http://www.inference.org.uk/mackay/itprnn/
http://videolectures.net/course_information_theory_pattern_recognition/


1948, Shanon's fundamental problem: Reliable communication over an unreliable channel
eg:



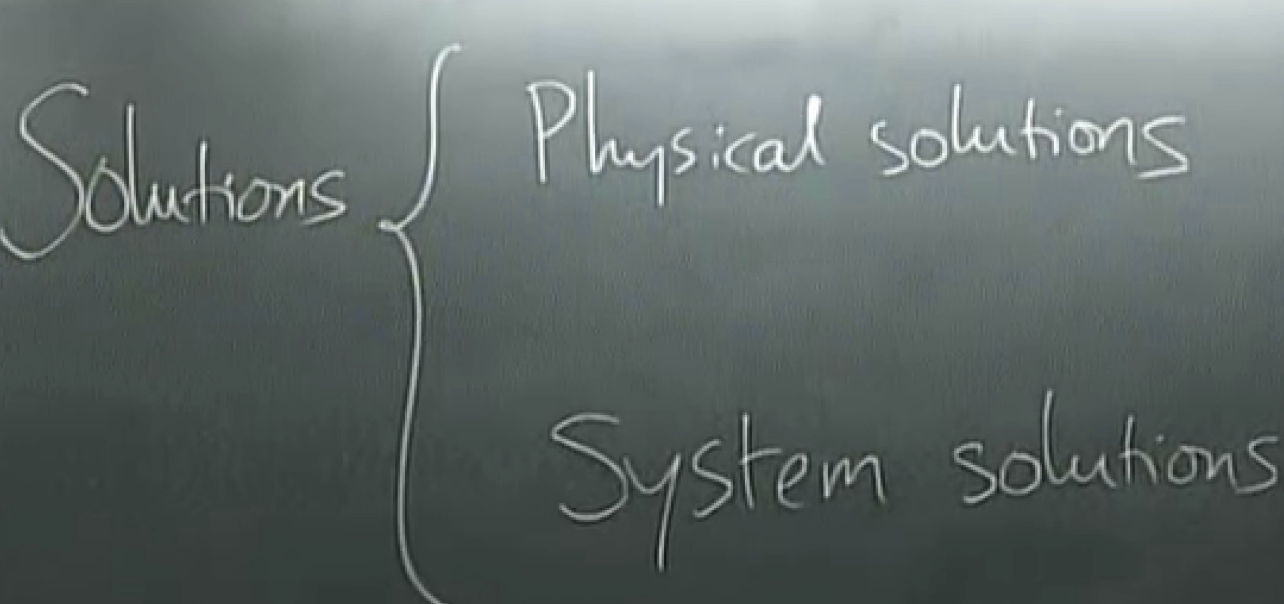
change the physics: replace equipment with a better one.
system solution: add encoding and decoding



hat means a guess
s -> hat{s}
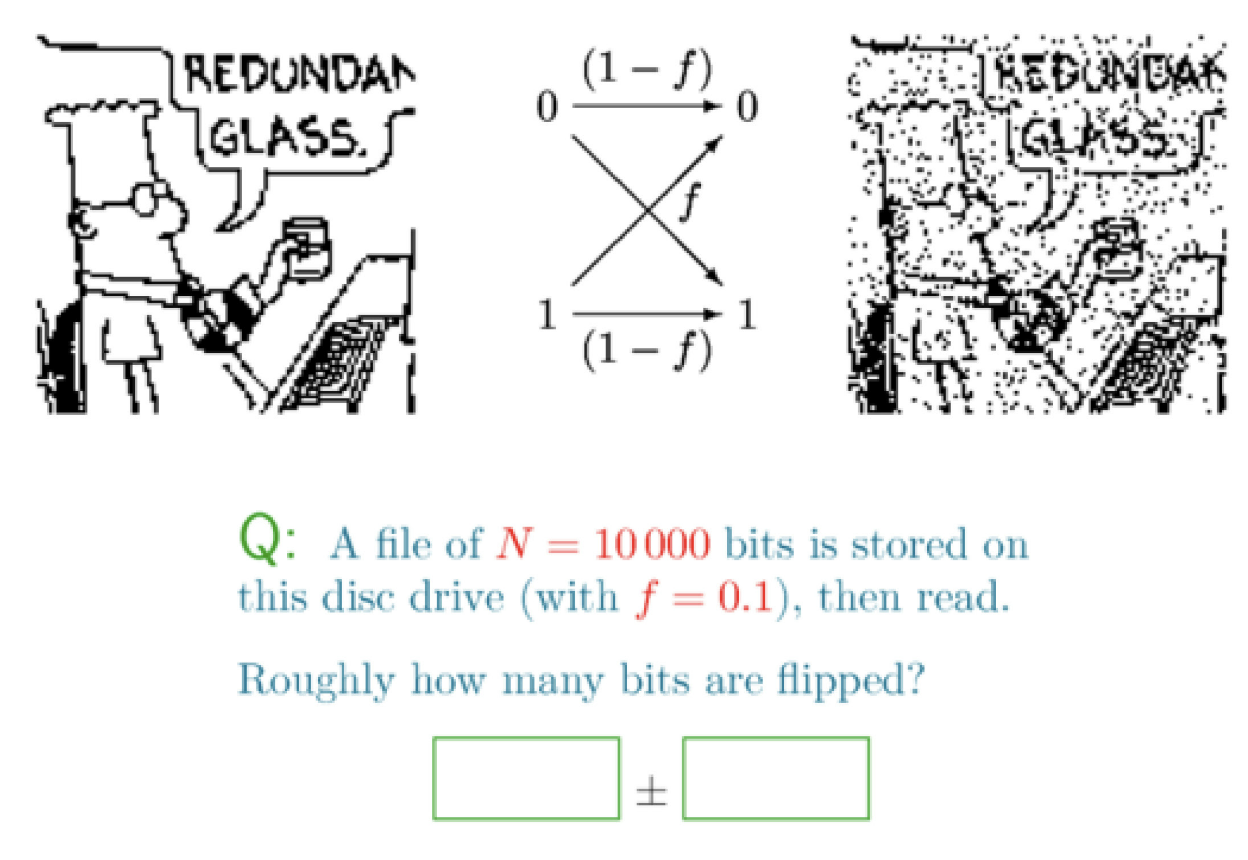
toy example: binary symmetric channel



