*容器 (1)顺序容器 vector[顺序表直接访问] depue[前后直接访问] list[双向链表]
vector 检索(用operator[ ])速度快

1.push_back 在数组的最后添加一个数据 2.pop_back 去掉数组的最后一个数据 3.at 得到编号位置的数据 4.begin 得到数组头的指针 5.end 得到数组的最后一个单元+1的指针 6.front 得到数组头的引用 7.back 得到数组的最后一个单元的引用 8.max_size 得到vector最大可以是多大 9.capacity 当前vector分配的大小 10.size 当前使用数据的大小 11.resize 改变当前使用数据的大小,如果它比当前使用的大,者填充默认值 12.reserve 改变当前vecotr所分配空间的大小 13.erase 删除指针指向的数据项 14.clear 清空当前的vector 15.rbegin 将vector反转后的开始指针返回(其实就是原来的end-1) 16.rend 将vector反转构的结束指针返回(其实就是原来的begin-1) 17.empty 判断vector是否为空 18.swap 与另一个vector交换数据
deque 检索效率没vector高 两端插入和list一样

析构函数: c.~ deque<Elem>() ;销毁所有元素,并释放内存。 非变动性操作 c.size(); //返回当前的元素数量 c.empty(); //判断大小是否为零。等同于c.size() == 0,但可能更快 c.max_size(); //可容纳元素的最大数量 c.at(idx) ; //返回索引为idx所标示的元素。如果idx越界,抛出out_of_range c[idx] ; //返回索引idx所标示的元素。不进行范围检查 c.front() ; //返回第一个元素,不检查元素是否存在 c.back(); //返回最后一个元素 c.begin(); //返回一个随机迭代器,指向第一个元素 c.end(); //返回一个随机迭代器,指向最后元素的下一位置 变动性操作: c1 = c2 ; //将c2的所有元素赋值给c1; c.assign(n , elem); //将n个elem副本赋值给c c.assing(beg , end); //将区间[beg;end]中的元素赋值给c; c.push_back(elem); //在尾部添加元素elem c.pop_back() ; //移除最后一个元素(但不回传) c.push_front() ; //在头部添加元素elem c.pop_front() ; //移除头部一个元素(但不回传) c.erase(pos) ; //移除pos位置上的元素,返回一元素位置 //如 c.erase( c.begin() + 5) //移除第五个元素 c.insert(pos , elem); //在pos位置插入一个元素elem,并返回新元素的位置 c.insert(pos , n , elem); //在pos位置插入n个元素elem,无返回值 c.insert(pos , beg , end); c.resize(num); //将容器大小改为num。可更大或更小。 c.resize(num , elem); //将容器大小改为num,新增元素都为 elem c.clear(); //移除所有元素,将容器清空
list 插入,删除元素效率高 只支持遍历 检索排序效率低

成员函数 c.begin() 返回指向链表第一个元素的迭代器。 c.end() 返回指向链表最后一个元素之后的迭代器。 c.front() 返回链表c的第一个元素。 c.back() 返回链表c的最后一个元素。 c.empty() 判断链表是否为空。 c.size() 返回链表c中实际元素的个数。 c.max_size() 返回链表c可能容纳的最大元素数量。 c.clear() 清除链表c中的所有元素。 c.rbegin() 返回逆向链表的第一个元素,即c链表的最后一个数据。 c.rend() 返回逆向链表的最后一个元素的下一个位置,即c链表的第一个数据再往前的位置。 c.assign(n,num) 将n个num拷贝赋值给链表c。 c.assign(beg,end) 将[beg,end)区间的元素拷贝赋值给链表c。 c.insert(pos,num) 在pos位置插入元素num。 c.insert(pos,n,num) 在pos位置插入n个元素num。 c.insert(pos,beg,end) 在pos位置插入区间为[beg,end)的元素。 c.erase(pos) 删除pos位置的元素。 c.push_back(num) 在末尾增加一个元素。 c.pop_back() 删除末尾的元素。 c.push_front(num) 在开始位置增加一个元素。 c.pop_front() 删除第一个元素。 c1.swap(c2); 将c1和c2交换。 swap(c1,c2); 同上。 c.sort() 将链表排序,默认升序 c.sort(comp) 自定义回调函数实现自定义排序 http://www.cnblogs.com/scandy-yuan/archive/2013/01/08/2851324.html
(2)关联容器 set[快查无重复] multiset[快查有重复] map[一对一映射无重] multimap[一对一映射有重]
set(默认排序)

