1.递归应用场景
看个实际应用场景,迷宫问题(回溯), 递归(Recursion)
2.递归的概念
简单的说: 递归就是方法自己调用自己,每次调用时 传入不同的变量.递归有助于编程者解决复杂的问题,同时可以让代码变得简洁。
3.递归调用机制
我列举两个小案例,来帮助大家理解递归,部分学员已经学习过递归了,这里在给大家回顾一下递归调用机制
- 打印问题
- 阶乘问题
- 使用图解方式说明了递归的调用机制

- 代码演示
public class RecursionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODOAuto-generated method stub
//通过打印问题,回顾递归调用机制
//test(4);
int res = factorial(3);
System.out.println("res=" + res);
}
//打印问题.
public static void test(int n) {
if (n > 2) {
test(n - 1);
} //else {
System.out.println("n=" + n);
// }
}
//阶乘问题
public static int factorial(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return factorial(n - 1) * n; // 1 * 2 * 3
}
}
}
4.递归能解决什么样的问题
递归用于解决什么样的问题
- 各种数学问题如: 8 皇后问题 , 汉诺塔, 阶乘问题, 迷宫问题, 球和篮子的问题(google 编程大赛)
- 各种算法中也会使用到递归,比如快排,归并排序,二分查找,分治算法等.
- 将用栈解决的问题-->第归代码比较简洁
5.递归需要遵守的重要规则
递归需要遵守的重要规则
- 执行一个方法时,就创建一个新的受保护的独立空间(栈空间)
- 方法的局部变量是独立的,不会相互影响, 比如 n 变量
- 如果方法中使用的是引用类型变量(比如数组),就会共享该引用类型的数据.
- 递归 必须向退出递归的条件逼近,否则就是无限递归,出现 StackOverflowError,死龟了:)
- 当一个方法执行完毕,或者遇到 return,就会返回, 遵守谁调用,就将结果返回给谁,同时当方法执行完毕或者返回时,该方法也就执行完毕
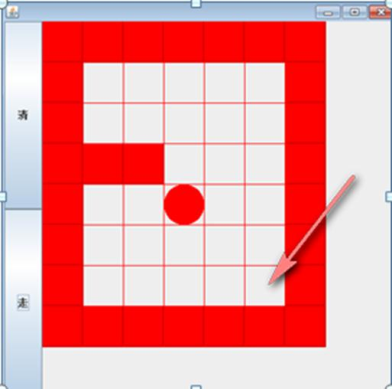
6.递归-迷宫问题
6.1迷宫问题
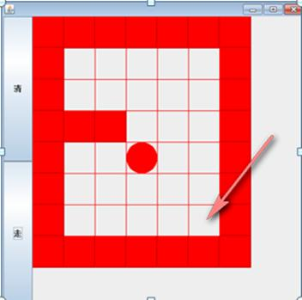
6.2代码实现:
public class MiGong {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 先创建一个二维数组,模拟迷宫
// 地图
int[][] map = new int[8][7];
// 使用 1 表示墙
// 上下全部置为 1
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
map[0][i] = 1;
map[7][i] = 1;
}
// 左右全部置为 1
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
map[i][0] = 1;
map[i][6] = 1;
}
//设置挡板, 1 表示
map[3][1] = 1;
map[3][2] = 1;
// map[1][2] = 1;
// map[2][2] = 1;
// 输出地图
System.out.println("地图的情况");
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 7; j++) {
System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
//使用递归回溯给小球找路
//setWay(map, 1, 1);
setWay2(map, 1, 1);
//输出新的地图, 小球走过,并标识过的递归
System.out.println("小球走过,并标识过的 地图的情况");
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 7; j++) {
System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//使用递归回溯来给小球找路
//说明
//1. map 表示地图
//2. i,j 表示从地图的哪个位置开始出发 (1,1)
//3. 如果小球能到 map[6][5] 位置,则说明通路找到.
//4. 约定: 当 map[i][j] 为 0 表示该点没有走过 当为 1 表示墙 ; 2 表示通路可以走 ; 3 表示该点已经走过,但是走不通
//5. 在走迷宫时,需要确定一个策略(方法) 下->右->上->左 , 如果该点走不通,再回溯
/**
* @param map 表示地图
* @param i 从哪个位置开始找
* @param j
* @return 如果找到通路,就返回 true, 否则返回 false
*/
public static boolean setWay(int[][] map, int i, int j) {
if (map[6][5] == 2) { // 通路已经找到 ok
return true;
} else {
if (map[i][j] == 0) { //如果当前这个点还没有走过
//按照策略 下->右->上->左 走
map[i][j] = 2; // 假定该点是可以走通.
if (setWay(map, i + 1, j)) {//向下走
return true;
} else if (setWay(map, i, j + 1)) { //向右走
return true;
} else if (setWay(map, i - 1, j)) { //向上
return true;
} else if (setWay(map, i, j - 1)) { // 向左走
return true;
} else {
//说明该点是走不通,是死路
map[i][j] = 3;
return false;
}
} else { // 如果 map[i][j] != 0 , 可能是 1, 2, 3
return false;
}
}
}
//修改找路的策略,改成 上->右->下->左
public static boolean setWay2(int[][] map, int i, int j) {
if (map[6][5] == 2) { // 通路已经找到 ok
return true;
} else {
if (map[i][j] == 0) { //如果当前这个点还没有走过
//按照策略 上->右->下->左
map[i][j] = 2; // 假定该点是可以走通.
