原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/luminji/archive/2011/05/27/2060127.html
一:Prism的下载和安装
1:在http://compositewpf.codeplex.com/上下载最新的包。
下载完毕后,运行之,选择解压目录解压之。解压完毕的根目录下有chm帮助文档。
2:运行RegisterPrismBinaries.bat注册Prism组件,注册完毕才能在VS的引用中直接找到Prism组件,否则需要手动添加这些组件。
3:运行Silverlight Only - Basic MVVM QuickStart.bat可以打开一个MVVM的简单事例。
二:MVVM理解
1:现在,我们自己创建一个普通的SilverLight样例,并且将它逐步重构成为MVVM模式。
这个 普通的SL样例需求有:在界面上放置文本框用来显示Name和Button用来显示文本框中的Name的值。
前台:

后台:
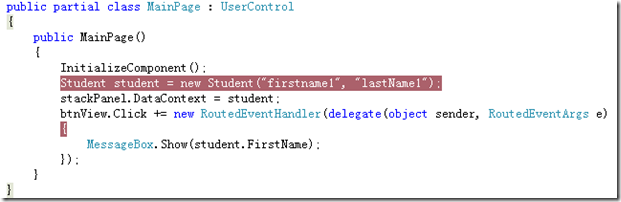
SL的目录结构:
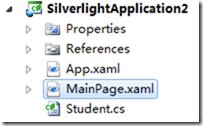
2:问题来了
如果我们需要让页面的值和Student实例的值保持一致,则必须要让类型继承自INotifyPropertyChanged接口,并像下面这样编码:
01 | public class Student : INotifyPropertyChanged |
04 | public string FirstName |
18 | public string LastName |
31 | public Student(string firstName, string lastName) |
33 | this.firstName = firstName; |
34 | this.lastName = lastName; |
37 | void Notify(string propName) |
39 | if (PropertyChanged != null) |
41 | PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propName)); |
45 | #region INotifyPropertyChanged Members |
46 | public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; |
如果应用程序中存在多个这样的类型,则每个类型都要实现自己的Notify方法,这显然是不合理的。所以,无论是Prism框架,还是轻量级的Mvvm light toolkit,都实现了一个超类来包装这种需求,在Prism里该超类是NotificationObject,而Mvvm light toolkit中是ObservableObject,当然,毫无例外滴,它们都继承自INotifyPropertyChanged。
3:现在,我们参照这两个类型,来实现自己的NotificationObject,以便加深印象
01 | public abstract class NotificationObject : INotifyPropertyChanged |
03 | public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; |
05 | protected virtual void RaisePropertyChanged(string propertyName) |
07 | PropertyChangedEventHandler handler = this.PropertyChanged; |
10 | handler(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName)); |
14 | protected void RaisePropertyChanged(params string[] propertyNames) |
16 | if (propertyNames == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("propertyNames"); |
18 | foreach (var name in propertyNames) |
20 | this.RaisePropertyChanged(name); |
24 | protected void RaisePropertyChanged<T>(Expression<Func<T>> propertyExpression) |
26 | var propertyName = ExtractPropertyName(propertyExpression); |
27 | this.RaisePropertyChanged(propertyName); |
30 | public static string ExtractPropertyName<T>(Expression<Func<T>> propertyExpression) |
32 | if (propertyExpression == null) |
34 | throw new ArgumentNullException("propertyExpression"); |
37 | var memberExpression = propertyExpression.Body as MemberExpression; |
38 | if (memberExpression == null) |
40 | throw new ArgumentException("PropertySupport_NotMemberAccessExpression_Exception", "propertyExpression"); |
43 | var property = memberExpression.Member as PropertyInfo; |
46 | throw new ArgumentException("PropertySupport_ExpressionNotProperty_Exception", "propertyExpression"); |
49 | var getMethod = property.GetGetMethod(true); |
50 | if (getMethod.IsStatic) |
52 | throw new ArgumentException("PropertySupport_StaticExpression_Exception", "propertyExpression"); |
55 | return memberExpression.Member.Name; |
相应的,Student类型修改为:
01 | public class Student : NotificationObject |
04 | public string FirstName |
14 | this.RaisePropertyChanged("FirstName"); |
19 | public string LastName |
29 | this.RaisePropertyChanged("LastName"); |
33 | public Student(string firstName, string lastName) |
35 | this.firstName = firstName; |
36 | this.lastName = lastName; |
4:问题再次出现,经过修改后的Student类型,是什么?
