静态资源处理
ResouceProperties类设置了静态资源有关的参数,指向了项目会寻找的资源的文件夹
以下四个目录存放的静态资源可以被识别
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/"
"classpath:/resources/"
"classpath:/static/"
"classpath:/public/"
也可以自定义静态资源路径
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/coding/
自定义了静态文件路径后原来的自动配置路径失效
网站图标
SpringBoot会在静态资源文件夹中查找favicon.ico,将其作为网站的图标
可以关闭默认图标
spring.mvc.favicon.enabled=false
在自己的静态资源放一个自定义的favicon.ico即可
模板引擎Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf是SpringBoot推荐的模板引擎
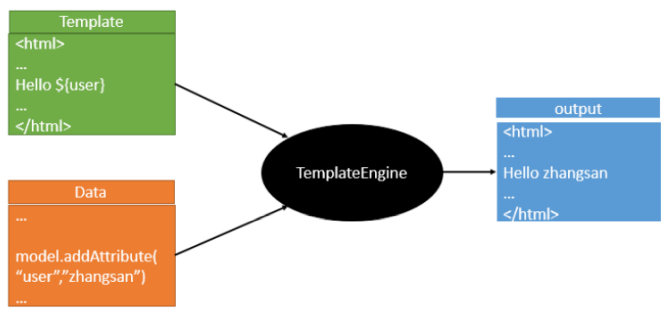
模板引擎的作用就是我们写一个页面模板,模板里面有一个表达式动态获取值,这些动态数据就是我们在后台封装的数据,我们把这个模板和这些数据交给模板引擎,模板引擎把表达式解析出来并把它填充到指定位置,最终生成一个完整的页面。
SpringBoot的Thymeleaf依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency>
通过thymeleaf的自动配置类ThymeleafProperties可以看出默认前缀和后缀
@ConfigurationProperties( prefix = "spring.thymeleaf" ) public class ThymeleafProperties { private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING; public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/"; public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html"; private boolean checkTemplate = true; private boolean checkTemplateLocation = true; private String prefix = "classpath:/templates/"; private String suffix = ".html"; private String mode = "HTML"; private Charset encoding; }
把html页面放在类路径下的templates文件夹下,themeleaf就可以帮我们自动渲染。(类路径在SpringBoot里一般指resources文件夹)
在html文件中导入命名空间约束,方便查看
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
SpringBoot自动配置好了SpringMVC,其ContentNegotiatingViewResolvers就是组合了所有的视图解析器,@EnableWebMvc将WebMvcConfigurationSupport组件导入进来,会使所有的SpringMVC自动配置都失效
Swagger在线测试API
SpringBoot集成Swagger==>springfox
导入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId> <version>2.7.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId> <version>2.7.0</version> </dependency>
编写swagger配置类
@Configuration @EnableSwagger2 public class SwaggerConfig { }
访问:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
配置Swagger
Swagger的实例是Docket,通过配置Docket来配置Swagger
@Bean public Docket docket(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo()); } //配置文档信息 private ApiInfo apiInfo() { Contact contact = new Contact("联系人名字", "http://xxx.xxx.com/联系人访问链接", "联系人邮箱"); return new ApiInfo( "Swagger学习", // 标题 "学习演示如何配置Swagger", // 描述 "v1.0", // 版本 "http://terms.service.url/组织链接", // 组织链接 contact, // 联系人信息 "Apach 2.0 许可", // 许可 "许可链接", // 许可连接 new ArrayList<>()// 扩展 ); }
配置扫描接口
swagger通过Docket的select()方法配置如何扫描接口
//通过select()方法来配置扫描接口,通过RequestHandlerSeletors配置如何扫描接口,path()配置如何通过path过滤 @Bean public Docket docket(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo()).select().apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.deng.controller")).paths(PathSelectors.ant("/test/**")).build(); }
配置Swagger开关
通过enable(boolean flag)配置是否启用Swagger
动态配置当项目处于test、dev环境时显示swagger,处于prod时不显示
@Bean public Docket docket(Environment environment){ // 设置要显示swagger的环境 Profiles of = Profiles.of("dev", "test"); // 判断当前是否处于该环境 // 通过 enable() 接收此参数判断是否要显示 boolean b = environment.acceptsProfiles(of); return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo()).enable(b).select().apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.deng.controller")).paths(PathSelectors.ant("/test/**")).build(); }
配置API分组
@Bean public Docket docket(Environment environment) { return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo()) .groupName("hello") // 配置分组 // 省略配置.... }
实体配置
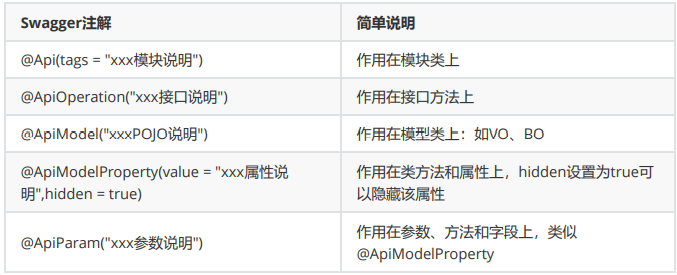
为实体添加注释
@ApiModel("用户实体")
public class User {
@ApiModelProperty("用户名")
public String username;
@ApiModelProperty("密码")
public String password;
}
异步任务
使用@Async来告诉Spring该方法是一个异步方法,并且要在主启动类上添加@EnableAsync开启异步注解功能
@Service public class AsyncService { @Async public void hello(){ try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("数据处理中...."); } }
@EnableAsync @SpringBootApplication public class TestApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(TestApplication.class, args); } }
使用异步任务,SpringBoot会自己开一个线程池进行调用。
定时任务
Spring提供了两个接口TaskExecutor接口和TaskScheduler接口,两个注解@EnableScheduling和@Scheduled来实现定时任务
cron表达式
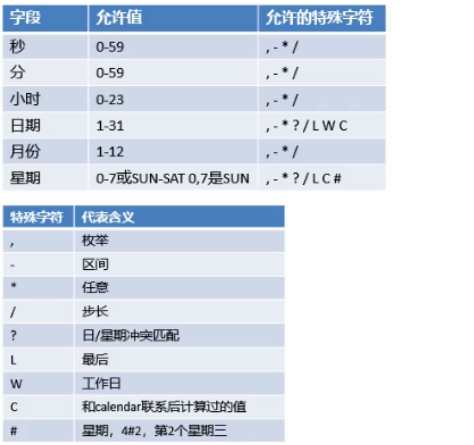
@Service public class ScheduledService { //秒 分 时 日 月 周几 //0 * * * * MON-FRI //注意cron表达式的用法; @Scheduled(cron = "0 * * * * 0-7") public void hello(){ System.out.println("hello....."); } }
@EnableScheduling //开启基于注解的定时任务 @SpringBootApplication public class SpringbootTaskApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringbootTaskApplication.class, args); } }
邮件任务
Springboot也做了邮件支持
导入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mail</artifactId> </dependency>
它引入了jakarta.mail依赖
配置文件:
spring:
mail:
username: 1780403059@qq.com
password: dwxsw3.1415926hh
host: smtp.qq.com
properties:
mail:
smtp:
ssl:
enable: true
@Autowired JavaMailSenderImpl mailSender; @Test public void test2(){ SimpleMailMessage mailMessage=new SimpleMailMessage(); mailMessage.setSubject("你好啊!"); mailMessage.setText("我爱你!"); mailMessage.setTo("1780403059@qq.com"); mailMessage.setFrom("1780403059@qq.com"); mailSender.send(mailMessage); }