1、集合输出
在之前我们利用了toString()及get()方法对集合进行了输出,其实那都不是集合的标准输出,集合输出有四种方式:Iterator、ListIterator、Enumeration、foreach。
(1)Iterator(迭代输出)
在jdk1.5之前,在Collection接口中就有iterator()方法来获取Iterator接口的实例化对象,而在jdk1.5之后该方法被提升到Iterable接口中,但是不管怎么提升,只要Collection有该方法,则List和Set也有此方法。
Iterator接口中的方法:
1. 判断是否有下一个元素: public boolean hasNext(); 2. 取得当前元素: public E next(); 3. 删除元素: public default void remove(); |
- /*
- * Iterator输出
- * */
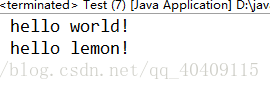
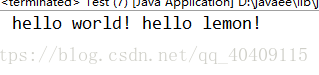
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
- list.add("hello");
- list.add("world!");
- list.add("
hello");
- list.add("lemon!");
- //实例化Iterator对象
- Iterator<String> iterable = list.iterator();
- //循环输出
- while(iterable.hasNext()) {
- System.out.print(" "+iterable.next());
- }
- }
- }
下面我们来观察在集合输出的过程中对集合中的元素进行更改的情况:
- /*
- * 输出过程中对集合内容进行更改
- * */
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
- list.add("hello");
- list.add("world!");
- list.add("
hello");
- list.add("lemon!");
- //实例化Iterator对象
- Iterator<String> iterable = list.iterator();
- //循环输出
- while(iterable.hasNext()) {
- String string = iterable.next();
- if(string.equals("hello")) {
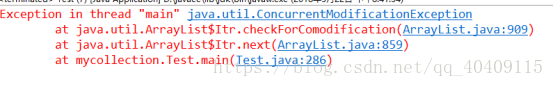
- //使用集合提供的remove()方法时,会抛出java.util.ConcurrentModificationException异常
- //list.remove(string);
- //使用Iterator的remove()方法则不会抛出异常
- iterable.remove();
- continue;
- }
- System.out.print(" "+string);
- }
- }
- }
使用list的remove()方法运行结果:
使用Iterator的remove()方法运行结果:
所以一般在集合输出时,我们不对其元素进行修改。
(2)ListIterator(双向迭代接口)
只有List接口有,而Set接口没有。
- /*
- * ListIterator双向迭代输出
- * */
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
- list.add("hello");
- list.add("world!");
- list.add("hello");
- list.add("lemon!");
- //实例化Iterator对象
- ListIterator<String> listIterator = list.listIterator();
- // //向前循环输出
- // while(listIterator.hasPrevious()) {
- // System.out.print(" "+listIterator.previous());
- // }
- //向后循环输出
- while(listIterator.hasNext()) {
- System.out.print(" "+listIterator.next());
- }
- System.out.println();
- //向前循环输出
- while(listIterator.hasPrevious()) {
- System.out.print(" "+listIterator.previous());
- }
- }
- }
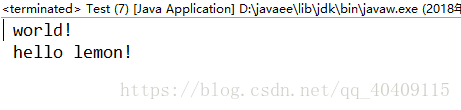
先向后输出在向前输出运行结果:
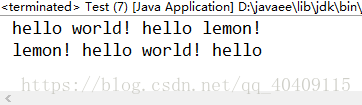
在向后输出之前先进行向前输出运行结果:
所以要使用双向迭代输出,不仅要是List的子类,而且必须先实现向后输出才可执行向前输出,要不然不能出现向前执行的结果,无法实现双向。
(3)Enumeration(枚举输出)
只有Vector类才有。
Enumeration的接口定义
判断是否有下一个元素:public boolean hasMoreElements(); 取得元素:public E nextElement(); |
但是要想取得这个接口的实例化对象,是不能依靠Collection、List、Set等接口的。只能够依靠Vector子类,因为Enumeration最早的设计就是为Vector服务的,在Vector类中提供有一个取得Enumeration接口对象的方法:
取得Enumeration接口对象:public Enumeration elements()
- /*
- * Enumeration枚举输出
- * */
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Vector< String> vector = new Vector<>();
- vector.add("hello");
- vector.add("lemon!");
- vector.add("hello");
- vector.add("world!");
- //取得对象
- Enumeration<String> enumeration = vector.elements();
- //循环输出
- while(enumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
- System.out.print(" "+enumeration.nextElement());
- }
- }
- }
(4)foreach
从JDK1.5开始foreach可以输出数组,实际上除了数组之外也可以输出集合.
