python 基本数字类型
python各系统安装方式

- 变量
描述一切可变化的值
#变量组成的三个部分
name='jin'
变量名 name 赋值符号 ‘=’ 值(values)‘jin’
#变量的三个特性:
id type values
#使用实例:
print(id(name))
print(type(name))
print(name)
- 数据类型
字符串类型 str 用来表示名字 爱好 描述性的东西用str字符串类型表示 数字类型 int 薪资 年龄 等数字用int表示 浮点型 float 身高 体重 坐标 等精确数字需要 浮点型去表示
#实例:
x=‘jin’
print(type(x)) #打印出x是什么类型 str
x=8
print(type(x)) #x 为int
#注意
字符串性质的 str数字 转换成 int 类型
例:
x=‘666’ #此时x 为str类型
int(x) #此时x 为int类型 值为666 而非‘666’
数据类型
列表 []
类型为list
列表用 , 分割开多个值 值可以是任意类型
作用:用来存储多个值 注意:当列表中只存有一个值的情况下 如 name=['liujin'] 记得加‘,’ 否则会按照字符串的有序排列进行取值
names=['liujin','mahuateng','mayun']
本质为# name=list(['liujin','mahuateng','mayun'])
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
names[0] 列表索引取值
列表套列表
user_info['liujin',18,['read','music','play']]
#取值 爱好的第三个 user_info[2][2]
字典 {}
类型 dict
在字典中存放的是键值对 每一个键值对的组成是 key:value
实例:
user_info={'name':'liujin','age':18,'hobbies':['readbook','play']}
print(user_info) #查看字典
print(user_info['name']) #查看key name
print(user_info['hobbies'][0])#查看 hobbies 第一个值
#key 必须为字符串 value 可以为任何值
列表套字典练习:
#取出第二个学生的第2个爱好
students=[
{'name':'mayun','age':38,'hobbies':['play','sleep']},
{'name':'liujin','age':18,'hobbies':['read','sleep']},
{'name':'wangjianlin','age':58,'hobbies':['music','read','sleep']},
]
print(students[1]['hobbies'][1])
布尔类型 True False
用途:判断
#所有数据类型都自带布尔值
1、None,0,空(空字符串,空列表,空字典等)三种情况下布尔值为False
2、其余均为True
liujin=18
liujin>10 #True
liujin<10 #False
猜年龄小程序
liujin=18
while True:
age=input('请输入年龄')
age=int(age)
if age < liujin:
print ('猜小了')
if age > liujin:
print('猜大了')
if age == liujin:
print('猜对了')
break
可变类型和不可变类型
定义:
id 不变的情况下 值变为可变类型
id 变直变 为不可变类型
可变
可变类型有:列表 字典
不可变
不可变类型:元组 集合
格式化输出 %s format
name = input(‘名字>>:’)
age = input ('年龄>>:')
print('my name is %s ,my age is %s' %(name,age))
#%s 占位符 后续需要穿进去一个值
#%d 只能接受数字类型
练习:格式化打印name =input('请输入你的名字').strip()
age=input("请输入你的年龄").strip()
print("""
-------------- user_info-------------
name :%s
age :%s
"""%(name,age))
format 使用方法
# 顺序制定
info='my name is {},age is {}'.format('liujin',18)
print(info)
#索引指定
info='my name is {1},age is {0}'.format('liujin',18) #my name is 18,age is liujin
print(info)
#指名道姓
info='my name is {x},age is {y}'.format(x='liujin',y=18)
print(info)
基本运算符
假设 a=10 b=20
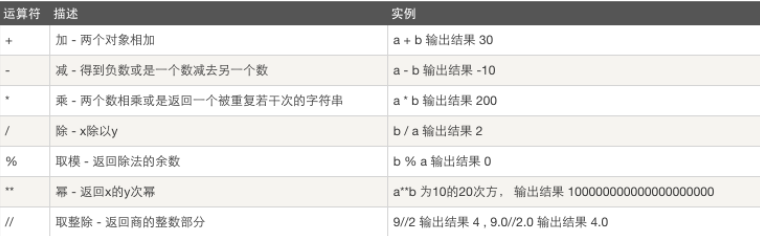
