StandardService#startInternal中, 除了调用了 engine.start()外, 还调用了 connector#start()
Connector#start()
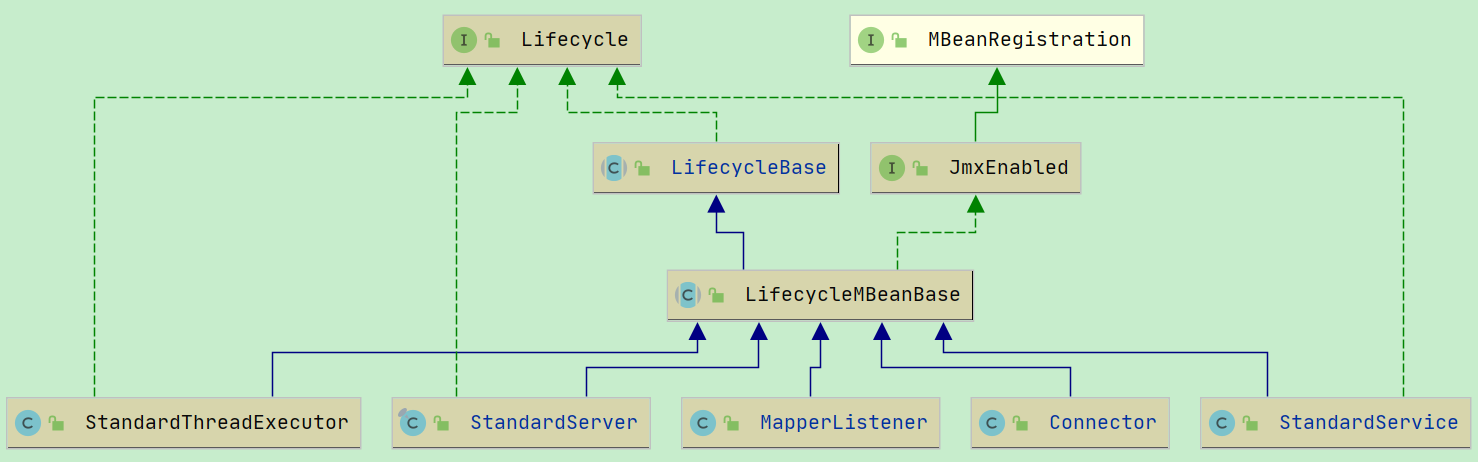
connector.start()最终调用的是 Connector#startInternal()方法.
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { // Validate settings before starting if (getPort() < 0) { throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString( "coyoteConnector.invalidPort", Integer.valueOf(getPort()))); } setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); try { //Http11NioProtocol#start() -> AbstractProtocol#start() protocolHandler.start(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new LifecycleException( sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerStartFailed"), e); } }
这里的 protocolHandler 就是 Http11NioProtocol
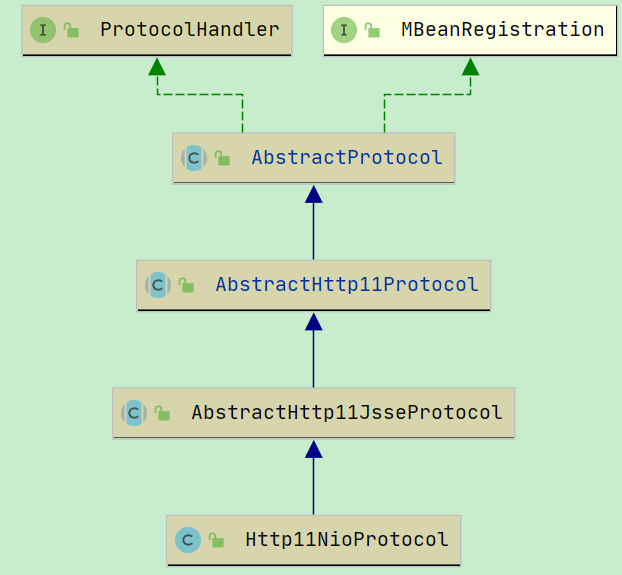
这里start调用的是 org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol#start
public void start() throws Exception { if (getLog().isInfoEnabled()) { getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.start", getName())); } //NioEndpoint#startInternal() endpoint.start(); // Start timeout thread asyncTimeout = new AsyncTimeout(); Thread timeoutThread = new Thread(asyncTimeout, getNameInternal() + "-AsyncTimeout"); int priority = endpoint.getThreadPriority(); if (priority < Thread.MIN_PRIORITY || priority > Thread.MAX_PRIORITY) { priority = Thread.NORM_PRIORITY; } timeoutThread.setPriority(priority); timeoutThread.setDaemon(true); timeoutThread.start(); }
endpoint 是 NipEndpoint, 他是与 Http11NioProtocol 对应的, 实在创建 Http11NioProtocol 的时候, 就写死传进来的.
