---恢复内容开始---
ServletConfig
配置Servlet初始化参数
在Servlet的配置文件web.xml中,可以使用一个或多个<init-param>标签为servlet配置一些初始化参数。
<servlet> <servlet-name>servletDemo</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.fpc.servletDemo</servlet-class> <!-- 配置servletDemo的初始化参数 --> <init-param> <param-name>name</param-name> <param-value>fpc</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>password</param-name> <param-value>123456</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>charset</param-name> <param-value>UTF-8</param-value> </init-param> </servlet>
通过ServletConfig获取Servlet的初始化参数
当servlet配置了初始化参数后,web容器在创建servlet实例对象时,会自动将这些初始化参数封装到ServletConfig对象中,并在调用servlet的init方法时,将ServletConfig对象传递给servlet,进而我们通过ServletConfig对象就可以得到当前servlet的初始化参数信息。
package com.fpc; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.util.Enumeration; import javax.servlet.ServletConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class servletDemo extends HttpServlet { int i = 1; private ServletConfig config; @Override public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub this.config = config; } @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //获取在web.xml中配置的初始化参数 String paramVal = this.config.getInitParameter("name");//获取指定的初始化参数 response.getWriter().write(paramVal); response.getWriter().write("<br/>"); //获取所有的初始化参数 Enumeration<String> e = config.getInitParameterNames(); while ( e.hasMoreElements() ) { String name = e.nextElement(); String value = config.getInitParameter(name); response.getWriter().write(name + " = " + value + "<br/>"); } } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub response.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); out.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">"); out.println("<HTML>"); out.println(" <HEAD><TITLE>A Servlet</TITLE></HEAD>"); out.println(" <BODY>"); out.print(" This is "); out.print(this.getClass()); out.println(", using the POST method"); out.println(" </BODY>"); out.println("</HTML>"); out.flush(); out.close(); } }
当servlet配置了初始化参数后,web容器在创建servlet实例对象时,会自动将这些初始化参数封装到ServletConfig对象中,并在调用servlet的init方法时将ServletConfig对象传递给servlet,进而程序员通过ServletConfig对象就可以得到当前servlet的初始化参数信息。
运行结果:

ServletContext
web容器在启动时,它会为每个web应用程序都创建一个对应的ServletContext对象,它代表当前web应用。
ServletConfig对象中维护了ServletContext对象的引用,开发人员在编写Servlet时,可以通过ServletConfig.getServletContext方法获得ServletContext对象。
由于一个web应用中的所有Servlet共享一个ServletContext对象,因此Servlet对象之间可以通过ServletContext对象来实现通讯。ServletContext对象通常也称之为context域对象。
多个Servlet通过ServletContext对象实现数据共享
例:ServletContextDemo1和ServletContextDemo2通过ServletContext对象实现数据共享ServletContextDemo1
package com.fpc; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class ServletContextDemo1 extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub String data = "fpc_20171206"; /* * ServletConfig对象维护了ServletContext对象的引用,开发人员在编写servlet时 * 可以通过ServletConfig.getServletContext()方法获得ServletContext对象 * * */ //获取ServletContext对象 ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletConfig().getServletContext(); //将数据存储到ServletContext对象中 servletContext.setAttribute("name_date", data); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.doPost(req, resp); } }
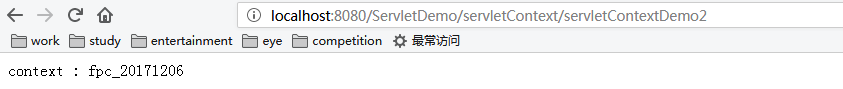
ServletContextDemo2
package com.fpc; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class ServletContextDemo2 extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletConfig().getServletContext(); String data = (String) servletContext.getAttribute("name_date"); resp.getWriter().write("context : " + data ); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.doPost(req, resp); } }