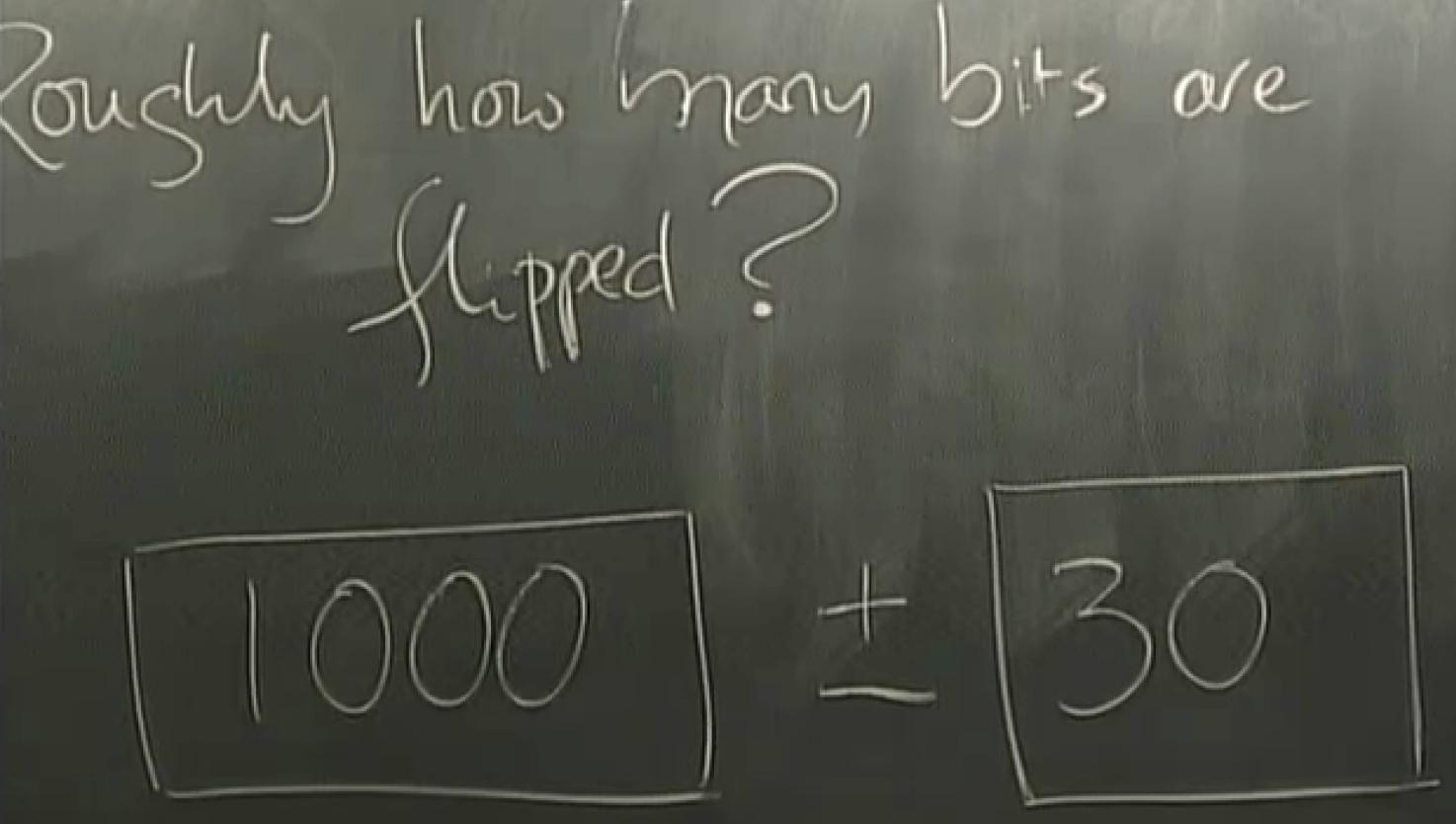

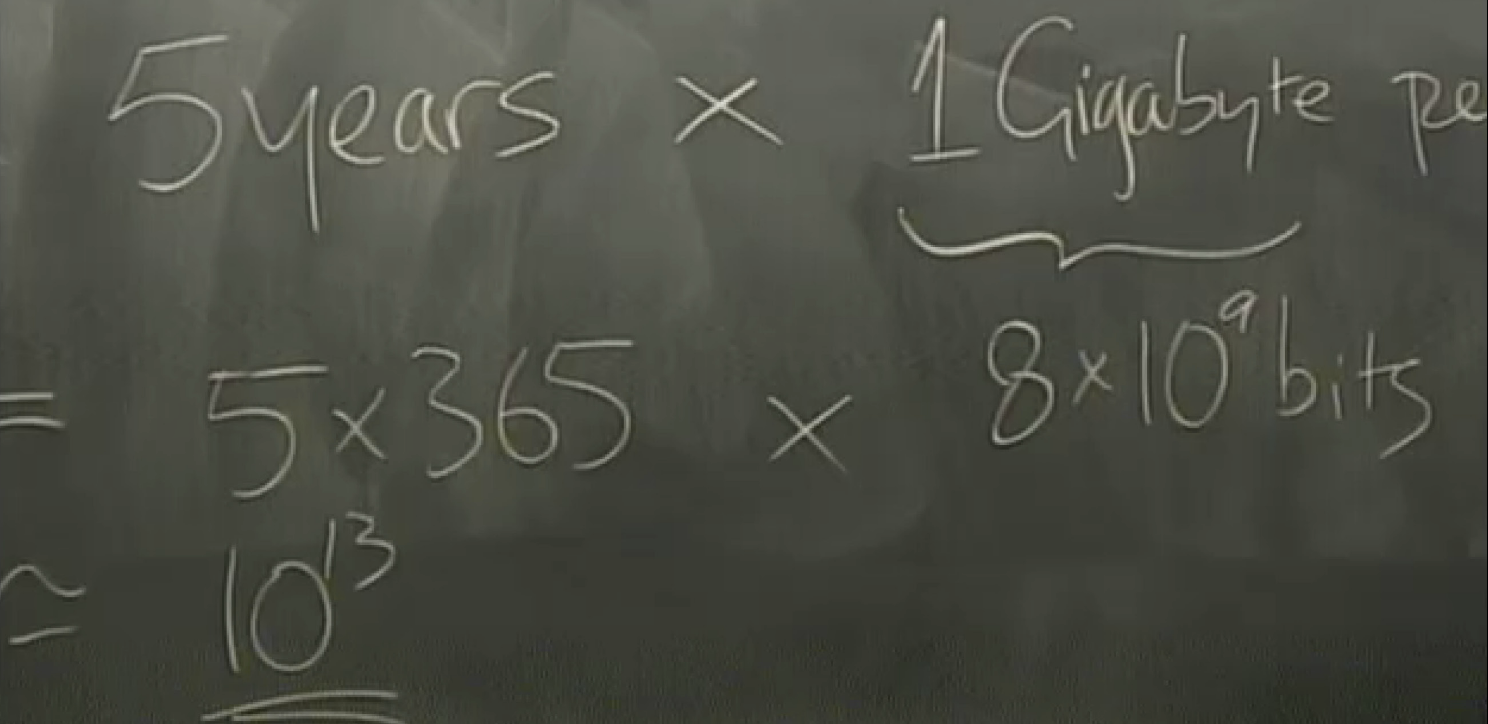
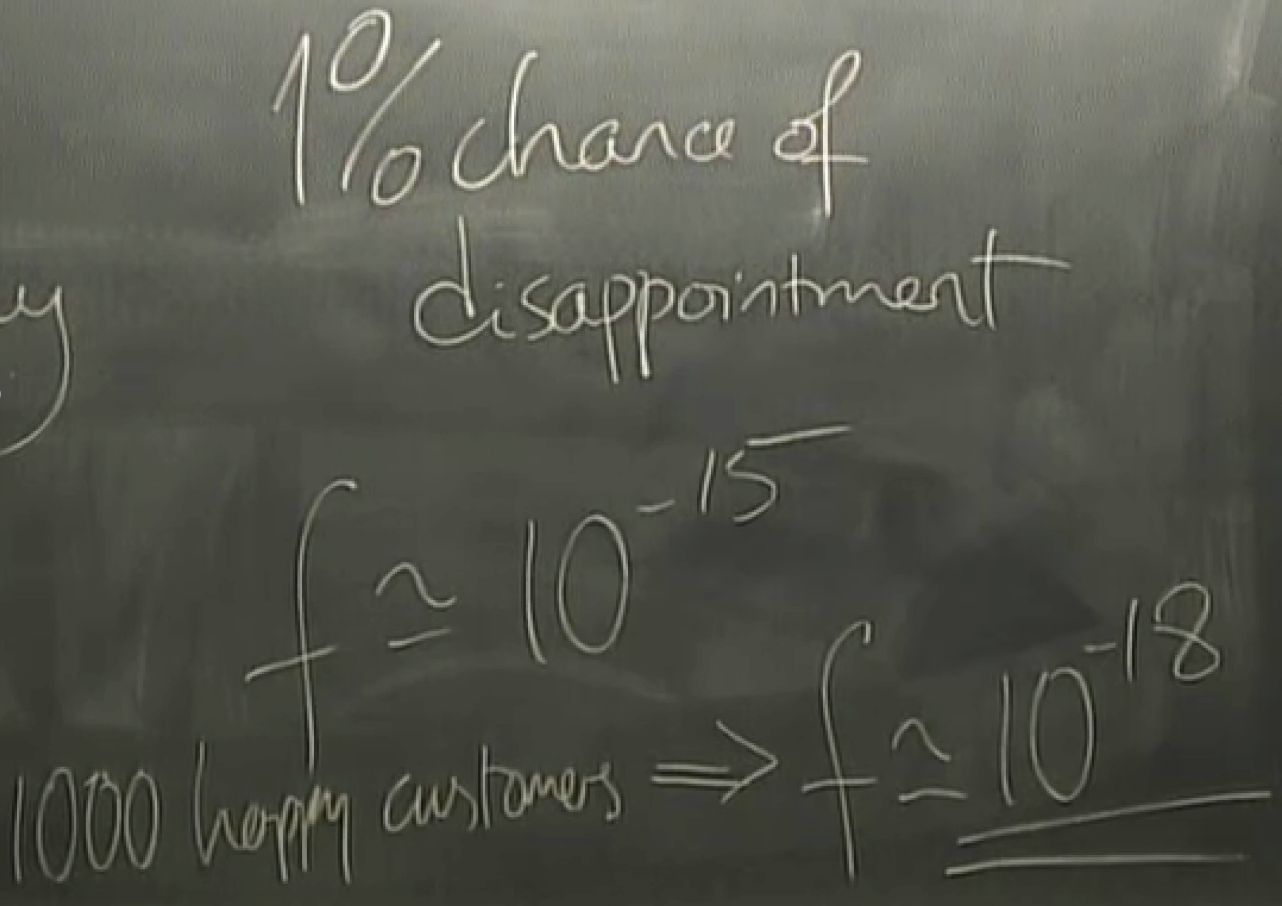