平衡二叉检索树使用中序遍历算法,检索效率高于vector、deque和list等容器,另外使用中序遍历可将键值按照从小到大遍历出来。 构造set集合主要目的是为了快速检索,不可直接去修改键值。 常用操作: 1.元素插入:insert() 2.中序遍历:类似vector遍历(用迭代器) 3.反向遍历:利用反向迭代器reverse_iterator。 例: set<int> s; ...... set<int>::reverse_iterator rit; for(rit=s.rbegin();rit!=s.rend();rit++) 4.元素删除:与插入一样,可以高效的删除,并自动调整使红黑树平衡。 set<int> s; s.erase(2); //删除键值为2的元素 s.clear(); 5.元素检索:find(),若找到,返回该键值迭代器的位置,否则,返回最后一个元素后面一个位置。 set<int> s; set<int>::iterator it; it=s.find(5); //查找键值为5的元素 if(it!=s.end()) //找到 cout<<*it<<endl; else //未找到 cout<<"未找到"; 6.自定义比较函数 (1)元素不是结构体: 例: //自定义比较函数myComp,重载“()”操作符 struct myComp { bool operator()(const your_type &a,const your_type &b) [ return a.data-b.data>0; } } set<int,myComp>s; ...... set<int,myComp>::iterator it; (2)如果元素是结构体,可以直接将比较函数写在结构体内。 例: struct Info { string name; float score; //重载“<”操作符,自定义排序规则 bool operator < (const Info &a) const { //按score从大到小排列 return a.score<score; } } set<Info> s; ...... set<Info>::iterator it
begin() ,返回set容器的第一个元素
end() ,返回set容器的最后一个元素
clear() ,删除set容器中的所有的元素
empty() ,判断set容器是否为空
max_size() ,返回set容器可能包含的元素最大个数
size() ,返回当前set容器中的元素个数
rbegin ,返回的值和end()相同
rend() ,返回的值和rbegin()相同
map

begin() 返回指向map头部的迭代器 clear() 删除所有元素 count() 返回指定元素出现的次数 empty() 如果map为空则返回true end() 返回指向map末尾的迭代器 equal_range() 返回特殊条目的迭代器对 erase() 删除一个元素 find() 查找一个元素 get_allocator() 返回map的配置器 insert() 插入元素 key_comp() 返回比较元素key的函数 lower_bound() 返回键值>=给定元素的第一个位置 max_size() 返回可以容纳的最大元素个数 rbegin() 返回一个指向map尾部的逆向迭代器 rend() 返回一个指向map头部的逆向迭代器 size() 返回map中元素的个数 swap() 交换两个map upper_bound() 返回键值>给定元素的第一个位置 value_comp() 返回比较元素value的函数
(3)容器适配器 stack[LIFO] queue[FIFO] priority_queue[优先级高的出]
stack

stack stack 模板类的定义在<stack>头文件中。 stack 模板类需要两个模板参数,一个是元素类型,一个容器类型,但只有元素类型是必要 的,在不指定容器类型时,默认的容器类型为deque。 定义stack 对象的示例代码如下: stack<int> s1; stack<string> s2; stack 的基本操作有: 入栈,如例:s.push(x); 出栈,如例:s.pop();注意,出栈操作只是删除栈顶元素,并不返回该元素。 访问栈顶,如例:s.top() 判断栈空,如例:s.empty(),当栈空时,返回true。 访问栈中的元素个数,如例:s.size()。 empty() 堆栈为空则返回真 pop() 移除栈顶元素(不会返回栈顶元素的值) push() 在栈顶增加元素 size() 返回栈中元素数目 top() 返回栈顶元素 emplace () swap()
queue
成员函数
-
empty()判断队列空,当队列空时,返回true。
-
size()访问队列中的元素个数。
-
push()会将一个元素置入queue中。
-
front()会返回queue内的第一个元素(也就是第一个被置入的元素)。
-
back()会返回queue中最后一个元素(也就是最后被插入的元素)。