先运行ServletContextDemo1,将数据data存储到ServletContext对象中,然后再运行ServletContextDemo2即㐓从ServletContext对象中取出数据了,这样就实现了数据共享,如下图所示:
获取web应用的初始化参数
在web.xml文件中使用<context-param>标签配置web应用的初始化参数:
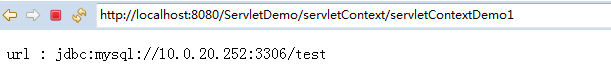
<!-- 配置web应用的初始化参数 --> <context-param> <param-name>url</param-name> <param-value>jdbc:mysql://10.0.20.252:306/test</param-value> </context-param>
获取web应用的初始化参数,代码如下:
String contextInitParam = servletContext.getInitParameter("url");
resp.getWriter().write("url : " + contextInitParam);
运行结果:
用ServletContext实现请求转发
ServletContextDemod1
package com.fpc; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class ServletContextDemo1 extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub String data = "<h1><font color='blue'>fpc_20171206</font></h1>"; resp.getOutputStream().write(data.getBytes()); ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();//获取ServletContext对象 RequestDispatcher rd = context.getRequestDispatcher("/servletContext/servletContextDemo2");//获取请求转发对象 rd.forward(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.doPost(req, resp); } }
ServletContextDemo2
package com.fpc; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class ServletContextDemo2 extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { resp.getOutputStream().write("ServletContextDemo2".getBytes()); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.doPost(req, resp); } }
运行结果:
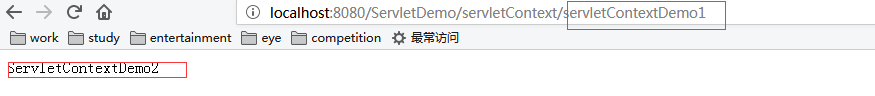
访问的是ServletContextDemo1,浏览器显示的却是ServletContextDemo2的内容,这就是使用了ServletContext实现了请求转发。
利用ServletContext对象读取资源文件
目录结构
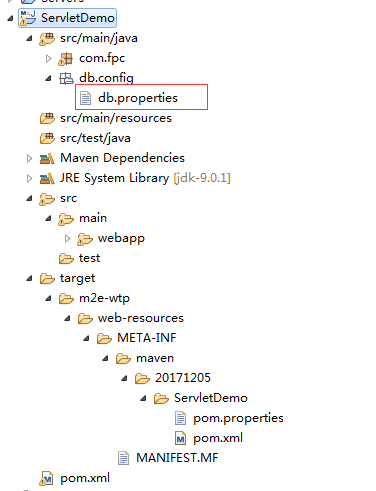
package com.fpc; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.Properties; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class ServletContextDemo2 extends HttpServlet { private void readFile(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException { //通过ServletContext获取文件的绝对路径 String path = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/db/config/db.properties"); InputStream in = new FileInputStream(path); Properties prop = new Properties(); prop.load(in); String driver = prop.getProperty("driver"); String url= prop.getProperty("url"); String username = prop.getProperty("name"); String password = prop.getProperty("password"); response.getWriter().write("dirver : " + driver + " url : " + url + " username : " + username + " password : " + password); } @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // resp.getOutputStream().write("ServletContextDemo2".getBytes()); //目的是控制浏览器用UTF-8进行编码;这样不会出现中文乱码 resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8"); resp.setHeader("content-type", "text/html;charset=UTF-8"); readFile(resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.doPost(req, resp); } }
运行结果:

访问路径为:/WEB-INF/classes/db/config/db.properties
在客户端缓存Servlet的输出
对于不经常变化的数据,在servlet中可以设置合理的缓存时间值,以避免浏览器频繁向服务器发送请求,提升服务器性能。
ServletContextDemo1
package com.fpc; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class ServletContextDemo1 extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub // String data = "<h1><font color='blue'>fpc_20171206</font></h1>"; // resp.getOutputStream().write(data.getBytes()); // ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();//获取ServletContext对象 // RequestDispatcher rd = context.getRequestDispatcher("/servletContext/servletContextDemo2");//获取请求转发对象 // rd.forward(req, resp); String data = "fpc_2017/12/06 14:07"; /* * 设置合理的缓存时间值,以避免浏览器向服务器发送请求,提升服务器的性能 * 这里是将数据的缓存时间设置为1天 * */ resp.setDateHeader("expires", System.currentTimeMillis() + 24 *3600*1000); resp.getOutputStream().write(data.getBytes()); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.doPost(req, resp); } }