容器最基本的实现是beanFactory,但是大部分企业引用都是使用ApplicationContext,这里介绍基础的BeanFactory是为了更好的理解spring内部原理。
(一)基本用法
(1)bean的声明
package com.ws.learn.entity; public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public void info(){ System.out.println("name:"+getName()+" age:"+getAge()); } }
(2)配置文件beanFactoryTest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <bean id="person" class="com.ws.learn.entity.Person"> <property name="name" value="test"/> <property name="age" value="18"/> </bean> </beans>
(3)测试
public class MyTest { public static void main(String[] args){ BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("beanFactoryTest.xml"));//读取beanFactoryTest.xml中的内容 Person p = bf.getBean("person",Person.class); p.info(); } }
(二)核心类介绍
(1)DefaultListableBeanFactory
XmlBeanFactory继承自DefaultListableBeanFactory,而DefaultListableBeanFactory是整个bean加载的核心部分,是Spring注册及加载bean的默认实现,而对于XmlBeanFactory与DefaultListableBeanFactory不同的地方其实是在XmlBeanFactory中使用了自定义的XML读取器XmlBeanDefinitionReader,实现了个性化的BeanDefinitionReader读取,DefaultListableBeanFactory继承了AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory并实现了ConfigURableListableBeanFactory以及BeanDefinitionRegistry接口。以下是DefaultListableBeanFactory的层次结构图以下相关类图
容器加载相关类图:
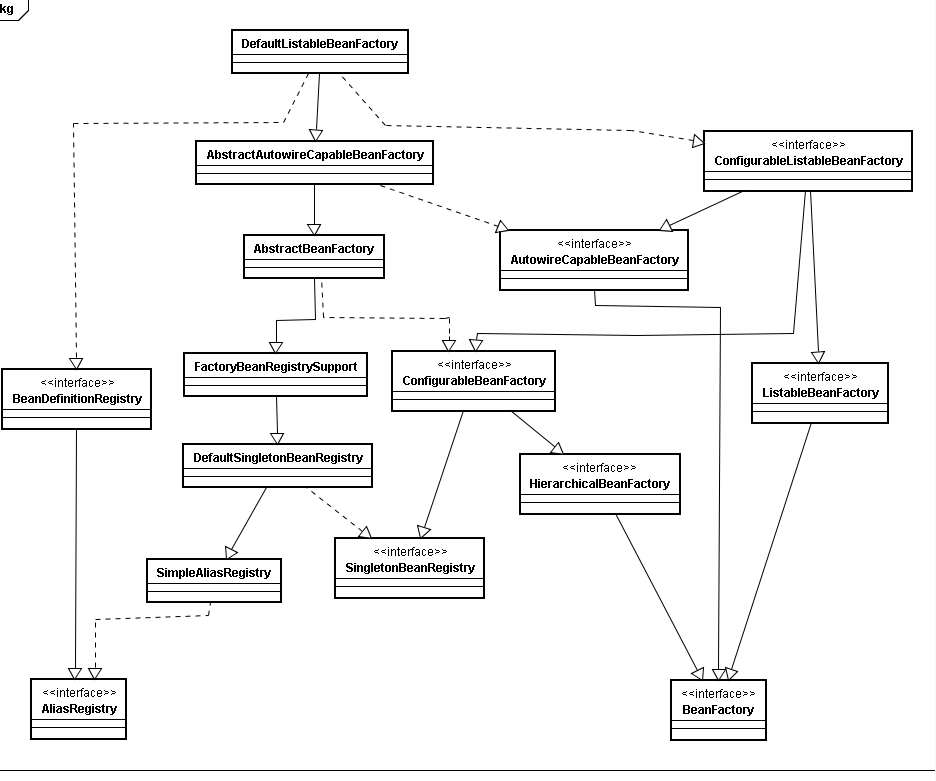
类图中各个类的作用:
- AliasRegistry:定义对alias的简单增删改等操作
- SimpleAliasRegistry:主要使用map作为alias的缓存,并对接口AliasRegistry进行实现
- SingletonBeanRegistry:定义对单例的注册及获取
- BeanFactory:定义获取bean及bean的各种属性
- DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry:对接口SingletonBeanRegistry各函数的实现
- HierarchicalBeanFactory:继承BeanFactory,也就是在BeanFactory定义的功能的基础上增加了对parentFactory的支持
- BeanDefinitionRegistry:定义对BeanDefinition的各种增删改操作
- FactoryBeanRegistrySupport:在DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry基础上增加了对FactoryBean的特殊处理功能
- ConfigurableBeanFactory:提供配置Factory的各种方法
- ListableBeanFactory:根据各种条件获取bean的配置清单
- AbstractBeanFactory:综合FactoryBeanRegistrySupport和ConfigurationBeanFactory的功能
- AutowireCapableBeanFactory:提供创建bean、自动注入、初始化以及应用bean的后处理器
- AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory:综合AbstractBeanFactory并对接口AutowireCapableBeanFactory进行实现
- ConfigurableListableBeanFactory:BeanFactory配置清单,指定忽略类型及接口等
- DefaultListableBeanFactory:综合上面所有功能,主要是对Bean注册后的处理
(2)XmlBeanDefinitionReader
XML配置文件的读取是Spring中重要的功能,因为Spring的大部分功能都是以配置作为切入点的,可以从XmlBeanDefinitionReader中梳理一下资源文件读取、解析及注册的大致脉络,首先看看各个类的功能
- ResourceLoader:定义资源加载器,主要应用于根据给定的资源文件地址返回对应的Resource
- BeanDefinitionReader:主要定义资源文件读取并转换为BeanDefinition的各个功能
- EnvironmentCapable:定义获取Environment方法
- DocumentLoader:定义从资源文件加载到转换为Document的功能
- AbstractBeanDefinitionReader:对EnvironmentCapable、BeanDefinitionReader类定义的功能进行实现
- BeanDefinitionDocumentReader:定义读取Document并注册BeanDefinition功能
- BeanDefinitionParserDelegate:定义解析Element的各种方法
整个XML配置文件读取的大致流程,在XmlBeanDefinitionReader中主要包含以下几步处理:

(1)通过继承自AbstractBeanDefinitionReader中的方法,来使用ResourceLoader将资源文件路径转换为对应的Resource文件
(2)通过DocumentLoader对Resource文件进行转换,将Resource文件转换为Document文件
(3)通过实现接口BeanDefinitionDocumentReader的DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类对Document进行解析,并使用BeanDefinitionParserDelegate对Element进行解析
(三)容器的基础XmlBeanFactory
BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("beanFactoryTest.xml"));
通过XmlBeanFactory初始化时序图看一看上面代码的执行逻辑
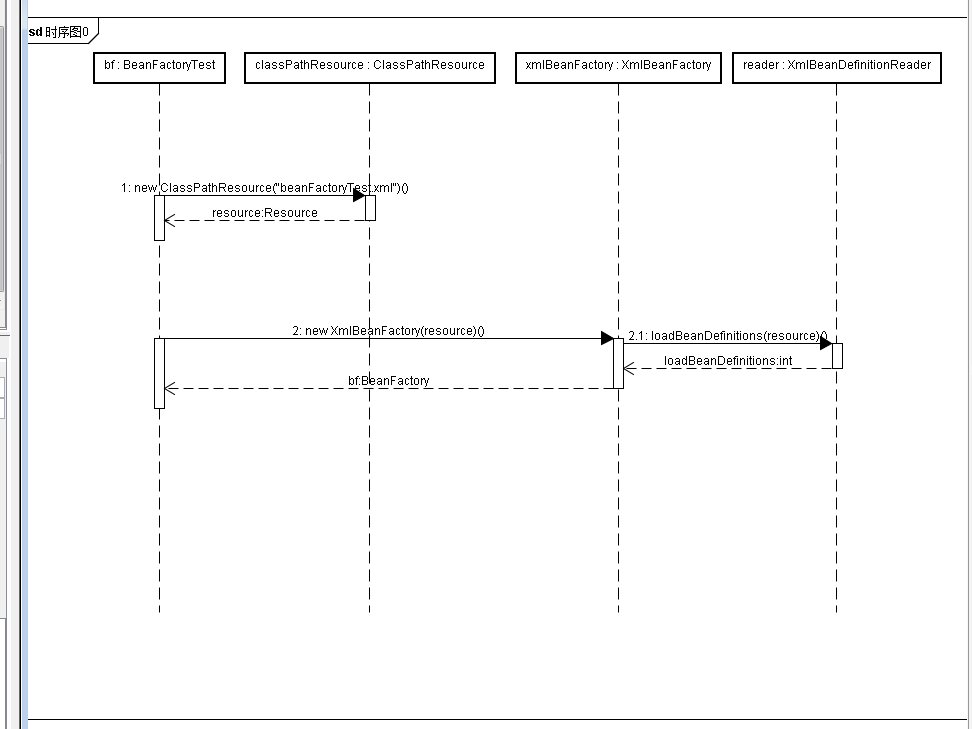
首先调用ClassPathResource的构造函数来构造Resource资源文件的实例对象,这样后续的资源处理就可以用Resource提供的各种服务来操作了。
配置文件封装
Spring的配置文件读取是通过ClassPathResource进行封装的,Spring对其内部使用到的资源实现了自己的抽象结构:Resource接口来封装底层资源
public interface InputStreamSource { /** * Return an {@link InputStream} for the content of an underlying resource. * <p>It is expected that each call creates a <i>fresh</i> stream. * <p>This requirement is particularly important when you consider an API such * as JavaMail, which needs to be able to read the stream multiple times when * creating mail attachments. For such a use case, it is <i>required</i> * that each {@code getInputStream()} call returns a fresh stream. * @return the input stream for the underlying resource (must not be {@code null}) * @throws java.io.FileNotFoundException if the underlying resource doesn't exist * @throws IOException if the content stream could not be opened */ InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException; }