是实体Model,领域Model,还是别的什么?实际上,因为没有采用任何架构模式,当前的Student类型什么也不是,揉杂了很多功能。它既要负责提供属性,也要负责控制。
在MVVM架构模式中,和MVC称谓不同的地方,就是VM(ViewModel)部分。VM负责:接受View请求并决定调用哪个模型构件去处理请求,同时它还负责将数据返回给View进行显示。也就是说,VM完成的角色可以理解为MVC中的Control。(另外需要注意的一点是,在MVC中有一个概念叫做表现模型,所谓表现模型是领域模型的一个扁平化投影,不应和MVVM中的VIEW MODEL相混淆)。
所以,我们现在要明确这些概念。首先,将Student类型的功能细分化,VM的部分,我们跟页面名称对应起来应该叫做MainViewModel。实际项目中,功能页面会相应名为StudentView.xaml,则对应的VM名便称之为StudentViewModel.cs。我们继续重构上面的代码。
三:建立MVVM的各个部分
首先,建立View文件夹,然后,将MainPage.xmal修改为StudentView.xaml后放置到该目录下。
其次,简历ViewModels文件夹,新建一个类StudentViewModel.cs,放置到该目录下。
最后,原类型Student需要继续拆分,将作为领域模型部分的功能独立出来,放置到DomainModel文件夹下。最后的结果看起来如下:
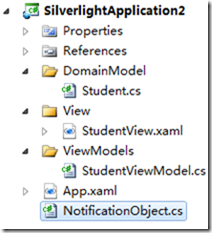
1:领域模型DomainModel部分
04 | public string FirstName |
17 | public string LastName |
37 | FirstName = "firstName" + DateTime.Now.ToString(); |
38 | LastName = "lastName" + DateTime.Now.ToString(); |
2:视图View部分
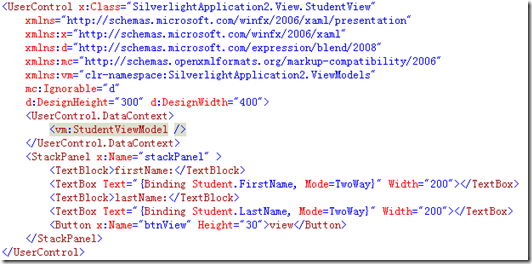
3:ViewModel部分
01 | public class StudentViewModel : NotificationObject |
03 | public StudentViewModel() |
05 | student = new Student(); |
09 | public Student Student |
18 | this.RaisePropertyChanged(() => this.student); |
4:若干解释
在这个简单的事例中,领域模型Student负责获取数据,而数据来源于何处不是我们关心的重点,所以,我们直接在Student中模拟了获取数据的过程,即Mock方法。
这相当于完成了一次OneWay的过程,即把后台数据推送到前台进行显示。这只能算是完成跟UI交互的一部分功能。UI交互还需要包括从UI中将数据持久化(如保存到数据库)。而UI跟后台的交互,就需要通过命令绑定的机制去实现了。
5:命令绑定
在本里中,我们演示两类命令,一类是属性类命令绑定,一类是事件类命令绑定。
首先,我们知道,VM负责UI和领域模型的联系,所以,绑定所支持的方法一定是在VM中,于是,我们在StudentViewModel中定义一个属性CanSubmit,及一个方法Submit:
注意,Submit方法中为了简单期间,使用了模拟方法。由于Mock方法中仍然可能设计到UI的变动(如随数据库的某些具体的值变动而变动),故领域模型Student可能也会需要继承NotificationObject,在本例中,Student改变为如下:
01 | public class Student : NotificationObject |
04 | public string FirstName |
13 | this.RaisePropertyChanged("FirstName"); |
18 | public string LastName |
27 | this.RaisePropertyChanged("LastName"); |
39 | FirstName = "firstName" + DateTime.Now.ToString(); |
40 | LastName = "lastName" + DateTime.Now.ToString(); |
其次,需要改变VIEW,如下:
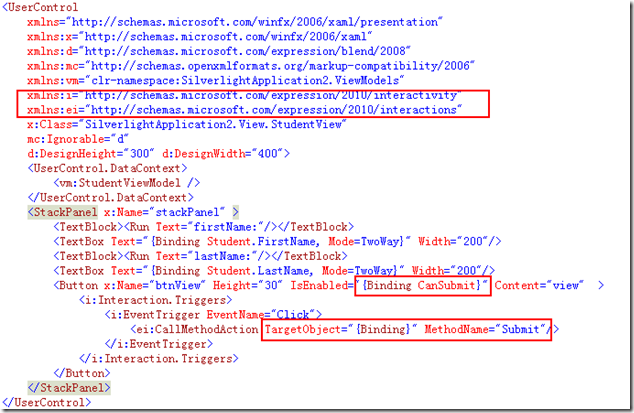
注意途中红线框起来的部分。
经过这一次的重构之后,基本满足了一个简单的MVVM模型的需要。代码下载在这里:https://files.cnblogs.com/luminji/SilverlightApplication2.rar