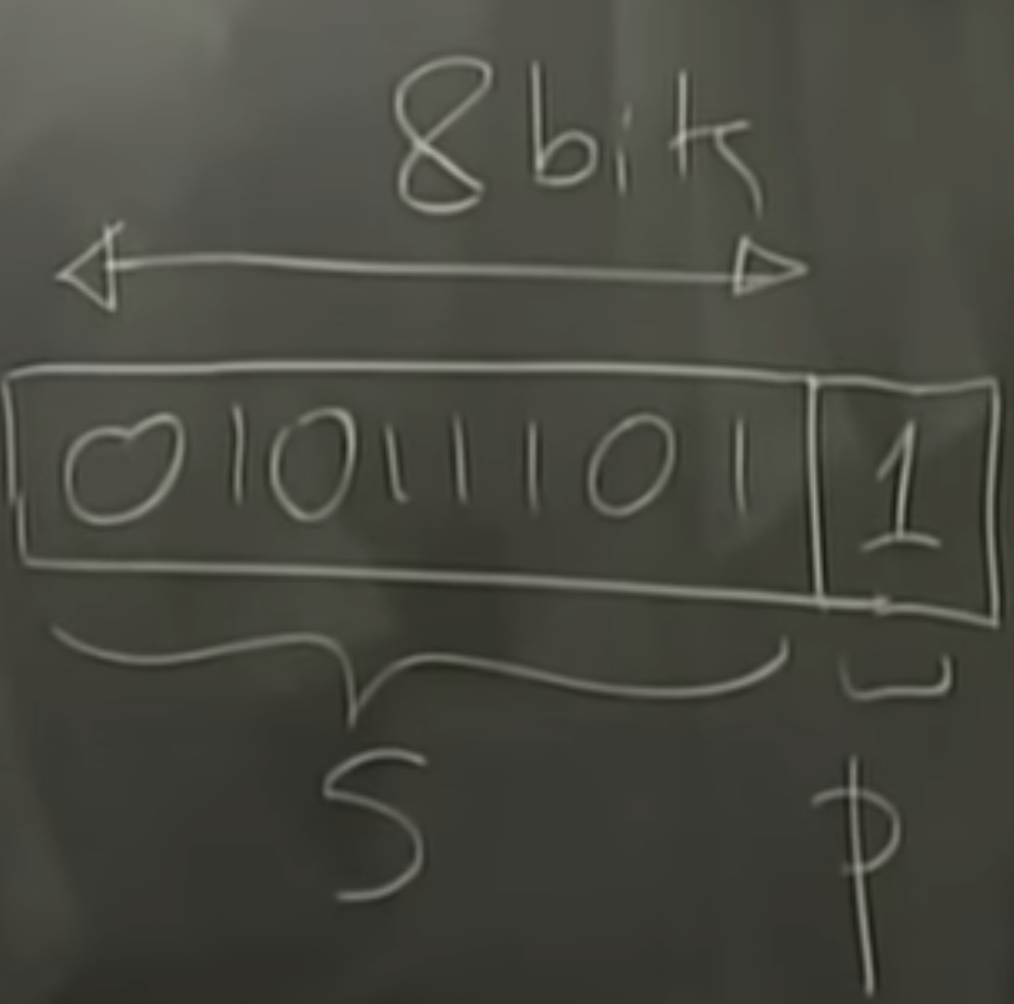
partity coding: even->0 for p; odd->1 for p

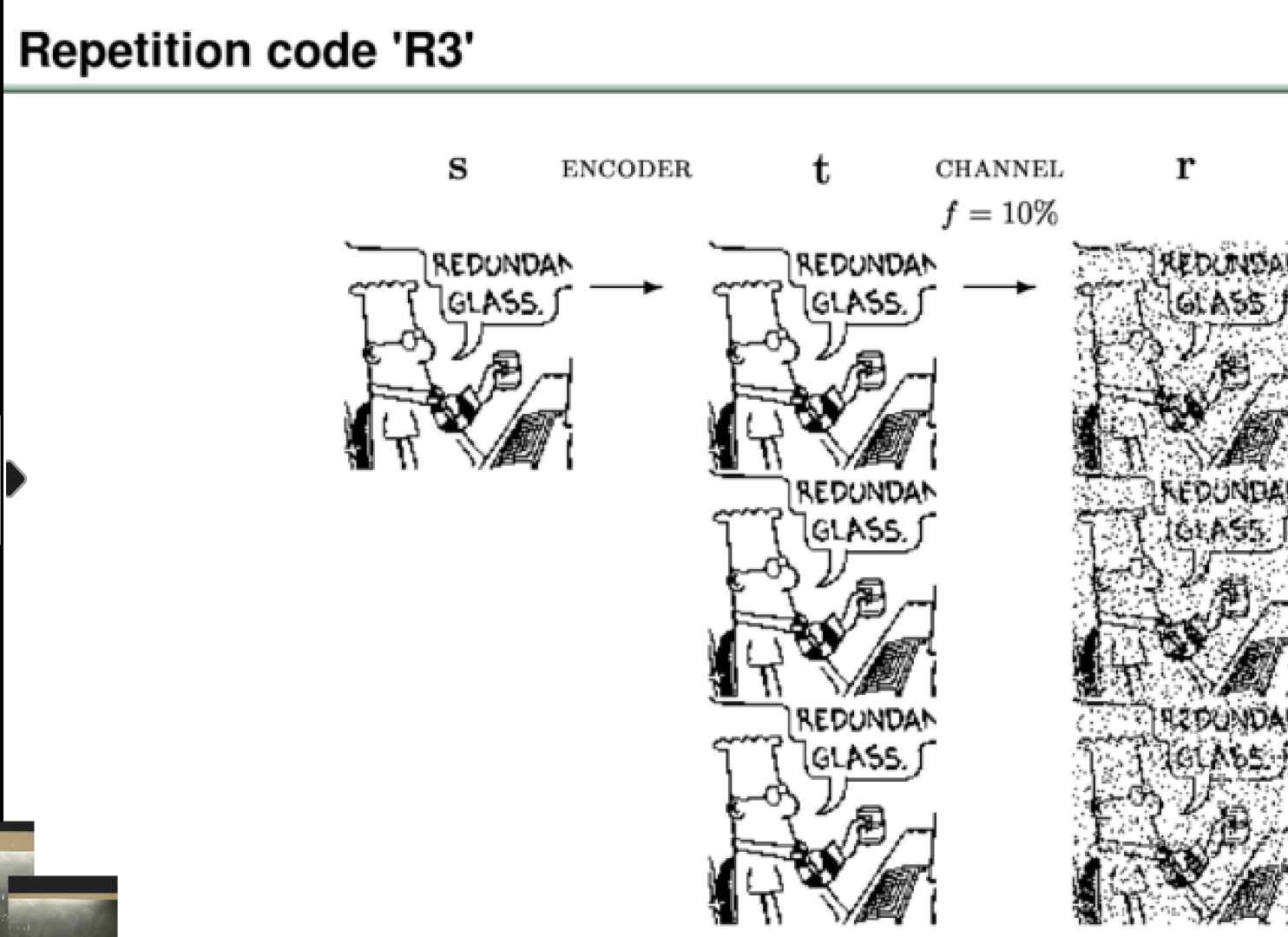
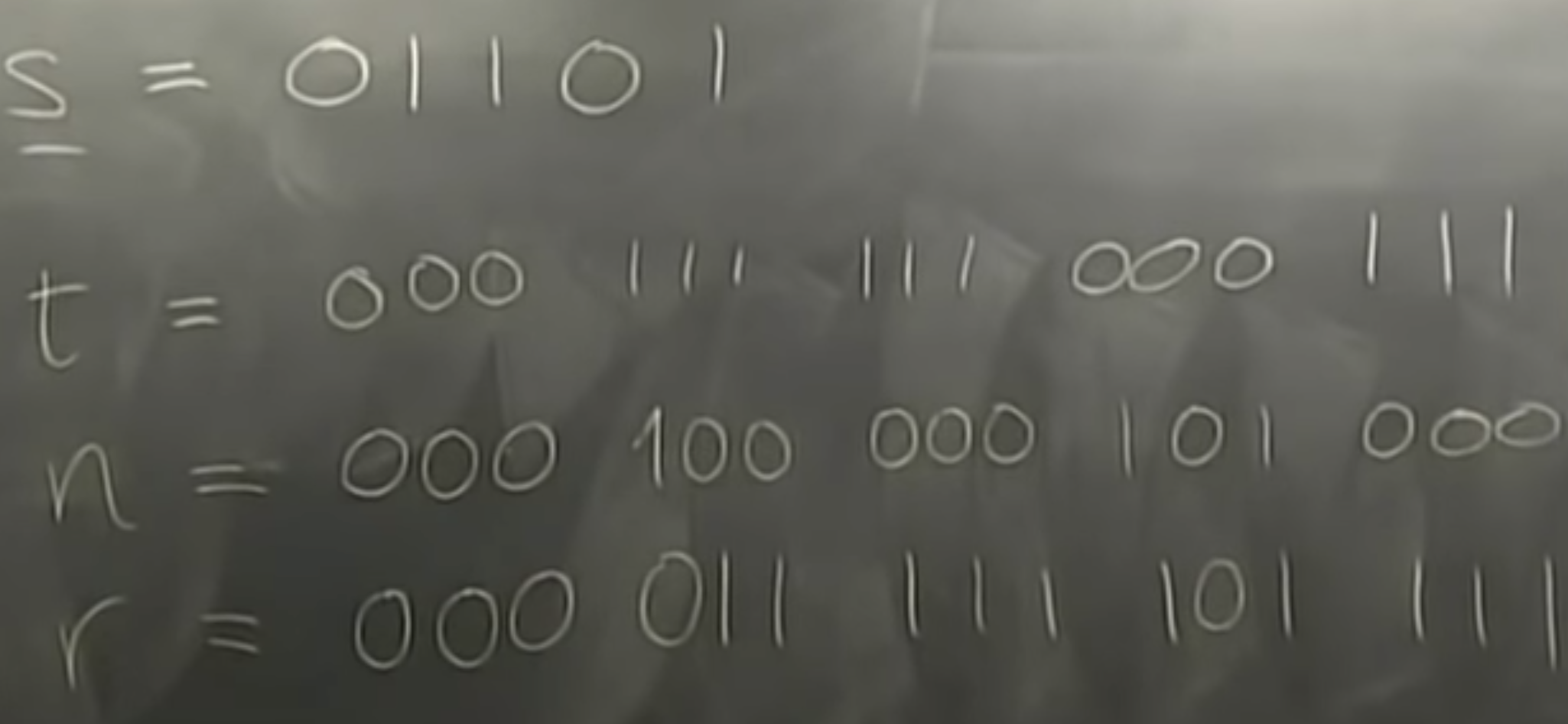