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource { /** * Determine whether this resource actually exists in physical form. * <p>This method performs a definitive existence check, whereas the * existence of a {@code Resource} handle only guarantees a valid * descriptor handle. */ boolean exists(); /** * Indicate whether the contents of this resource can be read via * {@link #getInputStream()}. * <p>Will be {@code true} for typical resource descriptors; * note that actual content reading may still fail when attempted. * However, a value of {@code false} is a definitive indication * that the resource content cannot be read. * @see #getInputStream() */ boolean isReadable(); /** * Indicate whether this resource represents a handle with an open stream. * If {@code true}, the InputStream cannot be read multiple times, * and must be read and closed to avoid resource leaks. * <p>Will be {@code false} for typical resource descriptors. */ boolean isOpen(); /** * Return a URL handle for this resource. * @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved as URL, * i.e. if the resource is not available as descriptor */ URL getURL() throws IOException; /** * Return a URI handle for this resource. * @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved as URI, * i.e. if the resource is not available as descriptor * @since 2.5 */ URI getURI() throws IOException; /** * Return a File handle for this resource. * @throws java.io.FileNotFoundException if the resource cannot be resolved as * absolute file path, i.e. if the resource is not available in a file system * @throws IOException in case of general resolution/reading failures * @see #getInputStream() */ File getFile() throws IOException; /** * Determine the content length for this resource. * @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved * (in the file system or as some other known physical resource type) */ long contentLength() throws IOException; /** * Determine the last-modified timestamp for this resource. * @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved * (in the file system or as some other known physical resource type) */ long lastModified() throws IOException; /** * Create a resource relative to this resource. * @param relativePath the relative path (relative to this resource) * @return the resource handle for the relative resource * @throws IOException if the relative resource cannot be determined */ Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException; /** * Determine a filename for this resource, i.e. typically the last * part of the path: for example, "myfile.txt". * <p>Returns {@code null} if this type of resource does not * have a filename. */ String getFilename(); /** * Return a description for this resource, * to be used for error output when working with the resource. * <p>Implementations are also encouraged to return this value * from their {@code toString} method. * @see Object#toString() */ String getDescription(); }
InputStreamSource封装任何能返回InputStream的类,比如File、Classpath下的资源和Byte Array等, 它只有一个方法定义:getInputStream(),该方法返回一个新的InputStream对象
Resource接口抽象了所有Spring内部使用到的底层资源:File、URL、Classpath等。首先,它定义了3个判断当前资源状态的方法:存在性(exists)、可读性(isReadable)、是否处于打开状态(isOpen)。另外,Resource接口还提供了不同资源到URL、URI、File类型的转换,以及获取lastModified属性、文件名(不带路径信息的文件名,getFilename())的方法,为了便于操作,Resource还提供了基于当前资源创建一个相对资源的方法:createRelative(),还提供了getDescription()方法用于在错误处理中的打印信息
对不同来源的资源文件都有相应的Resource实现:文件(FileSystemResource)、Classpath资源(ClassPathResource)、URL资源(UrlResource)、InputStream资源(InputStreamResource)、Byte数组(ByteArrayResource)等,相关类图如下所示:

(1)配置文件封装
public ClassPathResource(String path) { this(path, (ClassLoader) null); } public ClassPathResource(String path, ClassLoader classLoader) { Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null"); String pathToUse = StringUtils.cleanPath(path); if (pathToUse.startsWith("/")) { pathToUse = pathToUse.substring(1); } this.path = pathToUse; this.classLoader = (classLoader != null ? classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader()); }
(2)XmlBeanFactory