- /*
- * foreach输出
- * */
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Vector< String> vector = new Vector<>();
- vector.add("hello");
- vector.add("lemon!");
- vector.add("hello");
- vector.add("world!");
- for (String string : vector) {
- System.out.print(" "+string);
- }
- }
- }
2、栈和队列
(1)Stack栈(类)
栈是一种后进先出的数据结构,常见的浏览器的退出、文件的撤销等都属于栈的功能。
在Java中提供有Stack类,这个类是Vector的子类。
public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E>
Stack在使用时不是使用Vector的方法而是使用其自定义的方法,且在使用时不需要向上转型,因为要操作的方法不是有List定义的而是Stack自定义的。
常用方法:
入栈:public E push(E item) |
出栈:public synchronized E pop() |
返回栈顶元素:public synchronized E peek() |
- /*
- * Stack栈
- * */
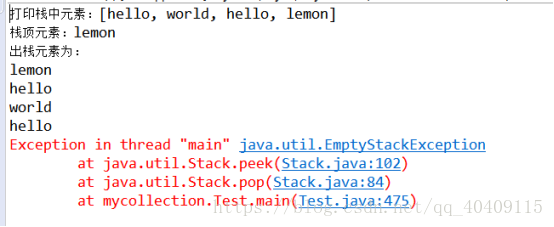
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
- //入栈
- stack.push("hello");
- stack.push("world");
- stack.push("hello");
- stack.push("lemon");
- System.out.println("打印栈中元素:"+stack);
- //取栈顶元素
- System.out.println("栈顶元素:"+stack.peek());
- //出栈
- System.out.println("出栈元素为:");
- System.out.println(stack.pop());
- System.out.println(stack.pop());
- System.out.println(stack.pop());
- System.out.println(stack.pop());
- //对空栈进行出栈操作
- System.out.println(stack.pop());
- }
- }
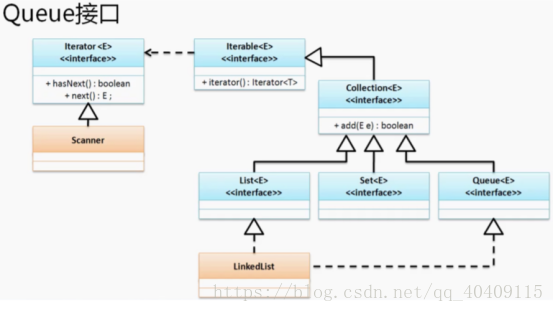
(2)Queue队列(接口)
Stack栈是后进先出,而与之对应的Queue队列则是先进先出。
在java.util包下的Queue接口实现队列操作,而Queue提供有一个子类LinkedList.
public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E>
常用方法:
入队列:public boolean add(E e) |
出队列:public E poll() |
取队首元素:public E peek() |
- /*
- * Queue队列
- * */
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
- //入队列
- queue.add("hello");
- queue.add("world");
- queue.add("hello");
- queue.add("lemon");
- //取队首元素
- System.out.println("队首元素:"+queue.peek());
- //出队列
- System.out.println("出队元素:");
- System.out.print(queue.poll());
- System.out.print(" "+queue.poll());
- System.out.print(" "+queue.poll());
- System.out.print(" "+queue.poll());
- }
- }
3、Collections工具类
Collections是一个集合操作的工具类,包括集合的反转、排序等操作。
- /*
- *Collections工具类
- * */
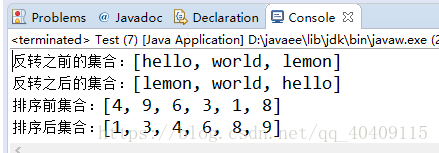
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
- //相当于调用三次add()方法
- Collections.addAll(list,"hello","world","lemon");
- System.out.println("反转之前的集合:"+list);
- //对集合进行反转
- Collections.reverse(list);
- System.out.println("反转之后的集合:"+list);
-
- List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
- Collections.addAll(list1, 4,9,6,3,1,8);
- System.out.println("排序前集合:"+list1);
- //对list1集合进行排序
- Collections.sort(list1);
- System.out.println("排序后集合:"+list1);
- }
- }