比较运算
假设 a=10 b=20
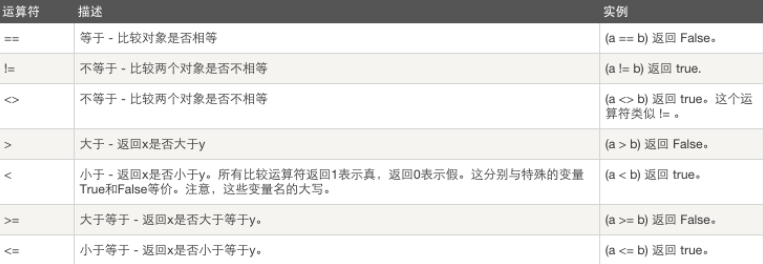
赋值运算
a=10 b=20
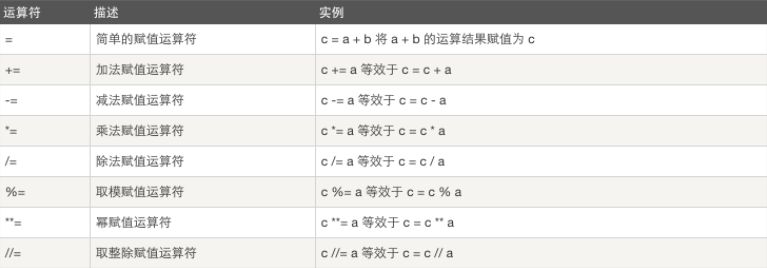
增量赋值 :
age=18
错误示范:
print(age+1) #19
print(age) #18
#加完之后age 的值并没有变!!!
age=age+1
print(age) #19
#相当于把age重新赋值
简写:
age+=1
print(age)#19
逻辑运算符
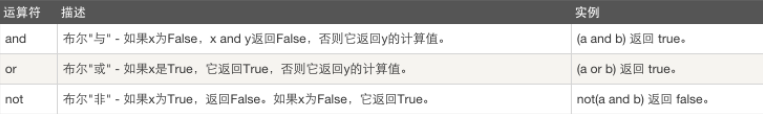
print(True or False and False)
#True
#从左到右运算 or生效后 后面的and没必要在运算
print((True or False) and False)
#先运算括号内的数据
身份运算
is 比较的是id
== 比较的是值
例子:
x=1
y=1
print(x is y)#False
print (x == y) #True
逻辑运算 if elif else while
#注意 tab建 在不同平台下空格数量不同 pycharm 下默认为4个
- if 判断
if True:
print(‘你好’)
elif x=1:
print (‘你好’)
else:
print(‘走开’)
- if 套 if
x=18
if x == 18:
if x>0:
print(True)
else:
print(False)
- while循环 #条件循环
while循环后的条件一旦成立,会执行 while下的体代码
死循环
while True:
print ('死循环')
#此时代码进入死循环
break 可以跳出循环
列:打印三次 hello
count=0
while True:
print ('hello')
count+=1
if count ==3:
break
- continue 可以跳过本次循环
x=0
while x<10:
x+=1
if x== 1 or x == 2 or x == 3:
continue
else:
print(x)
while 循环套while 循环
tag=True
while tag:
print("start")
while True:
print("end")
tag=False
break
依赖索引循环 不依赖索引循环
#依赖索引
x=0
salary=[20000,30000,50000,80000]
while x<len(salary):
print(salary[x])
x+=1
for line in range(len(salary)):
print(salary[line])
# 不依赖索引
for line in salary:
print(line)
数字除以任何比它大的数字都是 商0 余1
打印1到100所有奇数
#练习
for line in range(1,6):
if line % 2 ==1:
print(line)
#while 方式
count=0
while count <=10:
if count %2==1:
print('loop',count)
count+=1
打印1到100所有偶数
#练习
for line in range(1,6):
if line % 2 ==0:
print(line)
#while 方式
count=0
while count <=10:
if count %2==0:
print('loop',count)
count+=1 #之前会遇到else 加完数字跳不出去的问题,这里取消else 的使用直接用体代码代替
while 与 else 组合使用:
#与其它语言else 一般只与if 搭配不同,在Python 中还有个while ...else 语句,while 后面的else 作用是指,当while 循环正常执行完中间没有被break 中止的话,就会执行else后面的语句
count=0
while count<=10:
print('loop',count)
count+=1
else:
print("打印完毕")
# 练习,要求如下:
# 1 循环验证用户输入的用户名与密码
# 2 认证通过后,运行用户重复执行命令
# 3 当用户输入命令为quit时,则退出整个程序
name='liujin'
pwd='123456'
tag= True
while tag:
print("您好欢迎来到英雄联盟")
user_name = input("请输入您的账号").strip()
if user_name == 'quit':
break
password = input("请输入您的密码").strip()
if user_name == name and password == pwd:
print("登录成功")
while tag:
cmd=input("用户操作界面").strip()
if cmd == 'quit':
tag=False
break
print("run .... %s"%cmd)
练习:
#1. 使用while循环输出1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10
#2. 求1-100的所有数的和
#3. 输出 1-100 内的所有奇数
#4. 输出 1-100 内的所有偶数
#5. 求1-2+3-4+5 ... 99的所有数的和
#6. 用户登陆(三次机会重试)
#7:猜年龄游戏
# 要求:
# 允许用户最多尝试3次,3次都没猜对的话,就直接退出,如果猜对了,打印恭喜信息并退出
# #8:猜年龄游戏升级版
# 要求:
# 允许用户最多尝试3次
# 每尝试3次后,如果还没猜对,就问用户是否还想继续玩,如果回答Y或y, 就继续让其猜3次,以此往复,如果回答N或n,就退出程序
# 如何猜对了,就直接退出
#-----------1
# count = 0
# while count <10:
# count+=1
# if count == 4:
# continue
# else:
# print(count)
#-----------2
# print(sum(range(1,100)))
# count=0
# for line in range(1,100):
# count+=line
# else:
# print(count)
# ------------3
# for line in range(1,100):
# if line %2 == 1:
# print(line)
# count = 0
# while count <100:
# if count %2 ==1:
# print(count)
# count+=1
#------------------4
# for line in range (1,101):
# if line %2 == 0:
# print(line)
# count=0
# while count<=100:
# if count %2 ==0:
# print(count)
# count+=1
#------------------5
# 方法一
# ji=0
# ou=0
# for line in range(1,101):
# if line %2 == 1:
# # print(line)
# ji+=line
# else:
# print(ji)
# for line in range(1, 101):
# if line % 2 == 0:
# # print(line)
# ou += line
# else:
# print(ou)
# ji-=ou
# print(ji)
#方法2
# res=0
# count=1
# while count<=100:
# if count %2 == 0:
# res-=count
# else:
# res+=count
# count+=1
# print(res)
#-------------------6
# name='liujin'
# password='123456'
# count=1
# while count<=3:
# user_name=input('请输入名字').strip()
# pwd=input("请输入密码").strip()
# if user_name ==name and pwd == password:
# print("登录成功")
# else:
# print("账户密码错误")
# count+=1
#---------------------7
# age=18
# count=1
# while count<=3:
# user_input=input("plase input >>:").strip()
# user_input=int(user_input)
# if user_input <18:
# print("猜小了")
# count+=1
# elif user_input == 18:
# print("猜对了")
# break
# else:
# print("猜错了")
# count+=1
#------------------------8
# tag=True
# age=18
# count=1
# while tag:
# while count<=3:
# user_input=input("plase input >>:").strip()
# user_input=int(user_input)
# if user_input <18:
# print("猜小了")
# count+=1
# elif user_input == 18:
# print("猜对了")
# tag=False
# break
# else:
# print("猜错了")
# count+=1
# while tag:
# choose=input("输入y 继续 n退出>>:").strip()
# if choose == 'y' or choose == 'Y':
# count=0
# break
# if choose == 'N' or choose == 'n':
# tag=False
# break
# else:print("输入错误请重新输入")