public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory { private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this); /** * Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given resource, * which must be parsable using DOM. * @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from * @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException { this(resource, null); } /** * Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given input stream, * which must be parsable using DOM. * @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from * @param parentBeanFactory parent bean factory * @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException { super(parentBeanFactory); this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); } /** * Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given input stream, * which must be parsable using DOM. * @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from * @param parentBeanFactory parent bean factory * @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException { super(parentBeanFactory); this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); } }
(3)XmlBeanDefinitionReader
/** * Bean definition reader for XML bean definitions. * Delegates the actual XML document reading to an implementation * of the {@link BeanDefinitionDocumentReader} interface. * * <p>Typically applied to a * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory} * or a {@link org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext}. * * <p>This class loads a DOM document and applies the BeanDefinitionDocumentReader to it. * The document reader will register each bean definition with the given bean factory, * talking to the latter's implementation of the * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry} interface. * * @author Juergen Hoeller * @author Rob Harrop * @author Chris Beams * @since 26.11.2003 * @see #setDocumentReaderClass * @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader * @see DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader * @see BeanDefinitionRegistry * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory * @see org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext */ public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader extends AbstractBeanDefinitionReader { /** * Indicates that the validation should be disabled. */ public static final int VALIDATION_NONE = XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_NONE; /** * Indicates that the validation mode should be detected automatically. */ public static final int VALIDATION_AUTO = XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_AUTO; /** * Indicates that DTD validation should be used. */ public static final int VALIDATION_DTD = XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_DTD; /** * Indicates that XSD validation should be used. */ public static final int VALIDATION_XSD = XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_XSD; /** Constants instance for this class */ private static final Constants constants = new Constants(XmlBeanDefinitionReader.class); private int validationMode = VALIDATION_AUTO; private boolean namespaceAware = false; private Class<?> documentReaderClass = DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class; private ProblemReporter problemReporter = new FailFastProblemReporter(); private ReaderEventListener eventListener = new EmptyReaderEventListener(); private SourceExtractor sourceExtractor = new NullSourceExtractor(); private NamespaceHandlerResolver namespaceHandlerResolver; private DocumentLoader documentLoader = new DefaultDocumentLoader(); private EntityResolver entityResolver; private ErrorHandler errorHandler = new SimpleSaxErrorHandler(logger); private final XmlValidationModeDetector validationModeDetector = new XmlValidationModeDetector(); private final ThreadLocal<Set<EncodedResource>> resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded = new NamedThreadLocal<Set<EncodedResource>>("XML bean definition resources currently being loaded"); /** * Create new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given bean factory. * @param registry the BeanFactory to load bean definitions into, * in the form of a BeanDefinitionRegistry */ public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { super(registry); } /** * Set whether to use XML validation. Default is {@code true}. * <p>This method switches namespace awareness on if validation is turned off, * in order to still process schema namespaces properly in such a scenario. * @see #setValidationMode * @see #setNamespaceAware */ public void setValidating(boolean validating) { this.validationMode = (validating ? VALIDATION_AUTO : VALIDATION_NONE); this.namespaceAware = !validating; } /** * Set the validation mode to use by name. Defaults to {@link #VALIDATION_AUTO}. * @see #setValidationMode */ public void setValidationModeName(String