参考博客:图的深度优先遍历(递归、非递归;邻接表,邻接矩阵)
本代码有个问题:就是结点是对应存储下标的,要解决这个问题,可以增加一个定位函数(LocateVec),不修改也可以使代码简洁些
关于非连通图的bug已修改,就是增加了dfsTraverse函数循环遍历一遍结点:没访问过则再做一次dfs
样例一连通,样例二非连通
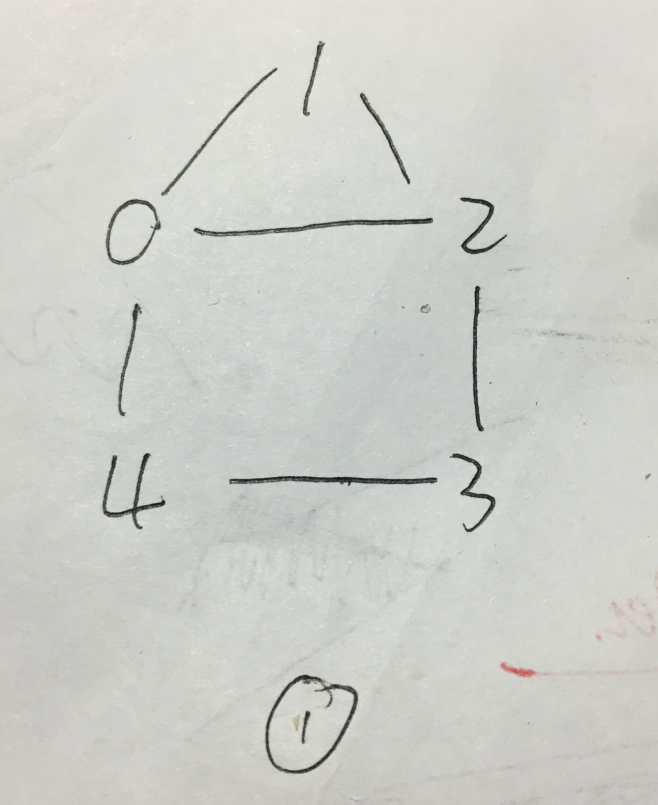
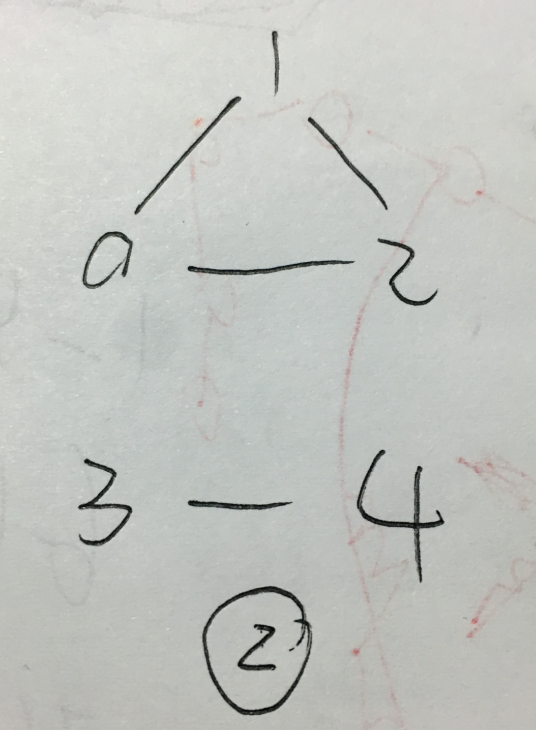
1.邻接表递归
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #define MAX 100 typedef struct EdgeNode// 边表结点 { int adjves;//存储顶点的下标 struct EdgeNode* next;//连接下一个邻点 }EdgeNode; typedef struct VertexNode//顶点表结点 { int ves;//顶点的值 EdgeNode* firstedge;//相连的顶点的值 }VertexNode,AdjList[MAX]; //邻接表 typedef struct { AdjList adjlist; int ves;//顶点 int edge;//边 int book[MAX];//判断是否有被访问过 }MGraph; void createMGraph(MGraph *G) { int i; int start; int end; EdgeNode *e; printf("please input the ves and edge: "); scanf("%d%d",&(G->ves),&(G->edge)); //初始化 printf("please input the ves: ");//此处设置顶点与存储下标相同且从零开始 for(i = 0; i < G->ves; i++)//输入顶点 { scanf("%d",&(G->adjlist[i].ves)); G->adjlist[i].firstedge = NULL; } //创建邻接矩阵 printf("please input the edges: "); for(i = 0; i < G->edge; i++) { scanf("%d%d",&start,&end); e =(EdgeNode*)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));//分配空间 e->adjves = end; e->next = G->adjlist[start].firstedge; G->adjlist[start].firstedge = e;//类似于链表的前插 e =(EdgeNode*)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));//分配空间 e->adjves = start; e->next = G->adjlist[end].firstedge; G->adjlist[end].firstedge = e;//类似于链表的前插 } } void dfs(MGraph *G,int ves) { EdgeNode *p; G->book[ves] = 1;//被访问过的结点置为1 printf("%d ",G->adjlist[ves].ves); p = G->adjlist[ves].firstedge;//取顶点 while(p) { if(G->book[p->adjves] == 0)//未被访问过 { dfs(G,p->adjves); } p = p->next; } } void dfsTraverse(MGraph *G){ int i; memset(G->book,0,sizeof(G->book));//清空标志位 for(i = 0; i < G->ves; i++) if(!G->book[i]) dfs(G, i); } int main() { MGraph G; createMGraph(&G); dfsTraverse(&G); return 0; } /* 输入样例_1: 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 1 2 2 3 2 0 3 4 0 4 输入样例_2: 5 4 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 0 2 1 2 3 4 */
