Mike has a sequence A = [a1, a2, ..., an] of length n. He considers the sequence B = [b1, b2, ..., bn] beautiful if the gcd of all its elements is bigger than 1, i.e. 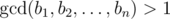 .
.
Mike wants to change his sequence in order to make it beautiful. In one move he can choose an index i (1 ≤ i < n), delete numbers ai, ai + 1 and put numbers ai - ai + 1, ai + ai + 1 in their place instead, in this order. He wants perform as few operations as possible. Find the minimal number of operations to make sequence A beautiful if it's possible, or tell him that it is impossible to do so.
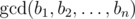 is the biggest non-negative number d such that d divides bi for every i (1 ≤ i ≤ n).
is the biggest non-negative number d such that d divides bi for every i (1 ≤ i ≤ n).
The first line contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — length of sequence A.
The second line contains n space-separated integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — elements of sequence A.
Output on the first line "YES" (without quotes) if it is possible to make sequence A beautiful by performing operations described above, and "NO" (without quotes) otherwise.
If the answer was "YES", output the minimal number of moves needed to make sequence A beautiful.
题解:当$gcd (x,y)! = 1$时,直接得出答案。
当$gcd (x,y) = = 1$,令$d = gcd (x - y,x + y)$,
所以,$d|(x - y),d|(x + y)$
由信安数基课本P4,$a|b,a|c o a|tb + sc$,
$d|2x,d|2y$$ o d|gcd (2x,2y) o d|2gcd (x,y) o d|2$,$d = = 1or2$因为若再继续下去,必须满足此等式,故不必继续。
可以看出最后的d一定整除偶数,所以n个数必须都为偶数.
所以此题即变为,把n个数变为偶数的最小步数。
当$a[i]\% 2 = = 1 ,a[i + 1]\% 2 = = 1$,步数增加1,
当a[i]和a[i+1]有一个为偶数时,步数增加2.
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef long long ll; 4 using namespace std; 5 ll n,a[100005],t=0; 6 ll gcd(ll a,ll b){ 7 while(b){ 8 ll temp=b; 9 b=a%b; 10 a=temp; 11 } 12 return a; 13 } 14 int main(){ 15 cin>>n; 16 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 17 cin>>a[i]; 18 t=gcd(t,a[i]); 19 } 20 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 21 a[i]%=2; 22 } 23 if(t!=1){ 24 cout<<"YES 0 "; 25 return 0; 26 } 27 ll ans=0; 28 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 29 if(a[i]){ 30 ans++; 31 if(!a[i+1]){ 32 ans++; 33 } 34 a[i]=a[i+1]=0; 35 } 36 } 37 cout<<"YES "<<ans<<endl; 38 39 }