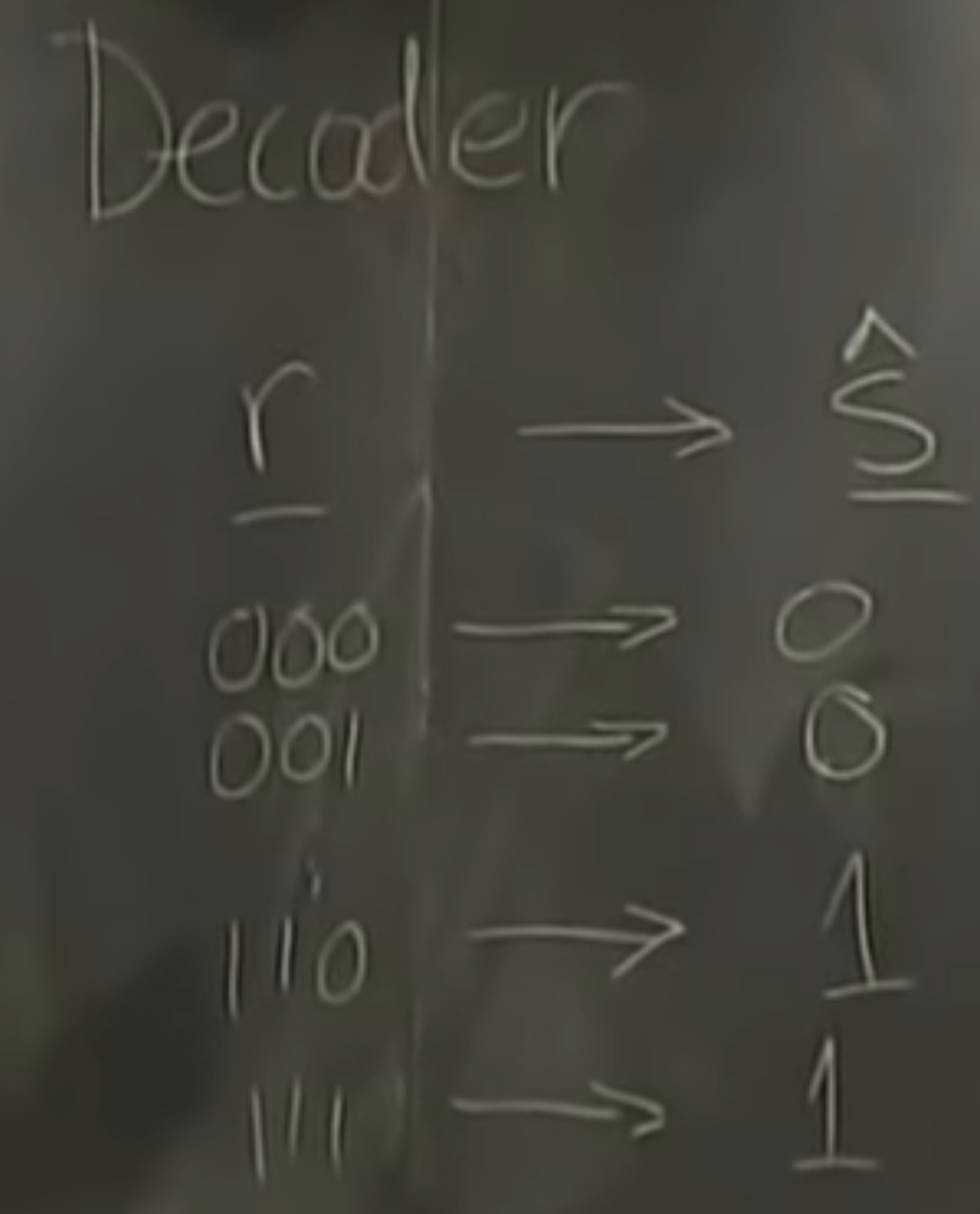
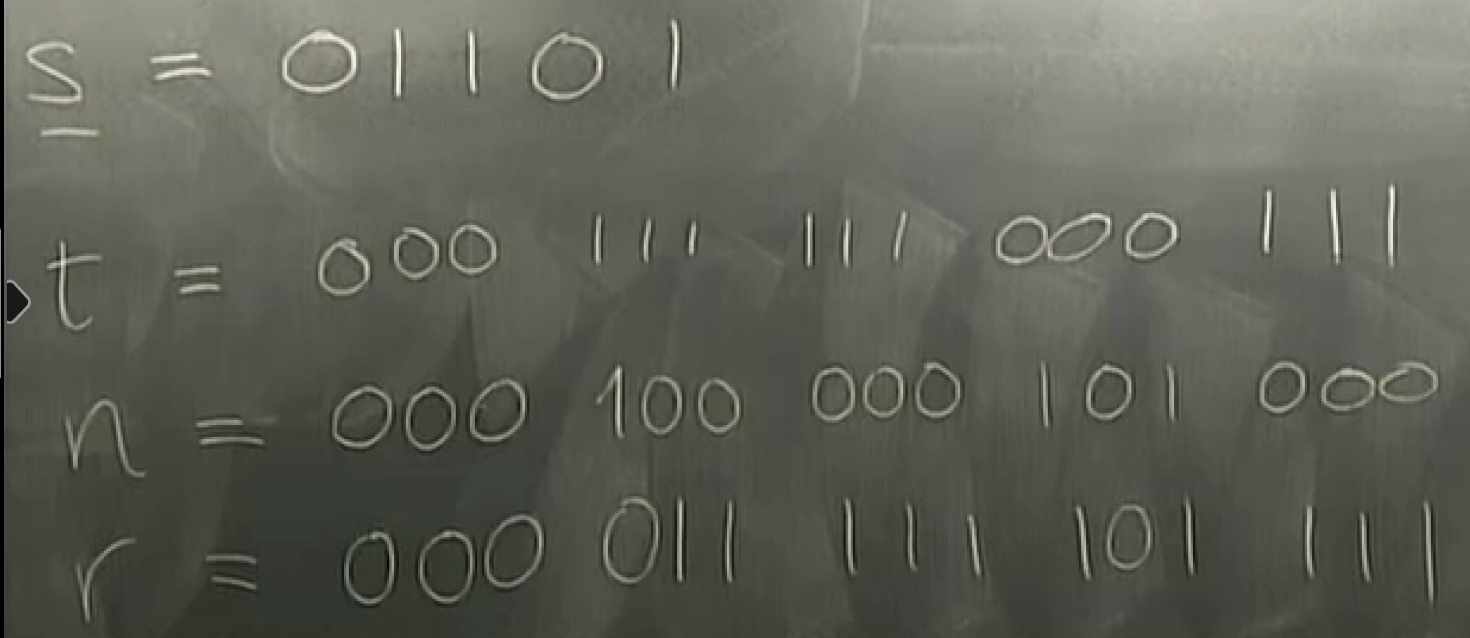
hat{s} = 0 1 1 1 1