if (setWay2(map, i - 1, j)) {//向上走
return true;
} else if (setWay2(map, i, j + 1)) { //向右走
return true;
} else if (setWay2(map, i + 1, j)) { //向下
return true;
} else if (setWay2(map, i, j - 1)) { // 向左走
return true;
} else {
//说明该点是走不通,是死路
map[i][j] = 3;
return false;
}
} else { // 如果 map[i][j] != 0 , 可能是 1, 2, 3
return false;
}
}
}
}
6.3.对迷宫问题的讨论
- 小球得到的路径,和程序员设置的 找路策略有关即:找路的上下左右的顺序相关
- 再得到小球路径时,可以先使用(下右上左),再改成( 上右下左),看看路径是不是有变化
- 测试回溯现象
- 思考: 如何求出最短路径? 思路-》代码实现.
public class MiGong {
public static final int UP = 1;
public static final int DOWN = 2;
public static final int LEFT = 3;
public static final int RIGHT = 4;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 0;
int[][] policys = new int[24][4];
for (int w = 1; w < 5; w++) {
for (int x = 1; x < 5; x++) {
for (int y = 1; y < 5; y++) {
for (int z = 1; z < 5; z++) {
if (x != y && y != z && x != z && w != x && w != y && w != z) {
policys[count][0] = w;
policys[count][1] = x;
policys[count][2] = y;
policys[count][3] = z;
count++;
}
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < policys.length; i++) {
searhRoute(policys[i]);
}
}
public static void searhRoute(int[] policy) {
//地图数组
int[][] map = new int[8][7];
//上下墙设置为1
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
map[0][i] = 1;
map[7][i] = 1;
}
//左右墙设置为1
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
map[i][0] = 1;
map[i][6] = 1;
}
//中间挡板设置为1
map[3][1] = 1;
map[3][2] = 1;
//boolean isSearch = setWay(map, 1, 1);
boolean isSearch = setWayByPolicy(map, 1, 1, policy);
//map输出
int length = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
if (map[i][j] == 2) {
length++;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int i = 0; i < policy.length; i++) {
System.out.print(policy[i]);
}
System.out.println("->length:" + length);
}
/**
* 找寻路线
*
* @param map 地图数组
* @param i 当前坐标i
* @param j 当前坐标j
* @return 是否找到通路
* 坐标值:
* 0:还未走,尚不确定可否走通
* 1:墙
* 2:可以走通
* 3:不可以走通
* 遵循走向策略:下-》右-》上-》左
*/
public static boolean setWay(int[][] map, int i, int j) {
//若走到map[6][5]==2,则走通迷宫
if (map[6][5] == 2) {
return true;
} else {
//若当前坐标还未走,则尝试走
if (map[i][j] == 0) {
//先假设当前坐标是可以走通的
map[i][j] = 2;
//向下走
if (setWay(map, i + 1, j)) {
return true;
}
//向右走
else if (setWay(map, i, j + 1)) {
return true;
}
//向上走
else if (setWay(map, i - 1, j)) {
return true;
}
//向左走
else if (setWay(map, i, j - 1)) {
return true;
} else {
//若都走不通,则当前点设置为不可以走通
map[i][j] = 3;
//此次路线找寻失败
return false;
}
} else {
//map[i][j]!=0,则可能为1,2,3
return false;
}
}
}
public static boolean setWayByPolicy(int[][] map, int i, int j, int[] policy) {
//若走到map[6][5]==2,则走通迷宫
if (map[6][5] == 2) {
return true;
} else {
//若当前坐标还未走,则尝试走
if (map[i][j] == 0) {
//先假设当前坐标是可以走通的
map[i][j] = 2;
List<IndexVal> ivlist = parse(policy, i, j);
//第一次方向
if (setWayByPolicy(map, ivlist.get(0).i, ivlist.get(0).j, policy)) {
return true;
}
//第二次方向
else if (setWayByPolicy(map, ivlist.get(1).i, ivlist.get(1).j, policy)) {
return true;
}
//第三次方向
else if (setWayByPolicy(map, ivlist.get(2).i, ivlist.get(2).j, policy)) {
return true;
}
//第四次方向
else if (setWayByPolicy(map, ivlist.get(3).i, ivlist.get(3).j, policy)) {
return true;
} else {
//若都走不通,则当前点设置为不可以走通
map[i][j] = 3;
//此次路线找寻失败
return false;
}
} else {
//map[i][j]!=0,则可能为1,2,3
return false;
}
}
}
public static List<IndexVal> parse(int[] policy, int i, int j) {
List<IndexVal> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int k = 0; k < policy.length; k++) {
switch (policy[k]) {
case UP:
list.add(new IndexVal(i - 1, j));
break;
case DOWN:
list.add(new IndexVal(i + 1, j));
break;
case LEFT:
list.add(new IndexVal(i, j - 1));
break;
case RIGHT:
list.add(new IndexVal(i, j + 1));
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return list;
}
static class IndexVal {
int i;
int j;
public IndexVal(int i, int j) {
this.i = i;
this.j = j;
}
}
}
7.递归-八皇后问题(回溯算法)
7.1.八皇后问题介绍
八皇后问题,是一个古老而著名的问题,是回溯算法的典型案例。该问题是国际西洋棋棋手马克斯·贝瑟尔于1848 年提出:在 8×8 格的国际象棋上摆放八个皇后,使其不能互相攻击,即: 任意两个皇后都不能处于同一行 、同一列或同一斜线上,问有多少种摆法(92)。

7.2.八皇后问题算法思路分析
- 第一个皇后先放第一行第一列
- 第二个皇后放在第二行第一列、然后判断是否 OK, 如果不 OK,继续放在第二列、第三列、依次把所有列都放完,找到一个合适
- 继续第三个皇后,还是第一列、第二列……直到第 8 个皇后也能放在一个不冲突的位置,算是找到了一个正确解
- 当得到一个正确解时,在栈回退到上一个栈时,就会开始回溯,即将第一个皇后,放到第一列的所有正确解,全部得到.
