int nextIndex;//下一个指针
构造函数ListItr(int index)过程:
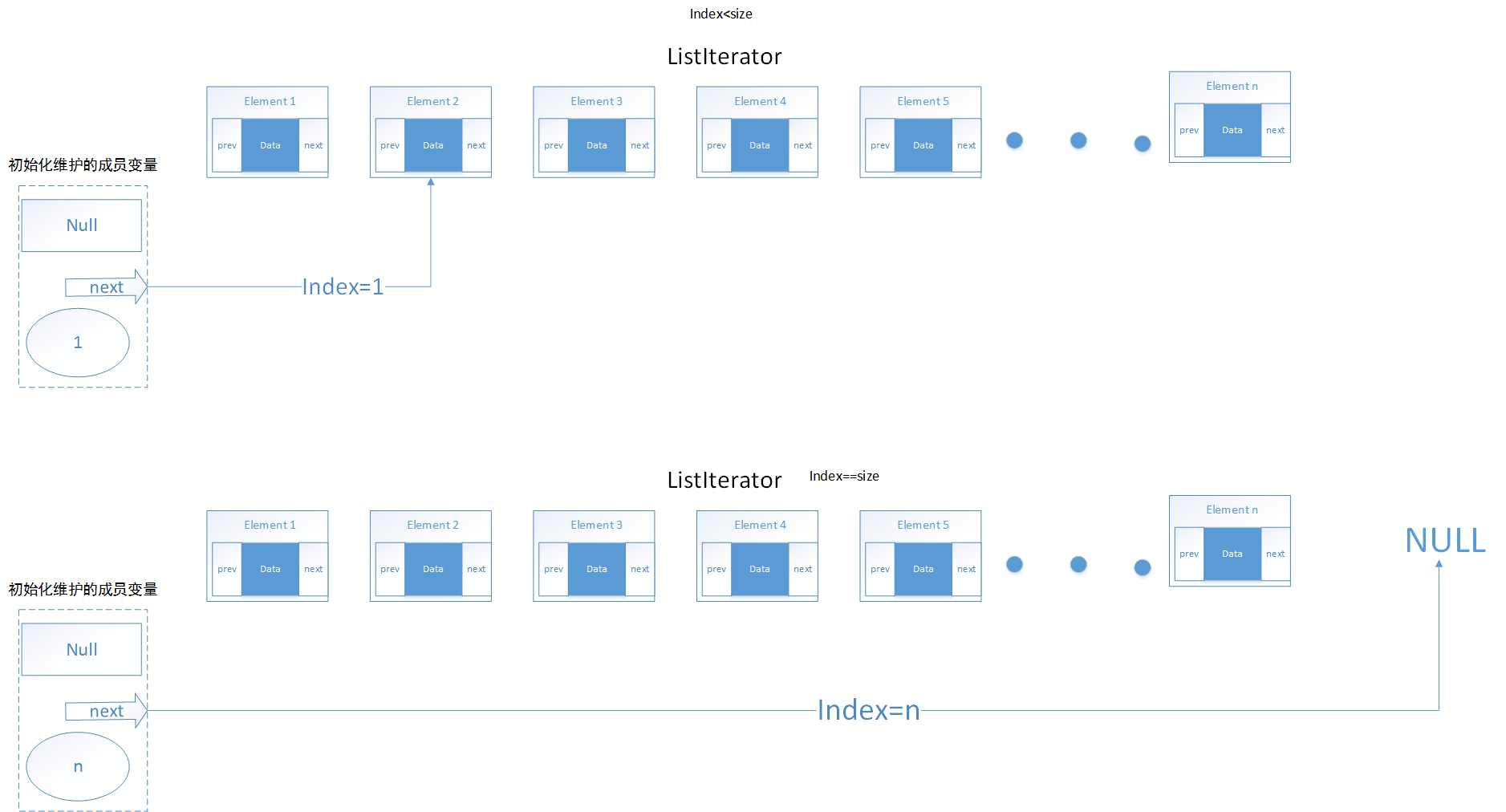
可以看出构造函数分为从中间开始和从末尾开始,如果从末尾开始,next要指向null,源码如下:
1 ListItr(int index) { 2 // assert isPositionIndex(index); 3 next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);//判断是否是末尾的位置 4 nextIndex = index; 5 }
向后遍历next()函数,其过程如下:
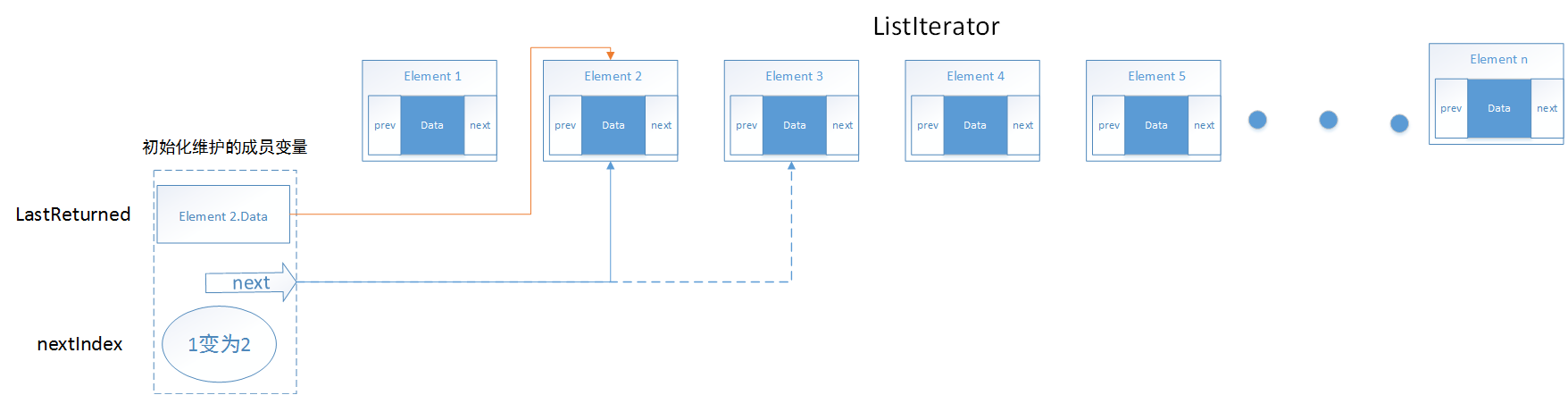
源码如下:
public E next() {
checkForComodification();//首先检查迭代对象是否被修改
if (!hasNext())//检查是否存在下一个节点
throw new NoSuchElementException();
//下面代码表示返回游标后的对象,并将游标后移一位
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
return lastReturned.item;