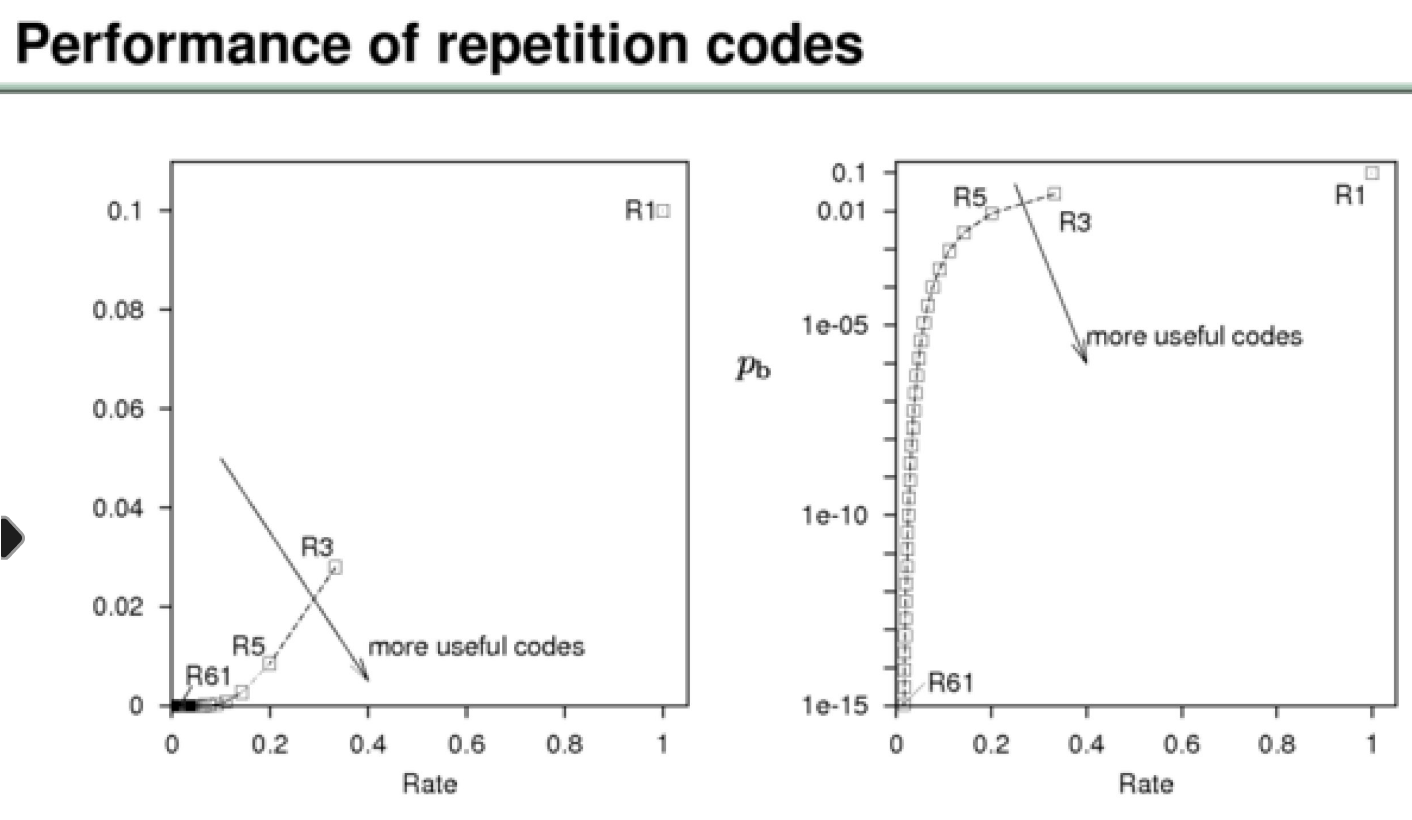
why the majority vote decoder is the best?
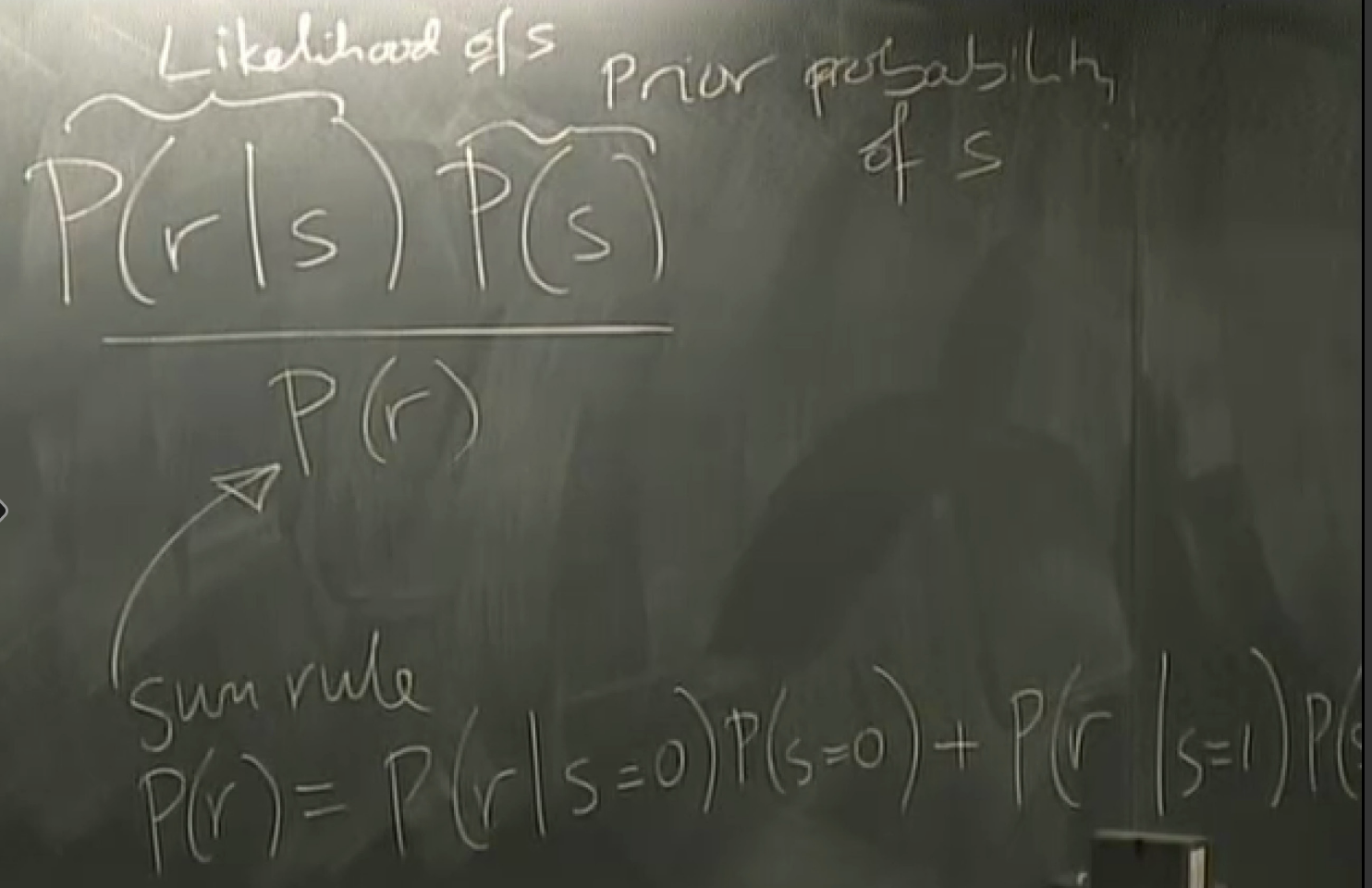