validationModeName) { setValidationMode(constants.asNumber(validationModeName).intValue()); } /** * Set the validation mode to use. Defaults to {@link #VALIDATION_AUTO}. * <p>Note that this only activates or deactivates validation itself. * If you are switching validation off for schema files, you might need to * activate schema namespace support explicitly: see {@link #setNamespaceAware}. */ public void setValidationMode(int validationMode) { this.validationMode = validationMode; } /** * Return the validation mode to use. */ public int getValidationMode() { return this.validationMode; } /** * Set whether or not the XML parser should be XML namespace aware. * Default is "false". * <p>This is typically not needed when schema validation is active. * However, without validation, this has to be switched to "true" * in order to properly process schema namespaces. */ public void setNamespaceAware(boolean namespaceAware) { this.namespaceAware = namespaceAware; } /** * Return whether or not the XML parser should be XML namespace aware. */ public boolean isNamespaceAware() { return this.namespaceAware; } /** * Specify which {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ProblemReporter} to use. * <p>The default implementation is {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.FailFastProblemReporter} * which exhibits fail fast behaviour. External tools can provide an alternative implementation * that collates errors and warnings for display in the tool UI. */ public void setProblemReporter(ProblemReporter problemReporter) { this.problemReporter = (problemReporter != null ? problemReporter : new FailFastProblemReporter()); } /** * Specify which {@link ReaderEventListener} to use. * <p>The default implementation is EmptyReaderEventListener which discards every event notification. * External tools can provide an alternative implementation to monitor the components being * registered in the BeanFactory. */ public void setEventListener(ReaderEventListener eventListener) { this.eventListener = (eventListener != null ? eventListener : new EmptyReaderEventListener()); } /** * Specify the {@link SourceExtractor} to use. * <p>The default implementation is {@link NullSourceExtractor} which simply returns {@code null} * as the source object. This means that - during normal runtime execution - * no additional source metadata is attached to the bean configuration metadata. */ public void setSourceExtractor(SourceExtractor sourceExtractor) { this.sourceExtractor = (sourceExtractor != null ? sourceExtractor : new NullSourceExtractor()); } /** * Specify the {@link NamespaceHandlerResolver} to use. * <p>If none is specified, a default instance will be created through * {@link #createDefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver()}. */ public void setNamespaceHandlerResolver(NamespaceHandlerResolver namespaceHandlerResolver) { this.namespaceHandlerResolver = namespaceHandlerResolver; } /** * Specify the {@link DocumentLoader} to use. * <p>The default implementation is {@link DefaultDocumentLoader} * which loads {@link Document} instances using JAXP. */ public void setDocumentLoader(DocumentLoader documentLoader) { this.documentLoader = (documentLoader != null ? documentLoader : new DefaultDocumentLoader()); } /** * Set a SAX entity resolver to be used for parsing. * <p>By default, {@link ResourceEntityResolver} will be used. Can be overridden * for custom entity resolution, for example relative to some specific base path. */ public void setEntityResolver(EntityResolver entityResolver) { this.entityResolver = entityResolver; } /** * Return the EntityResolver to use, building a default resolver * if none specified. */ protected EntityResolver getEntityResolver() { if (this.entityResolver == null) { // Determine default EntityResolver to use. ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader(); if (resourceLoader != null) { this.entityResolver = new ResourceEntityResolver(resourceLoader); } else { this.entityResolver = new DelegatingEntityResolver(getBeanClassLoader()); } } return this.entityResolver; } /** * Set an implementation of the {@code org.xml.sax.ErrorHandler} * interface for custom handling of XML parsing errors and warnings. * <p>If not set, a default SimpleSaxErrorHandler is used that simply * logs warnings using the logger instance of the view class, * and rethrows errors to discontinue the XML transformation. * @see SimpleSaxErrorHandler */ public void setErrorHandler(ErrorHandler errorHandler) { this.errorHandler = errorHandler; } /** * Specify the {@link BeanDefinitionDocumentReader} implementation to use, * responsible for the actual reading of the XML bean definition document. * <p>The default is {@link DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader}. * @param documentReaderClass the desired BeanDefinitionDocumentReader implementation class */ public void setDocumentReaderClass(Class<?