一、 调用生成的类对象
1. 通过反射的方式调用
2. 通过读取 .class 文件的方式调用
3. 通过接口的方式
二、创建对象(动态创建对象)
动态创建对象,动态创建一个Teacher对象,为其增加2个方法:
package com.dxz; import com.dxz.dto.GoodStudent; import javassist.*; import org.junit.Test; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class Create { @Test public void test1() throws Exception { ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault(); // 创建teacher类 CtClass teacherClass = pool.makeClass("com.dxz.dto.Teacher"); // 设置为公有类 teacherClass.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC); // 获取String类型 CtClass stringClass = pool.get("java.lang.String"); // 获取list类型 CtClass listClass = pool.get("java.util.List"); // 获取学生的类型 CtClass studentClass = pool.get("com.dxz.dto.GoodStudent"); // 给teacher添加name属性 CtField nameField = new CtField(stringClass, "name", teacherClass); nameField.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC); teacherClass.addField(nameField); // 给teacher类添加students属性 CtField studentList = new CtField(listClass, "students", teacherClass); studentList.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC); teacherClass.addField(studentList); // 给teacher类添加无参构造方法 CtConstructor ctConstructor = CtNewConstructor.make("public Teacher() {this.name =\"abc\";this.students = new java.util.ArrayList();}", teacherClass); teacherClass.addConstructor(ctConstructor); // 给teacher类添加addStudent方法 CtMethod m = new CtMethod(CtClass.voidType, "addStudent", new CtClass[]{studentClass}, teacherClass); m.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC); // 添加学生对象到students属性中, $1代表参数1 m.setBody("this.students.add($1);"); teacherClass.addMethod(m); // 给teacher类添加sayHello方法 m = new CtMethod(CtClass.voidType, "sayHello", new CtClass[]{}, teacherClass); m.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC); m.setBody("System.out.println(\"Hello, My name is \" + this.name);"); m.insertAfter("System.out.println(\"I have \" + this.students.size() + \" students\");"); teacherClass.addMethod(m); // 加载修改后的类 Class<?