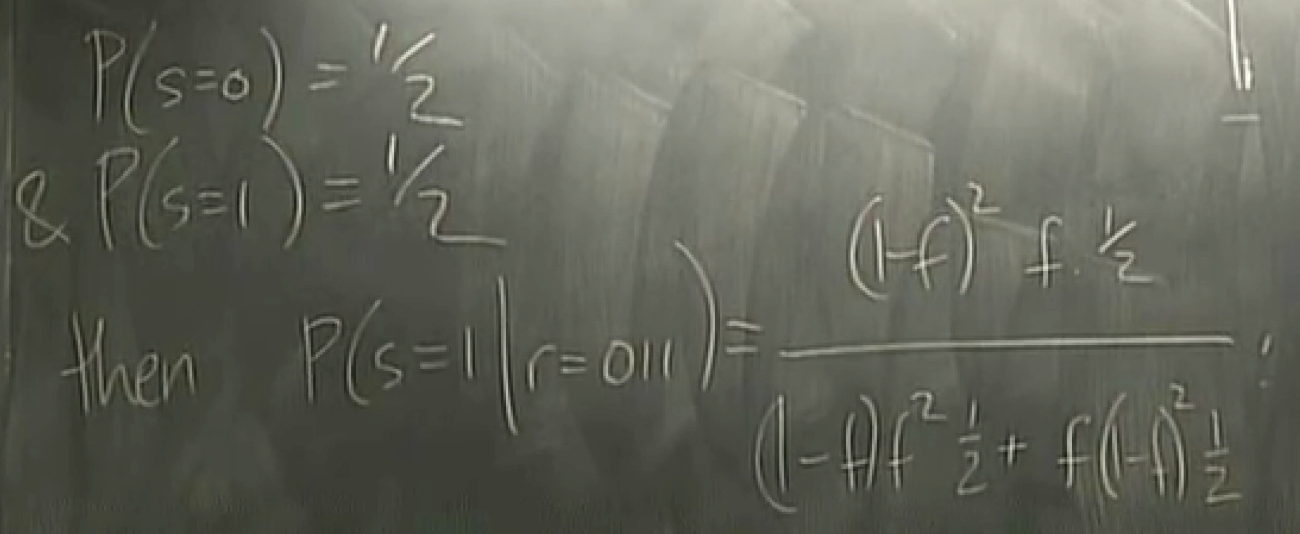
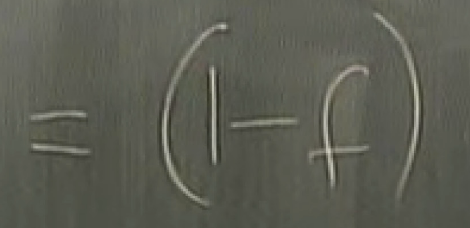

