作为Java开发者,我们每天都会创建大量的对象,但是,我们总是使用管理依赖系统(如Spring框架)来创建这些对象。其实还有其他方法可以创建对象,在接下来的文章中我会进行详细介绍。
1.使用new关键字
这是最常见的创建对象的方法,并且也非常简单。通过使用这种方法我们可以调用任何我们需要调用的构造函数。
Employee emp1 = new Employee();
反编译的字节码如下:

2.使用class类的newInstance方法
我们也可以使用class类的newInstance()方法来创建对象。此newInstance()方法调用无参构造函数以创建对象。
我们可以通过newInstance() 用以下方式创建对象:
public static void test2() throws Exception { Employee emp2 = (Employee) Class.forName("newobject.Employee").newInstance(); }
或者
Employee emp3 = Employee.class.newInstance();

3.使用构造函数类的 newInstance方法
与使用class类的newInstance()方法相似,java.lang.reflect.Constructor类中有一个可以用来创建对象的newInstance()函数方法。通过使用这个newInstance()方法我们也可以调用参数化构造函数和私有构造函数。
public static void test3() throws Exception { Constructor<Employee> constructor = Employee.class.getConstructor(); Employee emp3 = constructor.newInstance(); }
字节码如下:
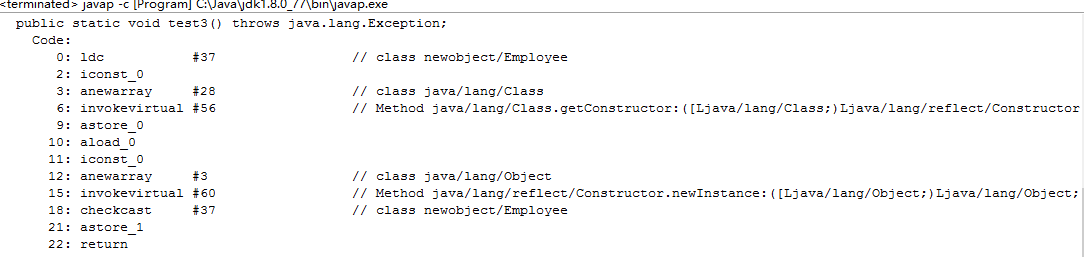
这些 newInstance() 方法被认为是创建对象的反射手段。实际上,内部类的newInstance()方法使用构造函数类的 newInstance() 方法。这就是为什么后者是首选并且使用不同的框架如Spring, Hibernate, Struts等。
4.使用clone方法
实际上无论何时我们调用clone() 方法,JAVA虚拟机都为我们创建了一个新的对象并且复制了之前对象的内容到这个新的对象中。使用 clone()方法创建对象不会调用任何构造函数。
为了在对象中使用clone()方法,我们需要在其中实现可克隆类型并定义clone()方法。
public static void test4(Employee emp0) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Employee emp4 = (Employee) emp0.clone(); }
字节码如下:

5.使用反序列化
无论何时我们对一个对象进行序列化和反序列化,JAVA虚拟机都会为我们创建一个单独的对象。在反序列化中,JAVA虚拟机不会使用任何构造函数来创建对象。
对一个对象进行序列化需要我们在类中实现可序列化的接口。
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("data.obj")); Employee emp5 = (Employee) in.readObject();
字节码如下:

正如我们在以上的字节代码片段中所看到的,除第一种被转换为一个新的函数和一个 invokespecial 指令以外,其它4种方法都被调用并转换为invokevirtual。
示例
让我们来看看准备创建对象的 Employee 类:
class Employee implements Cloneable, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String name;
public Employee() {
System.out.println("Employee Constructor Called...");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Employee other = (Employee) obj;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [name=" + name + "]";
}
@Override
public Object clone() {
Object obj = null;
try {
obj = super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return obj;
}
}
在下面的Java程序中我们用5种方式来创建 Employee对象。
public class ObjectCreation {
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
// By using new keyword
Employee emp1 = new Employee();
emp1.setName("Naresh");
System.out.println(emp1 + ", hashcode : " + emp1.hashCode());
// By using Class class's newInstance() method
Employee emp2 = (Employee) Class.forName("org.programming.mitra.exercises.Employee")
.newInstance();
// Or we can simply do this
// Employee emp2 = Employee.class.newInstance();
emp2.setName("Rishi");
System.out.println(emp2 + ", hashcode : " + emp2.hashCode());
// By using Constructor class's newInstance() method
Constructor<Employee> constructor = Employee.class.getConstructor();
Employee emp3 = constructor.newInstance();
emp3.setName("Yogesh");
System.out.println(emp3 + ", hashcode : " + emp3.hashCode());
// By using clone() method
Employee emp4 = (Employee) emp3.clone();
emp4.setName("Atul");
System.out.println(emp4 + ", hashcode : " + emp4.hashCode());
// By using Deserialization
// Serialization
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("data.obj"));
out.writeObject(emp4);
out.close();
//Deserialization
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("data.obj"));
Employee emp5 = (Employee) in.readObject();
in.close();
emp5.setName("Akash");
System.out.println(emp5 + ", hashcode : " + emp5.hashCode());
}
}
此程序输出结果如下:
Employee Constructor Called...
Employee [name=Naresh], hashcode : -1968815046
Employee Constructor Called...
Employee [name=Rishi], hashcode : 78970652
Employee Constructor Called...
Employee [name=Yogesh], hashcode : -1641292792
Employee [name=Atul], hashcode : 2051657
Employee [name=Akash], hashcode : 63313419
6、用unsafe
A o3 = (A) unsafe.allocateInstance(A.class); // unsafe
o3.a(); // 打印出0