这里的start最终也是调用 org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint#startInternal
public void startInternal() throws Exception { if (!running) { running = true; paused = false; processorCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE, socketProperties.getProcessorCache()); eventCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE, socketProperties.getEventCache()); nioChannels = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE, socketProperties.getBufferPool()); // Create worker collection if ( getExecutor() == null ) { createExecutor(); } initializeConnectionLatch(); // Start poller threads pollers = new Poller[getPollerThreadCount()]; for (int i=0; i<pollers.length; i++) { pollers[i] = new Poller(); Thread pollerThread = new Thread(pollers[i], getName() + "-ClientPoller-"+i); pollerThread.setPriority(threadPriority); pollerThread.setDaemon(true);
//启动 poller 线程 pollerThread.start(); } startAcceptorThreads(); } }
1. 多线程的方式, 启动了 poller 线程
2. 调用 startAcceptorThreads 方法, 启动了接收线程
protected final void startAcceptorThreads() { int count = getAcceptorThreadCount(); acceptors = new Acceptor[count]; for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { acceptors[i] = createAcceptor(); String threadName = getName() + "-Acceptor-" + i; acceptors[i].setThreadName(threadName); Thread t = new Thread(acceptors[i], threadName); t.setPriority(getAcceptorThreadPriority()); t.setDaemon(getDaemon()); t.start(); } }
Poller
//org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.Poller#run @Override public void run() { // Loop until destroy() is called while (true) { boolean hasEvents = false; try { if (!close) { hasEvents = events(); if (wakeupCounter.getAndSet(-1) > 0) { //if we are here, means we have other stuff to do //do a non blocking select keyCount = selector.selectNow(); } else { keyCount = selector.select(selectorTimeout); } wakeupCounter.set(0); } if (close) { //获取了 EventQueue 中所有的 PollerEvent, 然后依次调用 PollerEvent#run() 方法. //将 socket 注册到 selector 中. events(); timeout(0, false); try { selector.close(); } catch (IOException ioe) { log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.selectorCloseFail"), ioe); } break; } } catch (Throwable x) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(x); log.error("",x); continue; } //either we timed out or we woke up, process events first if ( keyCount == 0 ) hasEvents = (hasEvents | events()); Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null; // Walk through the collection of ready keys and dispatch // any active event. while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey sk = iterator.next(); NioSocketWrapper attachment = (NioSocketWrapper)sk.attachment(); // Attachment may be null if another thread has called // cancelledKey() if (attachment == null) { iterator.remove(); } else { iterator.remove(); //处理 OPEN_READ 和 OPEN_WRITE 事件 processKey(sk, attachment); } }//while //process timeouts timeout(keyCount,hasEvents); }//while getStopLatch().countDown(); }
while(true) , 设置死循环, 在没有请求进来的时候, 不会执行什么我想看到的功能, 也相当于是在等待客户端请求进来
Acceptor
protected class Acceptor extends AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor { @Override public void run() { int errorDelay = 0; // Loop until we receive a shutdown command while (running) { // Loop if endpoint is paused while (paused && running) { state = AcceptorState.PAUSED; try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // Ignore } } if (!running) { break; } state = AcceptorState.RUNNING; try { //if we have reached max connections, wait //最大连接数量的限制 countUpOrAwaitConnection(); SocketChannel socket = null; try { // Accept the next incoming connection from the server // socket 监听阻塞 socket = serverSock.accept(); //调试添加 监听到之后, 继续往下执行 System.out.println("调试添加 : " + socket); } catch (IOException ioe) { // We didn't get a socket countDownConnection(); if (running) { // Introduce delay if necessary errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay); // re-throw throw ioe; } else { break; } } // Successful accept, reset the error delay errorDelay = 0; // Configure the socket if (running && !paused) { // setSocketOptions() will hand the socket off to // an appropriate processor if successful // 调用 NioEndpoint#setSocketOptions() 方法, 对socket进行处理 if (!setSocketOptions(socket)) { closeSocket(socket); } } else { closeSocket(socket); } } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), t); } } state = AcceptorState.ENDED; } private void closeSocket(SocketChannel socket) { ...... } }
Acceptor会一直阻塞在这里, 监听socket, 等待客户端连接进来