(constructor)Construct queue (public member function ) emptyTest whether container is empty (public member function ) sizeReturn size (public member function ) frontAccess next element (public member function ) backAccess last element (public member function ) pushInsert element (public member function ) emplace Construct and insert element (public member function ) popRemove next element (public member function ) swap Swap contents (public member function )
priority_queue

(constructor)Construct priority queue (public member function ) emptyTest whether container is empty (public member function ) sizeReturn size (public member function ) topAccess top element (public member function ) pushInsert element (public member function ) emplace Construct and insert element (public member function ) popRemove top element (public member function ) swap Swap contents (public member function )
下面是选择顺序容器类型的一些准则 0.vector 不自动排序但允许重复 list也是 set有不重复元素的特性,但其自动排序
1.如果我们需要随机访问一个容器则vector要比list好得多 。
2.如果我们已知要存储元素的个数则vector 又是一个比list好的选择。
3.如果我们需要的不只是在容器两端插入和删除元素则list显然要比vector好
4.除非我们需要在容器首部插入和删除元素否则vector要比deque好。
5.如果只在容易的首部和尾部插入数据元素,则选择deque.
6.如果只需要在读取输入时在容器的中间位置插入元素,然后需要随机访问元素,则可考虑输入时将元素读入到一个List容器,接着对此容器重新拍学,使其适合顺序访问,然后将排序后的list容器复制到一个vector容器中
一.string
输出用法见代码。

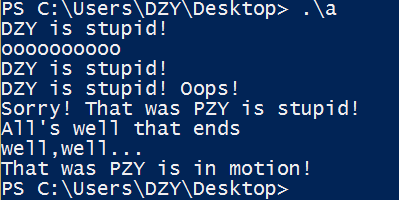
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { string one("DZY is stupid!"); cout<<one<<endl; string two(10,'o'); cout<<two<<endl; string three(one); cout<<three<<endl; one+=" Oops!"; cout<<one<<endl; two="Sorry! That was "; three[0]='P'; string four=two+three; cout<<four<<endl; char alls[]="All's well that ends well"; string five(alls,20); cout<<five<<endl; string six(alls+6,alls+10); cout<<six<<','; string seven(&five[6],&five[10]); cout<<seven<<"..."<<endl; string eight(four,7,16); cout<<eight<<"in motion!"<<endl; return 0; }
输入用法:

string stuff; cin>>stuff; getline(cin,stuff); getline(stuff,':'); //终止条件 operator>>(cin,stuff); #include <iostream> #include <fstream> //文件操作 #include <string> #include <cstdlib> int main() { using namespace std; ifstream fin; //文件 fin.open("tobuy.txt");//打开 if (fin.is_open() == false)//判断是否打开 { cerr << "Can't open file. Bye. "; exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } string item; int count = 0; getline(fin, item, ':'); //文件操作需要注意输入方式,终止条件 while (fin) // while input is good { ++count; cout << count <<": " << item << endl; getline(fin, item,':');//文件操作需要注意输入方式,终止条件 } cout << "Done "; fin.close(); //关闭文件 // std::cin.get(); // std::cin.get(); return 0; }
tobuy.txt

sardines:chocolate ice cream:pop corn:leeks:
cottage cheese:olive oil:butter:tofu:
string---find用法

find(const string&str ,size_type pos=0)const 从pos开始找否则返回string::nops find(const char*s ,size_type pos=0)const 从s开始找否则返回string::nops find(const char*s ,size_type pos=0 ,size_type n)const 从pos开始,查找s的前n个字符,否则返回string::nops find(char ch ,size_type pos=0)const 从pos开始找字符ch找到返回首次出现位置,否则返回string::nops rfind() 最后一次出现位置 find_firse_of() 找首次出现位置 find_last_of() 最后一次出现位置 find_firse_not_of() 找第一个不包含在已知参数中的字符 find_last_not_of() 找最后一个不包含在已知参数中的字符
举例

#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <string> using namespace std; int main() { string s = "helllo"; if (s.find("e") == string::npos) //yes cout << "no" << endl; else cout << "yes" << endl; if (s.find("z") == string::npos) //no cout << "no" << endl; else cout << "yes" << endl; }
二.lower_bound();upper_bound()
lower_bound(a,a+n,k)在已排好序的a中利用二分法找出ai>=k的最小指针(返回值);upper_bound(a,a+n,k).......ai<=k;两个联合起来就是找k;