> documentReaderClass) { if (documentReaderClass == null || !BeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class.isAssignableFrom(documentReaderClass)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "documentReaderClass must be an implementation of the BeanDefinitionDocumentReader interface"); } this.documentReaderClass = documentReaderClass; } /** * Load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ @Override public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource)); } /** * Load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param encodedResource the resource descriptor for the XML file, * allowing to specify an encoding to use for parsing the file * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null"); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource()); } Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get(); if (currentResources == null) { currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4); this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources); } if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!"); } try { InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream(); try { InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) { inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding()); } return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); } finally { inputStream.close(); } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex); } finally { currentResources.remove(encodedResource); if (currentResources.isEmpty()) { this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove(); } } } /** * Load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param inputSource the SAX InputSource to read from * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public int loadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { return loadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, "resource loaded through SAX InputSource"); } /** * Load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param inputSource the SAX InputSource to read from * @param resourceDescription a description of the resource * (can be {@code null} or empty) * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public int loadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, String resourceDescription) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, new DescriptiveResource(resourceDescription)); } /** * Actually load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param inputSource the SAX InputSource to read from * @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors * @see #doLoadDocument * @see #registerBeanDefinitions */ protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { try { Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (SAXParseException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); } catch (SAXException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); } catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } } /** * Actually load the specified document using the configured DocumentLoader. * @param inputSource the SAX InputSource to read from * @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file * @return the DOM Document * @throws Exception when thrown from the DocumentLoader * @see #setDocumentLoader * @see DocumentLoader#loadDocument */ protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception { return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware()); } /** * Gets the validation mode for the specified {@link Resource}. If no explicit * validation mode has been configured then the validation mode is * {@link #detectValidationMode detected}. * <p>Override this method if you would like full control over the validation * mode, even when something other than {@link #VALIDATION_AUTO} was set. */ protected int getValidationModeForResource(Resource