> cls = teacherClass.toClass(); // 实例teacher对象 Object teacher = cls.newInstance(); // 获取teacher的addStudent方法 Method method = cls.getDeclaredMethod("addStudent", GoodStudent.class); System.out.println("invoke1 begin----------"); Object invoke1 = method.invoke(teacher, new GoodStudent()); //获取teacher的sayHellow方法 Method method2 = cls.getDeclaredMethod("sayHello"); System.out.println("invoke2 begin----------"); Object invoke2 = method2.invoke(teacher); //这里会将这个动态创建的类对象编译为.class文件 teacherClass.writeFile("E:\\agentdemo-out\\"); } }
结果:
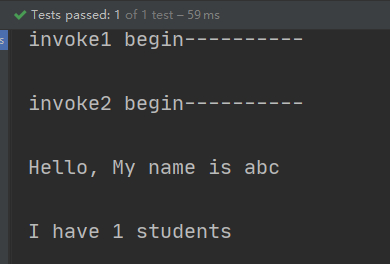
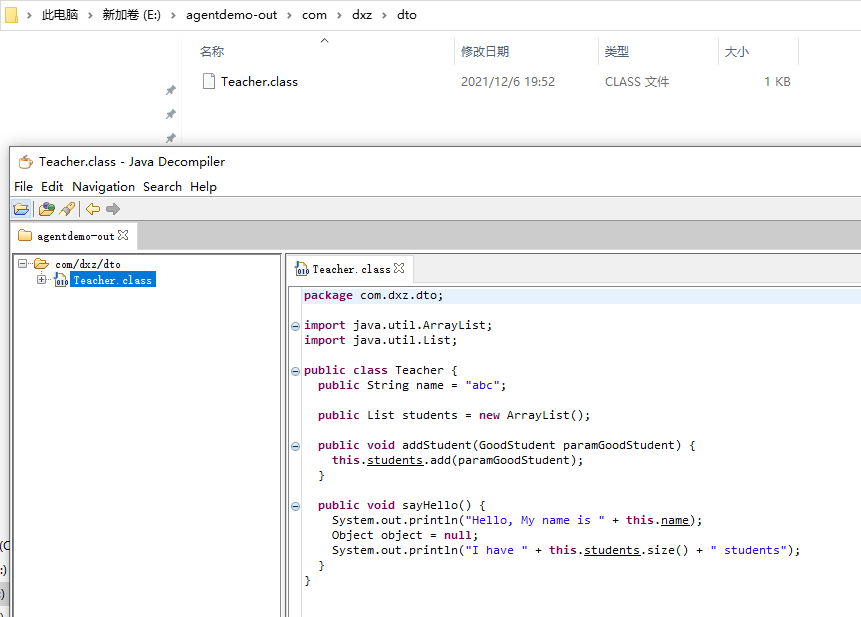
查看动态生产的Teacher如下:
三、 修改现有的类对象
前面说到新增一个类对象。这个使用场景目前还没有遇到过,一般会遇到的使用场景应该是修改已有的类。比如常见的日志切面,权限切面。我们利用javassist来实现这个功能。
四、新增一个方法
有如下类对象:
package com.dxz.service; public class PersonService { public void getPerson(){ System.out.println("get Person"); } public void personFly(){ System.out.println("oh my god,I can fly"); } }
然后对他进行修改:
package com.dxz; import javassist.ClassPool; import javassist.CtClass; import javassist.CtMethod; import javassist.Modifier; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class UpdatePerson { public static void update() throws Exception { ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault(); CtClass cc = pool.get("com.dxz.service.PersonService"); CtMethod personFly = cc.getDeclaredMethod("personFly"); personFly.insertBefore("System.out.println(\"起飞之前准备降落伞\");"); personFly.insertAfter("System.out.println(\"成功落地。。。。\");"); //新增一个方法 CtMethod ctMethod = new CtMethod(CtClass.voidType, "joinFriend", new CtClass[]{}, cc); ctMethod.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC); ctMethod.setBody("{System.out.println(\"i want to be your friend\");}"); cc.addMethod(ctMethod); Object person = cc.toClass().newInstance(); // 调用 personFly 方法 Method personFlyMethod = person.getClass().getMethod("personFly"); personFlyMethod.invoke(person); //调用 joinFriend 方法 Method execute = person.getClass().getMethod("joinFriend"); execute.invoke(person); } public static void main(String[] args) { try { update(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
结果:
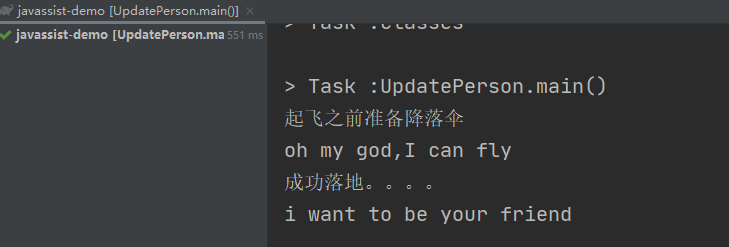
在personFly方法前后加上了打印日志。然后新增了一个方法joinFriend。执行main函数可以发现已经添加上了。