}
向前移动previous()过程如下:

源码如下:
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();//检查对象是否被修改
if (!hasPrevious())//检测对象是否存在
throw new NoSuchElementException();
//返回游标前一个节点,并将游标前移一位
lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev;
nextIndex--;
return lastReturned.item;
}
移除对象过程remove()过程如下:
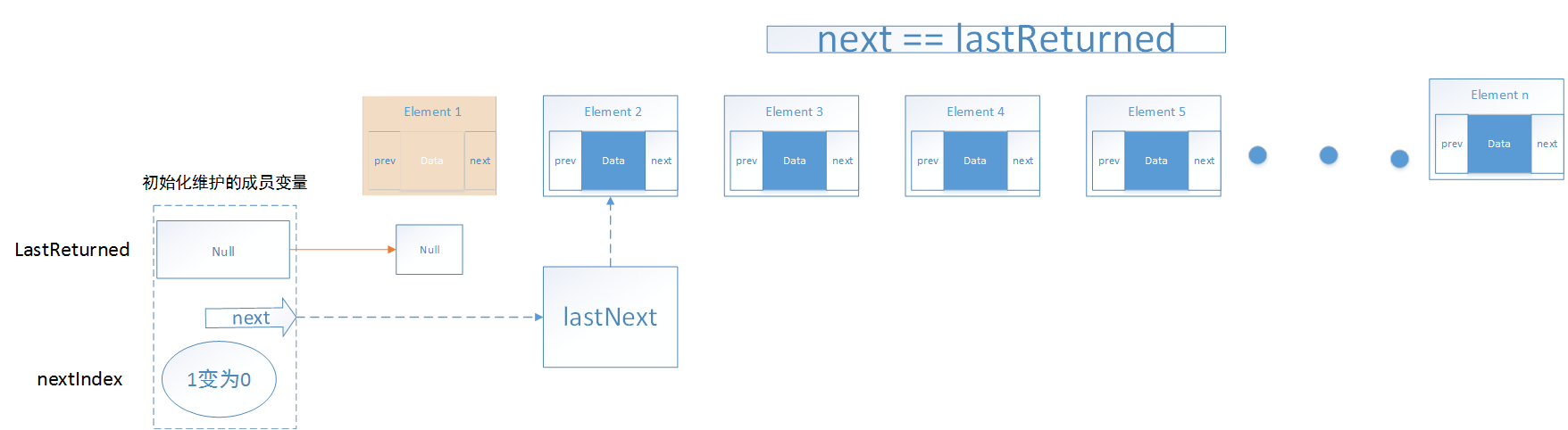
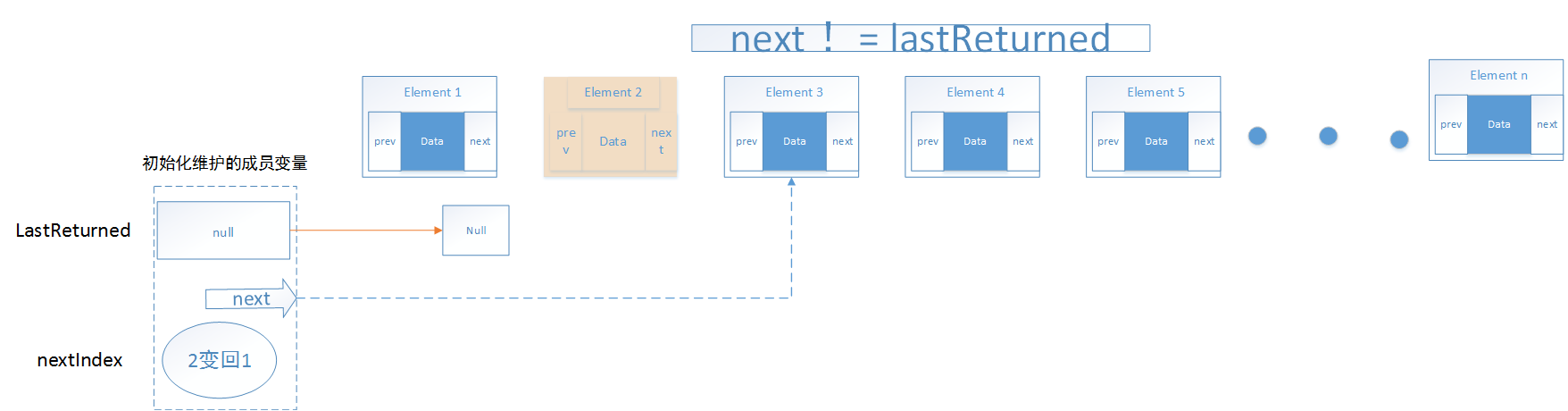
源码如下:
1 public void remove() { 2 checkForComodification();//检测对象是否修改 3 if (lastReturned == null)//检测对象是否存在 4 throw new IllegalStateException(); 5 6 Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next;//先将移除的代码后的节点信息保留下来 7 unlink(lastReturned);//移除该节点 8 if (next == lastReturned)//如果next指向的节点被删除了,需要指向下一个节点 9 next = lastNext; 10 else 11 nextIndex--; 12 lastReturned = null;//返回节点为空 13 expectedModCount++; 14 }
检查对吗通过设置修改变量,如在迭代器中修改会同时改变modCount和expectedModCount,源码如下:
public void remove() {
//省略
unlink(lastReturned);//此处包含modCount++
//省略
expectedModCount++;
}
public void add(E e) {
//省略
if (next == null)
linkLast(e);//此处包含modCount++
else
linkBefore(e, next);//此处包含modCount++
//省略
expectedModCount++;
}
而在LinkedList中的修改只改动了modeCount++,如
/**
* Unlinks non-null last node l.