resource) { int validationModeToUse = getValidationMode(); if (validationModeToUse != VALIDATION_AUTO) { return validationModeToUse; } int detectedMode = detectValidationMode(resource); if (detectedMode != VALIDATION_AUTO) { return detectedMode; } // Hmm, we didn't get a clear indication... Let's assume XSD, // since apparently no DTD declaration has been found up until // detection stopped (before finding the document's root tag). return VALIDATION_XSD; } /** * Detects which kind of validation to perform on the XML file identified * by the supplied {@link Resource}. If the file has a {@code DOCTYPE} * definition then DTD validation is used otherwise XSD validation is assumed. * <p>Override this method if you would like to customize resolution * of the {@link #VALIDATION_AUTO} mode. */ protected int detectValidationMode(Resource resource) { if (resource.isOpen()) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Passed-in Resource [" + resource + "] contains an open stream: " + "cannot determine validation mode automatically. Either pass in a Resource " + "that is able to create fresh streams, or explicitly specify the validationMode " + "on your XmlBeanDefinitionReader instance."); } InputStream inputStream; try { inputStream = resource.getInputStream(); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Unable to determine validation mode for [" + resource + "]: cannot open InputStream. " + "Did you attempt to load directly from a SAX InputSource without specifying the " + "validationMode on your XmlBeanDefinitionReader instance?", ex); } try { return this.validationModeDetector.detectValidationMode(inputStream); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Unable to determine validation mode for [" + resource + "]: an error occurred whilst reading from the InputStream.", ex); } } /** * Register the bean definitions contained in the given DOM document. * Called by {@code loadBeanDefinitions}. * <p>Creates a new instance of the parser class and invokes * {@code registerBeanDefinitions} on it. * @param doc the DOM document * @param resource the resource descriptor (for context information) * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of parsing errors * @see #loadBeanDefinitions * @see #setDocumentReaderClass * @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions */ public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(); int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource)); return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore; } /** * Create the {@link BeanDefinitionDocumentReader} to use for actually * reading bean definitions from an XML document. * <p>The default implementation instantiates the specified "documentReaderClass". * @see #setDocumentReaderClass */ protected BeanDefinitionDocumentReader createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader() { return BeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class.cast(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(this.documentReaderClass)); } /** * Create the {@link XmlReaderContext} to pass over to the document reader. */ public XmlReaderContext createReaderContext(Resource resource) { return new XmlReaderContext(resource, this.problemReporter, this.eventListener, this.sourceExtractor, this, getNamespaceHandlerResolver()); } /** * Lazily create a default NamespaceHandlerResolver, if not set before. * @see #createDefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver() */ public NamespaceHandlerResolver getNamespaceHandlerResolver() { if (this.namespaceHandlerResolver == null) { this.namespaceHandlerResolver = createDefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver(); } return this.namespaceHandlerResolver; } /** * Create the default implementation of {@link NamespaceHandlerResolver} used if none is specified. * Default implementation returns an instance of {@link DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver}. */ protected NamespaceHandlerResolver createDefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver() { return new DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver(getResourceLoader().getClassLoader()); } }
EncodedResource
private EncodedResource(Resource resource, String encoding, Charset charset) { super(); Assert.notNull(resource, "Resource must not be null"); this.resource = resource; this.encoding = encoding; this.charset = charset; }