样例一结果:
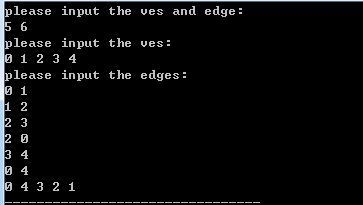
样例二结果:
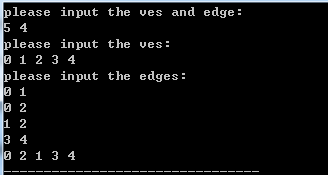
2.邻接表非递归
#include<iostream> #include<stdlib.h> #include<stack> #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #define MAX 100 using namespace std; typedef struct EdgeNode// 边表结点 { int adjves;//存储顶点的下标 struct EdgeNode* next;//连接下一个邻点 }EdgeNode; typedef struct VertexNode//顶点表结点 { int ves;//顶点的值 EdgeNode* firstedge;//相连的顶点的值 }VertexNode,AdjList[MAX]; //邻接表 typedef struct { AdjList adjlist; int ves;//顶点 int edge;//边 int book[MAX];//判断是否有被访问过 }MGraph; void createMGraph(MGraph *G) { int i; int start; int end; EdgeNode *e; printf("please input the ves and edge: ");//此处设置顶点与存储下标相同且从零开始 scanf("%d%d",&(G->ves),&(G->edge)); //初始化 printf("please input the ves: "); for(i = 0; i < G->ves; i++)//输入顶点 { scanf("%d",&(G->adjlist[i].ves)); G->adjlist[i].firstedge = NULL; } //创建邻接矩阵 printf("please input the edges: "); for(i = 0; i < G->edge; i++) { scanf("%d%d",&start,&end); e =(EdgeNode*)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));//分配空间 e->adjves = end; e->next = G->adjlist[start].firstedge; G->adjlist[start].firstedge = e;//类似于链表的前插 e =(EdgeNode*)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));//分配空间 e->adjves = start; e->next = G->adjlist[end].firstedge; G->adjlist[end].firstedge = e;//类似于链表的前插 } } void dfs(MGraph *G,int i) { stack <int>s; EdgeNode *p; G->book[i]=1; s.push(i); printf("%d ", G->adjlist[i].ves); p = G->adjlist[i].firstedge; while(!s.empty()) { p = G->adjlist[s.top()].firstedge; while(p) { if(G->book[p->adjves] == 0) { G->book[p->adjves]=1; printf("%d ",G->adjlist[p->adjves].ves); s.push(p->adjves); p = G->adjlist[p->adjves].firstedge; } else p=p->next; } if(p == NULL) { s.pop(); } } } void dfsTraverse(MGraph *G){ int i; memset(G->book,0,sizeof(G->book));//清空标志位 for(i = 0; i < G->ves; i++) if(!G->book[i]) dfs(G, i); } int main() { MGraph G; createMGraph(&G); dfsTraverse(&G); return 0; }
样例和运行结果与递归的一致