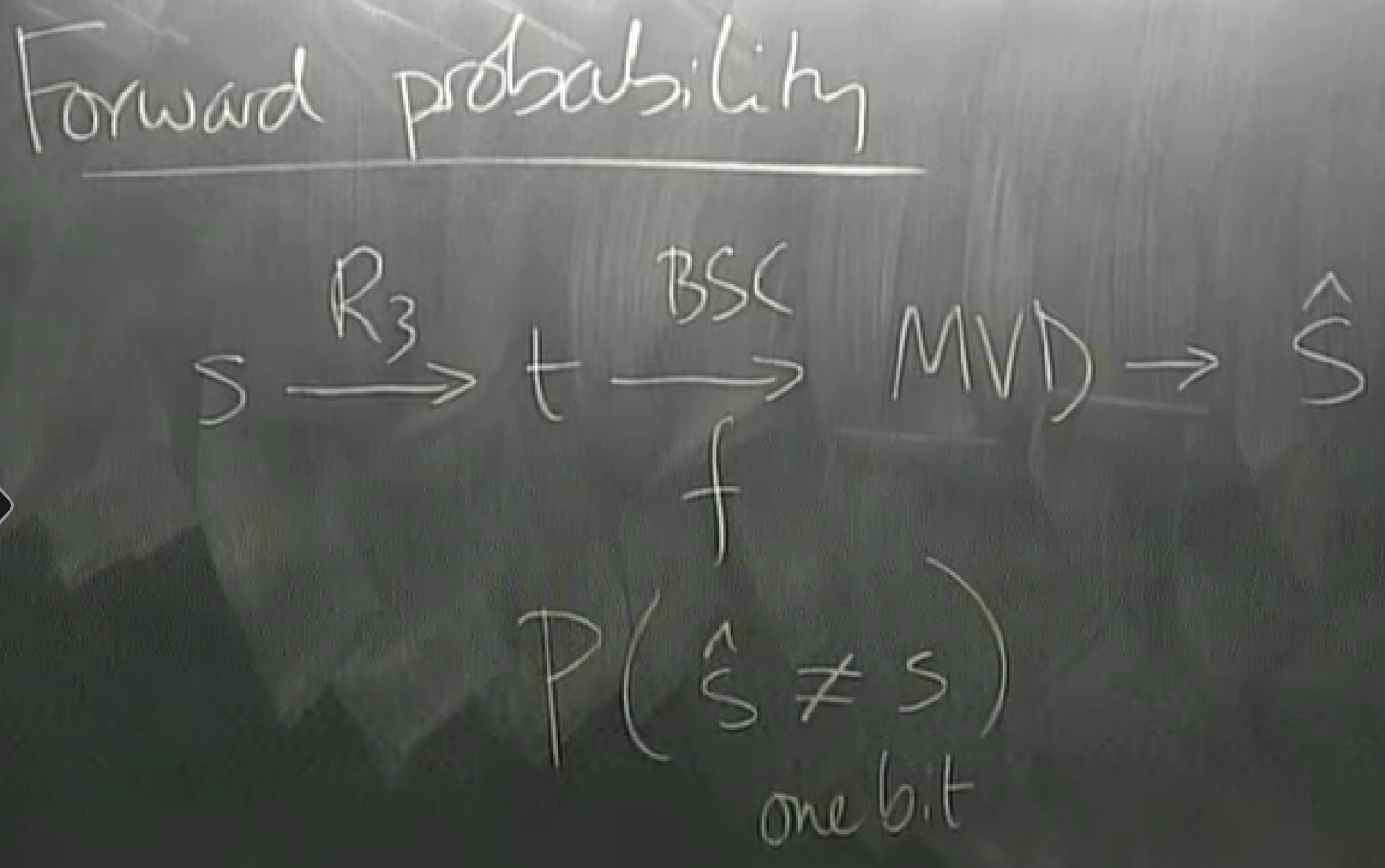

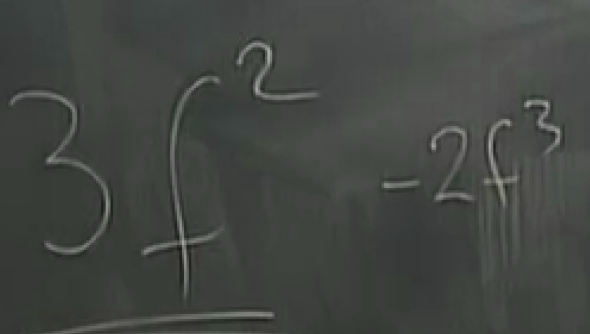


answer: 61
74 hamming code
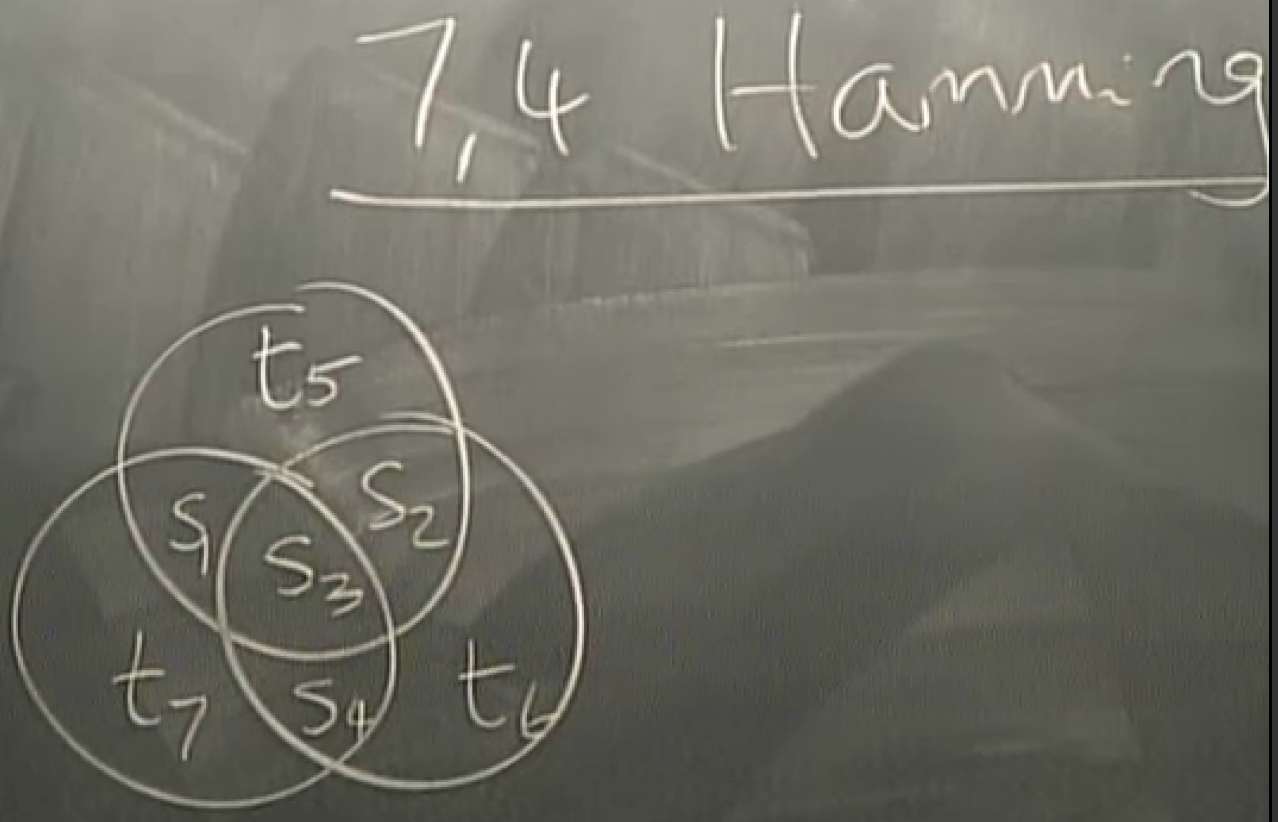


encoder: even for 0 and odd for 1
decoder:
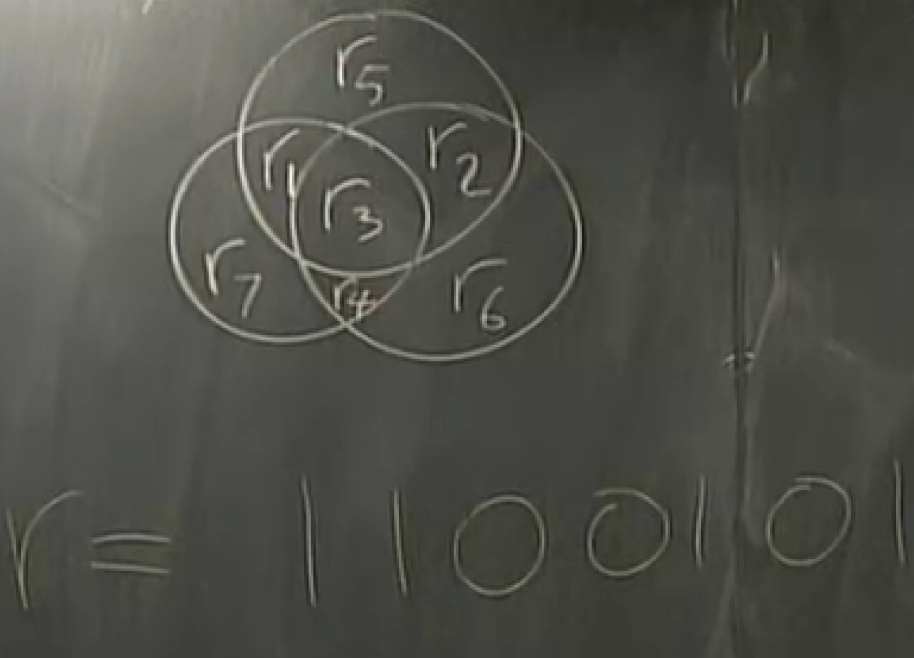
the second one got flipped but we dont know yet.
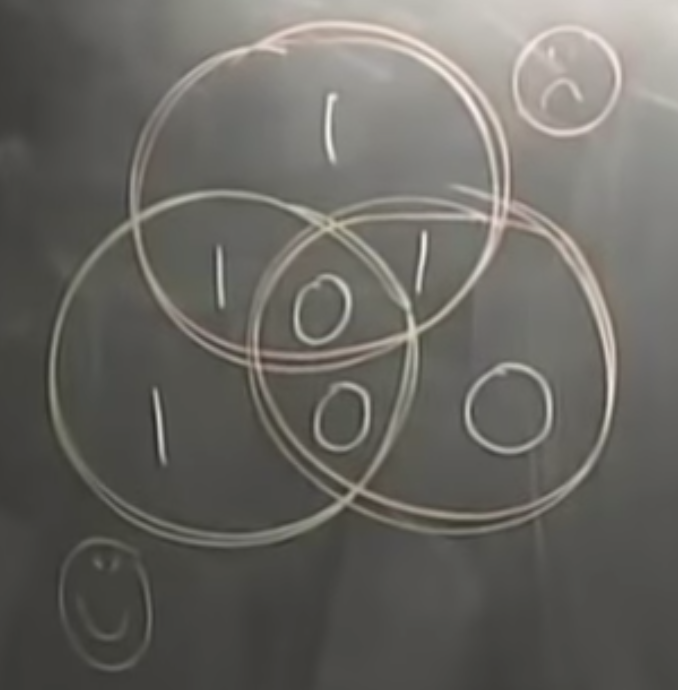
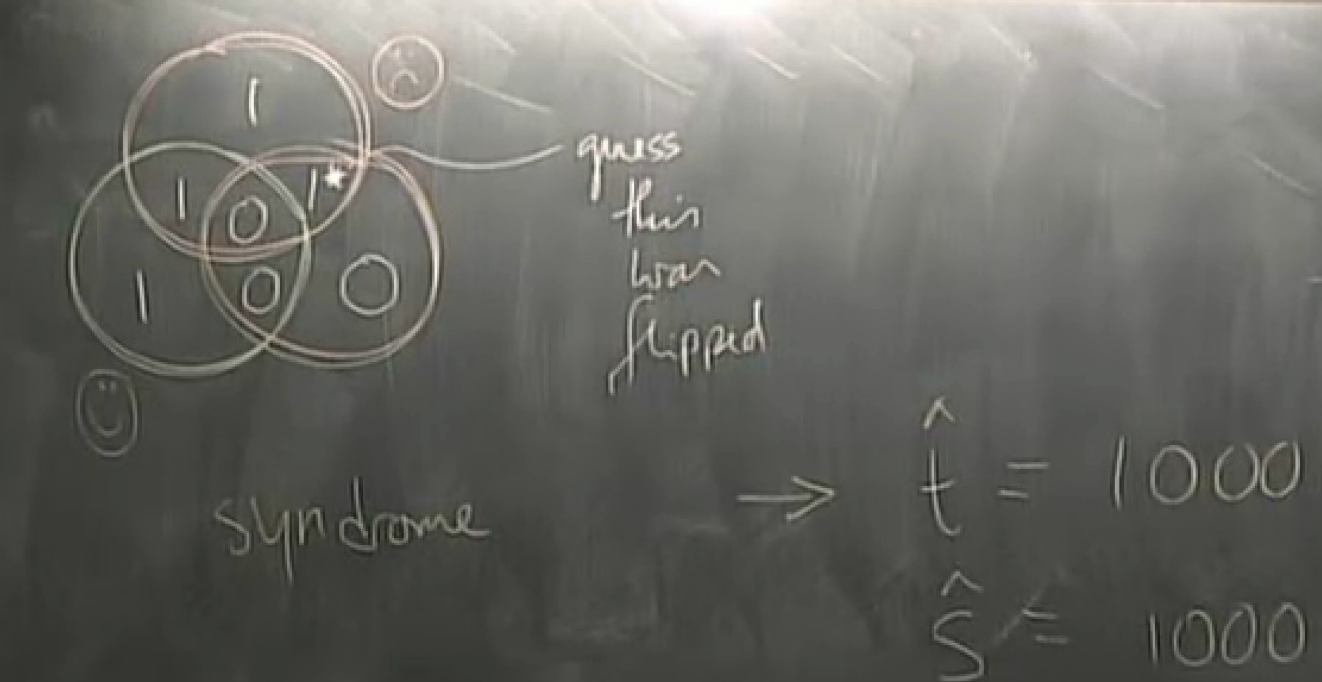
t = 1000101
any single flip can be detected and corrected, but if >1, then in trouble
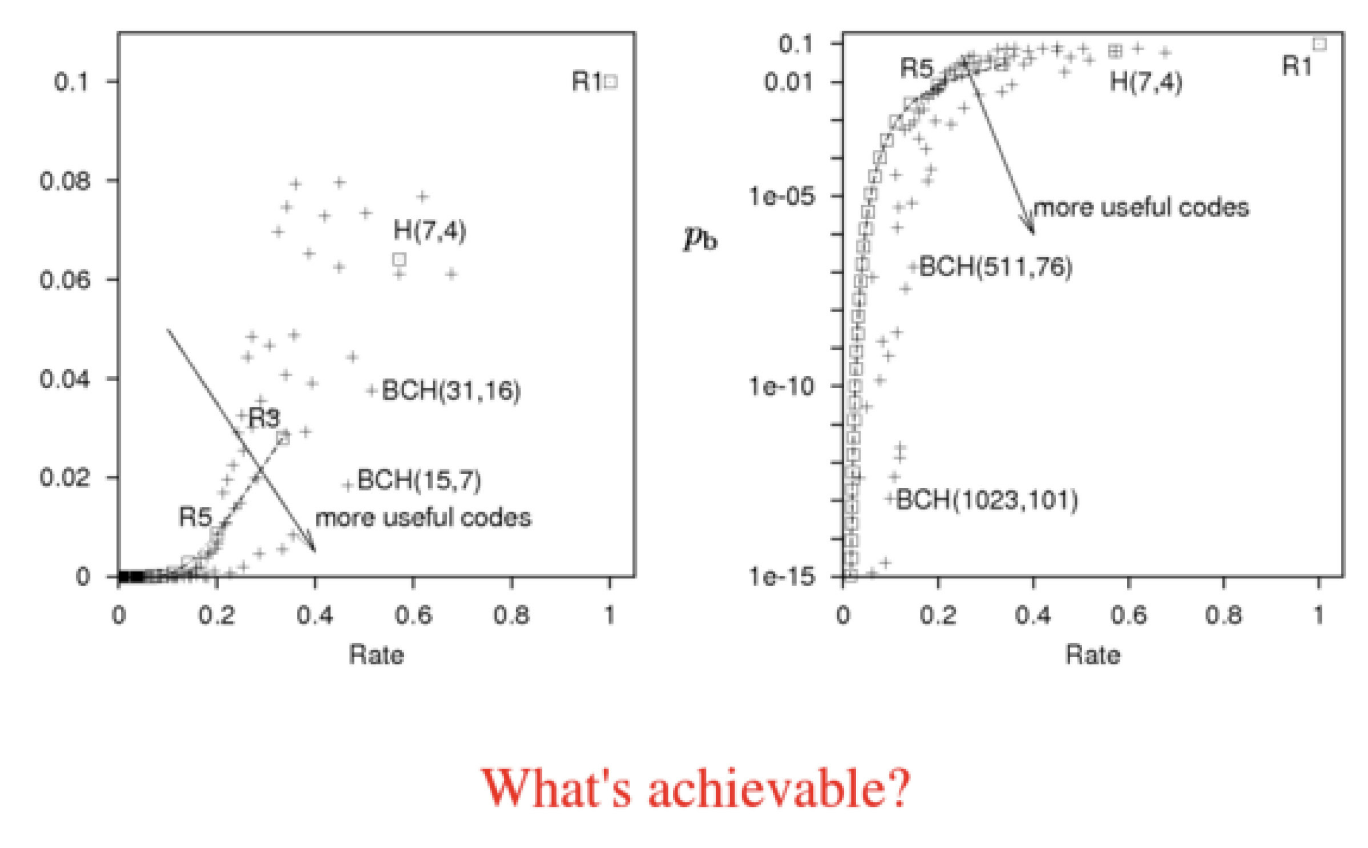
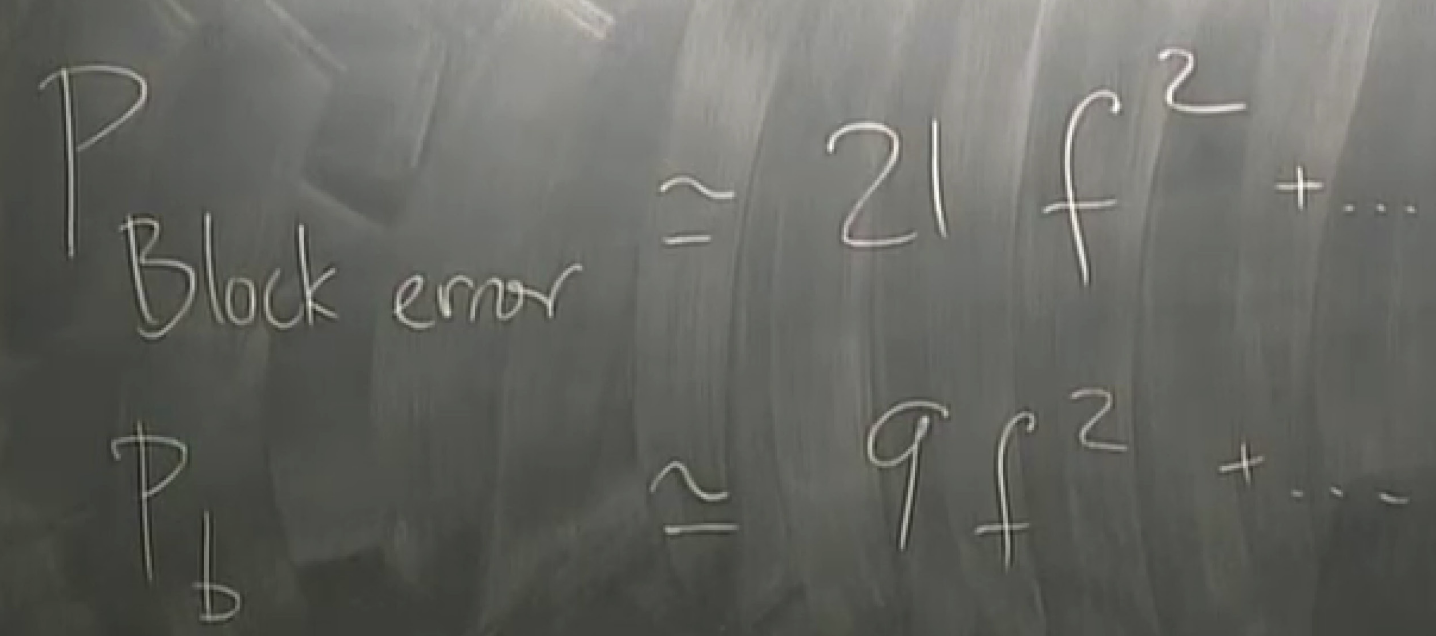

