
只要不放弃,希望迟早都会到来!
1. Bean的初始化
如果把bean的生命周期看作一个婴儿诞生过程的,那么创建实例相当于婴儿从母体出来,一丝不挂光秃秃;属性赋值相当于给宝宝的头带帽子,上身穿衣服、下神穿裤子、还有脚丫穿袜子;而初始化相当于教宝宝一些常规的动作,比如给宝宝吸奶,打嗝拍打,哄睡觉等,本篇继续分析初始化源码。
2. 初始化流程概览
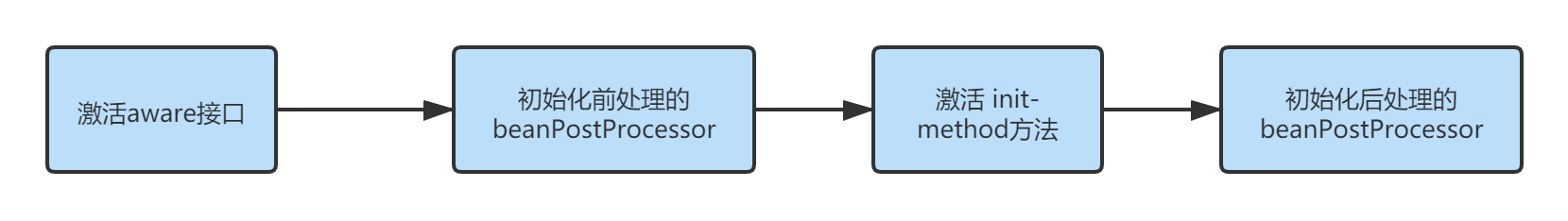
3. 源码分析
进入initializeBean方法:
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 激活aware接口
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 初始化前处理的beanPostProcessor , 比如aware接口,InitDestroyBeanPostProcessor,
// ImportAwareBeanPostPorcessor 对ImportAware的支持
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
// 激活 init-method方法
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 初始化后处理的beanPostProcessor
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
看到流程中主要分为上述流程概览中所述的四个步骤:
step1:激活aware接口;
step2:初始化前处理的beanPostProcessor;
step3:激活 init-method方法;
step4:初始化后处理的beanPostProcessor.
下面逐一分析。
激活aware接口,源码如下:
private void invokeAwareMethods(String beanName, Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader();
if (bcl != null) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);
}
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}
分别对BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware、BeanFactoryAwareaware接口进行处理,设置对应的属性;接下来进入applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization方法:
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
该方法对初始化前的beanPostProcessor进行处理,对比如InitDestroyBeanPostProcessor,对@PostConstruct的支持, ApplicationContextAwareProcessor对某个Aware接口方法的调用,ImportAwareBeanPostPorcessor对ImportAware的支持等;
接下来InitializingBean接口和init-method 属性调用对应方法为invokeInitMethods:
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}
else {
// 调用afterPropertiesSet方法
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) {
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) &&
!(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
// 调用自定义的init方法
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}
afterPropertiesSet 和 Init-method 和有@PostConstruct 注解的方法其实核心功能都是一样的,只是调用时序不一样而已,都是在该类实例化和 IOC 做完后调用的,我们可以在这些方法中做一些在 spring 或者 servlet 容器启动的时候的初始化工作。比如缓存预热,比如缓存数据加载到内存,比如配置解析,等等初始化工作调用顺序为先调用@PostConstruct(注解使用)、然后是 afterPropertiesSet、InitMethod(xml 配置)方法。
最后一步,初始化后处理的beanPostProcessor,这里最主要的是完成代理的生成,该内容放到后面AOP阶段再深入。
4. 总结
本篇主要分析了bean的初始化相关操作,包括@PostConstruct注解的支持,Aware接口的支持,以及初始化后的afterPropertiesSet方法以及InitMethod方法的支持,最后完成BeanPostProcessor的后置处理,生成aop代理实例,后续将继续分析spring bean的循环依赖问题。