*/
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
//省略
modCount++;
return element;
}
而且,在迭代器源码操作函数中都有改动检测代码,判断两个计数变量是否相同
checkForComodification();//检测对象是否修改
if (lastReturned == null)//检测对象是否存在
throw new IllegalStateException();
也就是说,在迭代器操作过程中,如果使用迭代器提供的remove和add方法,可以顺利通过,如果使用LinkedList提供的修改方法,会导致异常的产生,此举是为了保证在多线程环境中对象保持一致性。
第三个类是DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E>,实现逆序的迭代器,因此将next和previos功能反向即可,源码如下:
/**
* Adapter to provide descending iterators via ListItr.previous
*/
private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E> {
private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size());
public boolean hasNext() {
return itr.hasPrevious();
}
public E next() {
return itr.previous();
}
public void remove() {
itr.remove();
}
}
由于在LinedList源码中是由其中主要几个函数实现的,主要的实现结构如下所示,粉色表示构造函数,黄色表示比较简单的函数
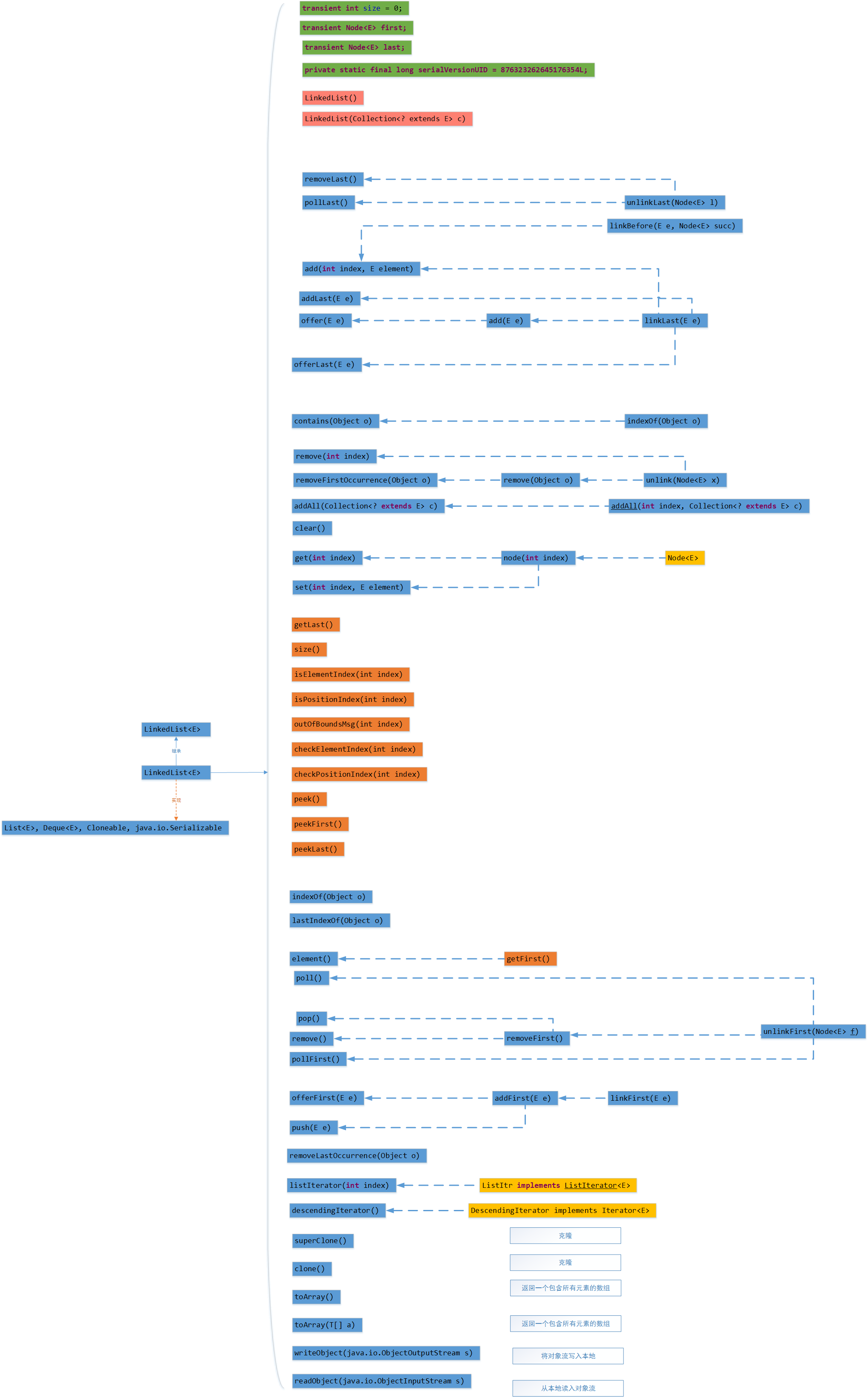

首先构造函数,可以看出,构造函数直接将所有节点添加进链表
public LinkedList() {
}
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
针对较复杂的函数,可以看出,很多函数是分别有几个基本的函数实现的。
unlinkLast函数源码如下:
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
linkBefore函数实现在链表第一个添加元素,源码如下:
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
同理,linkLast源码如下:
1 void linkLast(E e) { 2 final Node<E> l = last; 3 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); 4 last = newNode; 5 if (l == null) 6 first = newNode; 7 else 8 l.next = newNode; 9 size++; 10 modCount++; 11 }
indexOf实现返回某个元素的所在位置,此函数直接从链表头部开始搜索开始就行:
1 public int indexOf(Object o) { 2 int index = 0; 3 if (o == null) { 4 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 5 if (x.item == null) 6 return index; 7 index++; 8 } 9 } else { 10 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 11 if (o.equals(x.item)) 12 return index; 13 index++; 14 } 15 } 16 return -1; 17 }
addAll函数实现添加所有的节点
1 public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { 2 checkPositionIndex(index); 3 4 Object[] a = c.toArray(); 5 int numNew = a.length; 6 if (numNew == 0)//判定要添加的节点长度 7 return false; 8 9 Node<E> pred, succ; 10 //判断插入位置是否是最后 11 if (index == size) {//在链表的最后连接 12 succ = null; 13 pred = last; 14 } else {//从中间插入 15 succ = node(index); 16 pred = succ.prev; 17 } 18 19 for (Object o : a) {//依次添加链接节点 20 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; 21 Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); 22 if (pred == null) 23 first = newNode; 24 else 25 pred.next = newNode; 26 pred = newNode; 27 } 28 29 if (succ == null) { 30 last = pred;//从最后位置加入,更新last指针 31 } else { 32 pred.next = succ;//将插入后的链表连接起来 33 succ.prev = pred; 34 } 35 36 size += numNew; 37 modCount++; 38 return true; 39 }
node函数实现返回特定位置的节点
1 Node<E> node(int index) { 2 // assert isElementIndex(index); 3 4 if (index < (size >> 1)) {//size>>1相当于/2,判断从链表的前方添加近还是后方添加近 5 Node<E> x = first; 6 for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) 7 x = x.next; 8 return x; 9 } else { 10 Node<E> x = last; 11 for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) 12 x = x.prev; 13 return x; 14 } 15 }
indexOf和lasIndexOf函数返回从前或从后的位置数目,源码如下:
1 public int indexOf(Object o) { 2 int index = 0; 3 if (o == null) { 4 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 5 if (x.item == null) 6 return index; 7 index++; 8 } 9 } else { 10 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 11 if (o.equals(x.item)) 12 return index; 13 index++; 14 } 15 } 16 return -1; 17 } 18 public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { 19 int index = size; 20 if (o == null) { 21 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { 22 index--; 23 if (x.item == null) 24 return index; 25 } 26 } else { 27 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { 28 index--; 29 if (o.equals(x.item)) 30 return index; 31 } 32 } 33 return -1; 34 }
unlinkFirst实现断开第一个节点的功能:
1 private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { 2 // assert f == first && f != null; 3 final E element = f.item; 4 final Node<E> next = f.next; 5 f.item = null; 6 f.next = null; // help GC 7 first = next; 8 if (next == null) 9 last = null; 10 else 11 next.prev = null; 12 size--; 13 modCount++; 14 return element; 15 }
linkFitst添加头节点,处理好fitst指针即可:
1 private void linkFirst(E e) { 2 final Node<E> f = first; 3 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); 4 first = newNode; 5 if (f == null) 6 last = newNode; 7 else 8 f.prev = newNode; 9 size++; 10 modCount++; 11 }
其他的函数较为简单,不做分析