Shanon proved that you can get the error probability arbitrarily small , without the rate having to go to zero
and the boundary between achievable and unachievable is the green line
C is the capacity

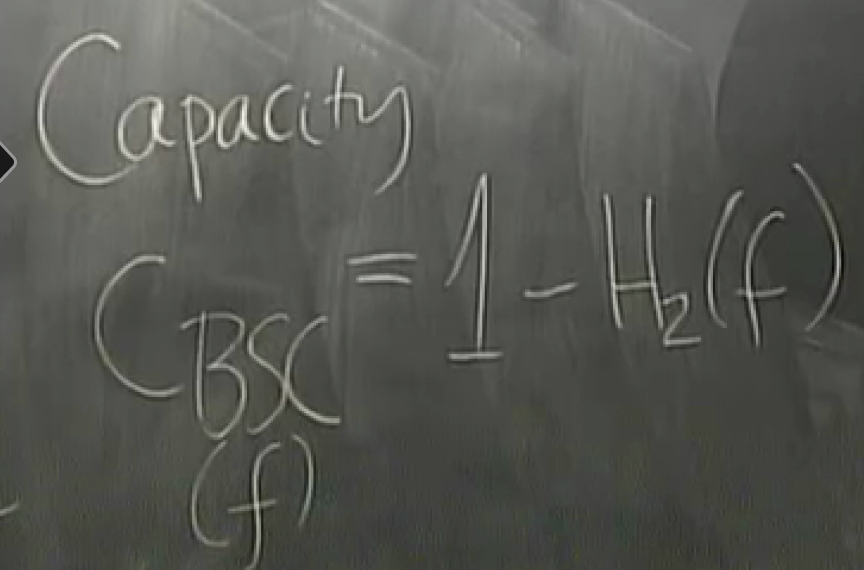
binary symmetric channel : bsc
binary entropy function
eg, f=0.1 => H2f = 0.53 => only two disk in the box and there exists an encoding system and a decoding system that can correct as many errors as you want (< all errors).
=> shanon's noisy channel coding theorem