- 然后回头继续第一个皇后放第二列,后面继续循环执行 1,2,3,4 的步骤
- 示意图:

-
说明:
理论上应该创建一个二维数组来表示棋盘,但是实际上可以通过算法,用一个一维数组即可解决问题. arr[8] ={0 , 4, 7, 5, 2, 6, 1, 3} //对应 arr 下标 表示第几行,即第几个皇后,arr[i] = val , val 表示第 i+1 个皇后,放在第 i+1 行的第 val+1 列 -
八皇后问题算法代码实现(韩老师)
public class Queue8 {
//定义一个 max 表示共有多少个皇后
int max = 8;
//定义数组 array, 保存皇后放置位置的结果,比如 arr = {0 , 4, 7, 5, 2, 6, 1, 3}
int[] array = new int[max];
static int count = 0;
static int judgeCount = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试一把 , 8 皇后是否正确
Queue8 queue8 = new Queue8();
queue8.check(0);
System.out.printf("一共有%d 解法", count);
System.out.printf("一共判断冲突的次数%d 次", judgeCount); // 1.5w
}
//编写一个方法,放置第 n 个皇后
//特别注意: check 是 每一次递归时,进入到 check 中都有 for(int i = 0; i < max; i++),因此会有回溯
private void check(int n) {
if (n == max) { //n = 8 , 其实 8 个皇后就既然放好
print();
return;
}
//依次放入皇后,并判断是否冲突
for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) {
//先把当前这个皇后 n , 放到该行的第 1 列
array[n] = i;
//判断当放置第 n 个皇后到 i 列时,是否冲突
if (judge(n)) { // 不冲突
//接着放 n+1 个皇后,即开始递归
check(n + 1); //
}
//如果冲突,就继续执行 array[n] = i; 即将第 n 个皇后,放置在本行得 后移的一个位置
}
}
//查看当我们放置第 n 个皇后, 就去检测该皇后是否和前面已经摆放的皇后冲突
/**
* @param n 表示第 n 个皇后
* @return
*/
private boolean judge(int n) {
judgeCount++;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 说明
//1. array[i] == array[n] 表示判断 第 n 个皇后是否和前面的 n-1 个皇后在同一列
//2. Math.abs(n-i) == Math.abs(array[n] - array[i]) 表示判断第 n 个皇后是否和第 i 皇后是否在同一斜线
// n = 1 放置第 2 列 1 n = 1 array[1] = 1
// Math.abs(1-0) == 1 Math.abs(array[n] - array[i]) = Math.abs(1-0) = 1
//3. 判断是否在同一行, 没有必要,n 每次都在递增
if (array[i] == array[n] || Math.abs(n - i) == Math.abs(array[n] - array[i])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
//写一个方法,可以将皇后摆放的位置输出
private void print() {
count++;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
* 八皇后问题算法代码实现(自己)
public class Empress8 {
static int maxSize = 8;
static int[] board = new int[maxSize];
static int count = 0;
static int conflictCount = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
check(0);
System.out.println("count:" + count);
System.out.println("conflictCount:" + conflictCount);
}
/**
* 检查
*
* @return
*/
public static void check(int n) {
if (n == maxSize) {
print();
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < maxSize; i++) {
//第n+1行依此等于1-8列(0-7)
board[n] = i;
//判断是否冲突
if (isNotConflict(n)) {
//如果不冲突,则添加下一行
check(n + 1);
}
//冲突则,列+1再判断是否冲突
}
}
/**
* 第n个是否冲突
*
* @param n
* @return
*/
public static boolean isNotConflict(int n) {
conflictCount++;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (board[i] == board[n] || Math.abs(n - i) == Math.abs(board[n] - board[i])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void print() {
count++;
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
System.out.print(board[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}