另外需要注意的是:上面的insertBefore() 和 setBody()中的语句,如果你是单行语句可以直接用双引号,但是有多行语句的情况下,你需要将多行语句用{}括起来。javassist只接受单个语句或用大括号括起来的语句块。
五、新增一个成员变量
package com.dxz; import javassist.*; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.URL; public class AddField { public static void main(String[] args) throws CannotCompileException, IOException { URL resource = AddField.class.getClassLoader().getResource(""); String file = resource.getFile(); System.out.println("文件存储路径:" + file); ClassPool cp = ClassPool.getDefault(); CtClass ctClass = cp.makeClass("com.dxz.dto.Hello"); //添加一个hello1的方法 CtMethod ctMethod = new CtMethod(CtClass.voidType, "hello1", new CtClass[]{CtClass.intType, CtClass.doubleType}, ctClass); ctMethod.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC); ctClass.addMethod(ctMethod); //添加一个int类型的,名字为value的变量 CtField ctField = new CtField(CtClass.intType, "value", ctClass); ctField.setModifiers(Modifier.PRIVATE); ctClass.addField(ctField); //保持为.class文件 ctClass.writeFile(file); } }
结果:
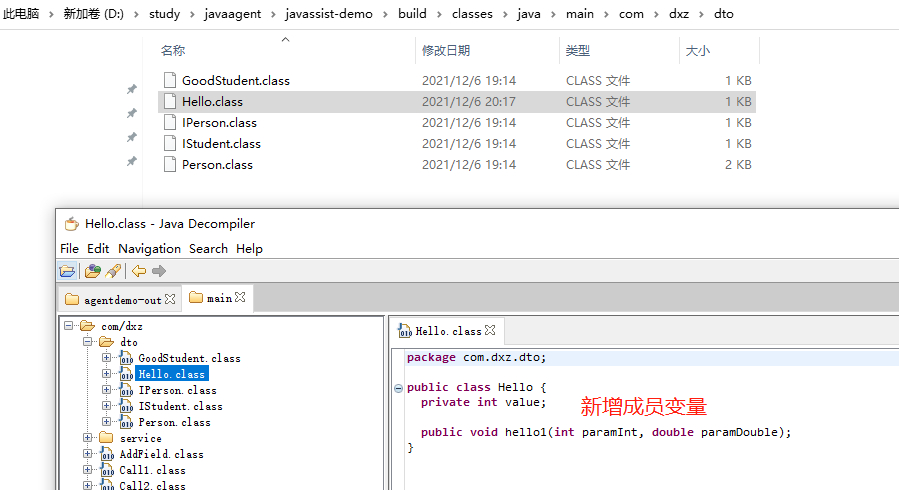
(六)、给变量新增get和set方法
package com.dxz; import javassist.*; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.URL; public class AddMethod { public static void main(String[] args) throws CannotCompileException, IOException, IOException { URL resource = AddMethod.class.getClassLoader().getResource(""); String file = resource.getFile(); System.out.println("文件存储路径:" + file); ClassPool cp = ClassPool.getDefault(); CtClass ctClass = cp.makeClass("com.dxz.service.Hello"); //添加一个hello1的方法 CtMethod ctMethod = new CtMethod(CtClass.voidType, "hello1", new CtClass[]{CtClass.intType, CtClass.doubleType}, ctClass); ctMethod.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC); ctClass.addMethod(ctMethod); //添加一个int类型的,名字为value的变量 CtField ctField = new CtField(CtClass.intType, "value", ctClass); ctField.setModifiers(Modifier.PRIVATE); ctClass.addField(ctField); //为value变量添加set方法 CtMethod setValue = new CtMethod(CtClass.voidType, "setValue", new CtClass[]{CtClass.intType}, ctClass); setValue.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC); ctClass.addMethod(setValue); //为value变量添加get方法 CtMethod getValue = new CtMethod(CtClass.intType, "getValue", new CtClass[]{}, ctClass); getValue.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC); ctClass.addMethod(getValue); //保持为.class文件 ctClass.writeFile(file); } }
结果
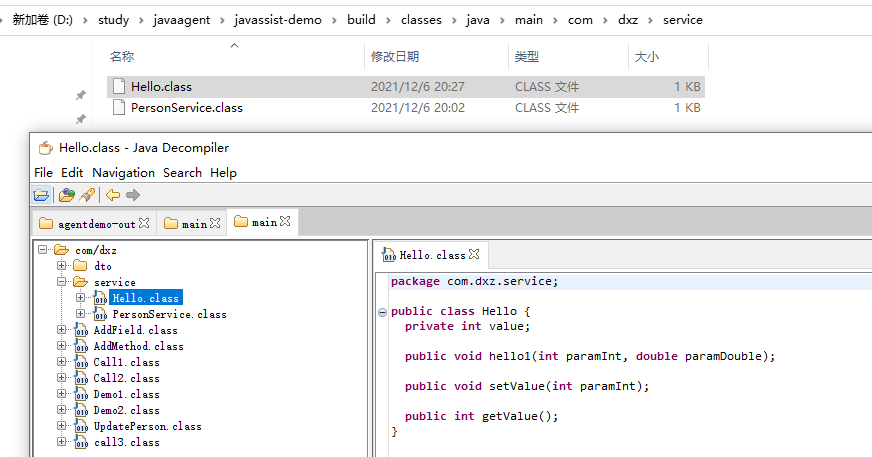
(七)、给方法内部添加代码
你是不是很好奇,set和get方法内部并没有代码,当程序运行的时候,肯定会出错的。
我们预想的结果:
private int value; public void setValue(int var1) { this.value = var1; } public int getValue() { return this.value; }
修改如下:
//设置方法体 setValue.setBody("this.value = var1;"); ctClass.addMethod(setValue); //为value变量添加get方法 CtMethod getValue = new CtMethod(CtClass.intType, "getValue", new CtClass[]{}, ctClass); getValue.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC); //设置方法体 getValue.setBody("return this.value;"); ctClass.addMethod(getValue);
结果:
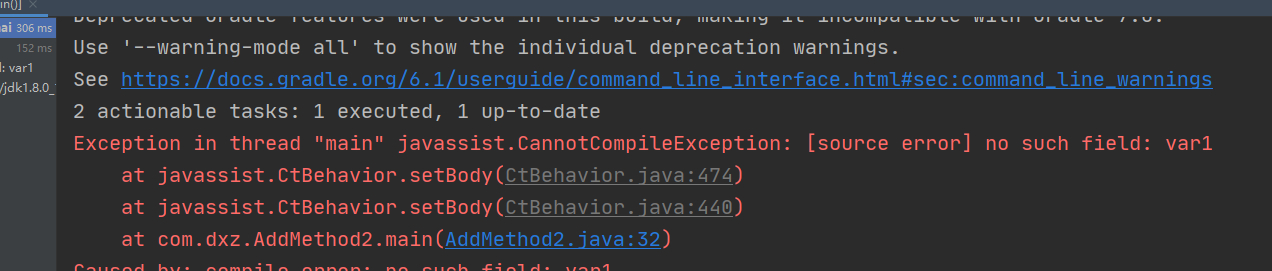

这个原因我们前面其实提到了,因为在编译的时候,会把变量名抹掉,传递的参数会依次在局部变量表中的顺序。
举个例子,如果要传递:
public void test(int a,int b,int c){ ... }
那么a,b,c就对应本地变量表中的1,2,3的位置:
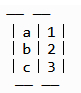
那么我们获取变量时就不能使用原始的名字了,在Javassist中访问方法中的参数使用的是$1, 2 , 2, 2,…,而不是直接使用原始的名字。
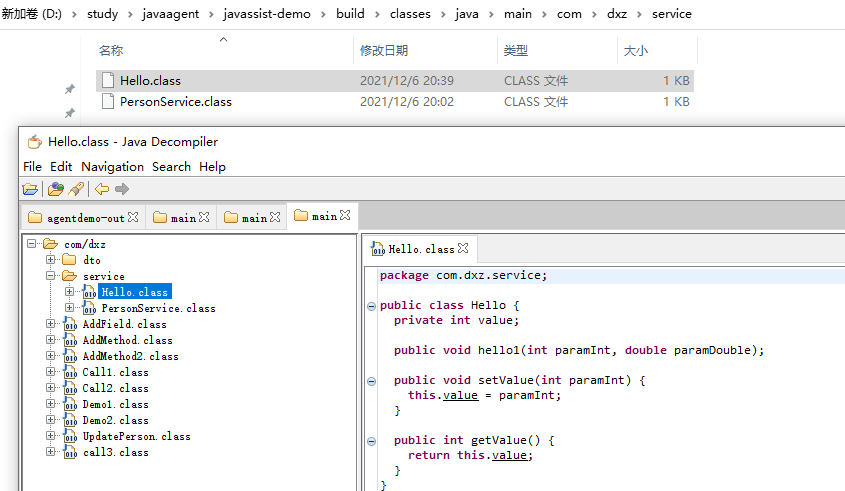
//设置方法体 setValue.setBody("this.value = $1;");
新的结果:
再扩展一下,2个参数的情况:
//添加一个hello2的方法 CtMethod ctMethod2 = new CtMethod(CtClass.voidType, "hello2", new CtClass[]{CtClass.intType, CtClass.doubleType}, ctClass); ctMethod2.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC); ctMethod2.setBody("this.value = $1 + $2;"); ctClass.addMethod(ctMethod2);
结果:
因为我们value是int,$1是int,$2是double,所以做了强制转型处理。

(八)、在方法体的前后分别插入代码
//添加一个hello3的方法 CtMethod ctMethod3 = new CtMethod(CtClass.voidType, "hello3", new CtClass[]{CtClass.intType, CtClass.doubleType}, ctClass); ctMethod3.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC); ctMethod3.setBody("this.value = $1 + $2;"); ctMethod3.insertBefore("System.out.println(\"我在前面插入了:\"+$1);"); ctMethod3.insertAfter("System.out.println(\"我在最后插入了:\"+$1);"); ctClass.addMethod(ctMethod3);
结果:

参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/rickiyang/p/11336268.html