Select boot-target : – via /etc/systemd/system/default.target symlink; – appending number or systemd.unit=<target> to bootargs.
root@ubuntu:/# systemctl status Openvmi-Xvfb-Manger.service * Openvmi-Xvfb-Manger.service - Openvmi Xvfb Manger Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/Openvmi-Xvfb-Manger.service; enabled; ven dor preset: enabled) Active: inactive (dead)
root@ubuntu:/# find ./ -name Openvmi-Xvfb-Manger.service ./lib/systemd/system/Openvmi-Xvfb-Manger.service ./etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/Openvmi-Xvfb-Manger.service
优先级 systemd的使用大幅提高了系统服务的运行效率, 而unit的文件位置一般主要有三个目录: Table 1. Load path when running in system mode (--system). ┌────────────────────────┬─────────────────────────────┐ │Path │ Description │ ├────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┤ │/etc/systemd/system │ Local configuration │ ├────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┤ │/run/systemd/system │ Runtime units │ ├────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┤ │/lib/systemd/system │ Units of installed packages │ └────────────────────────┴─────────────────────────────┘ 这三个目录的配置文件优先级依次从高到低,如果同一选项三个地方都配置了,优先级高的会覆盖优先级低的
systemctl list-unit-files -t service
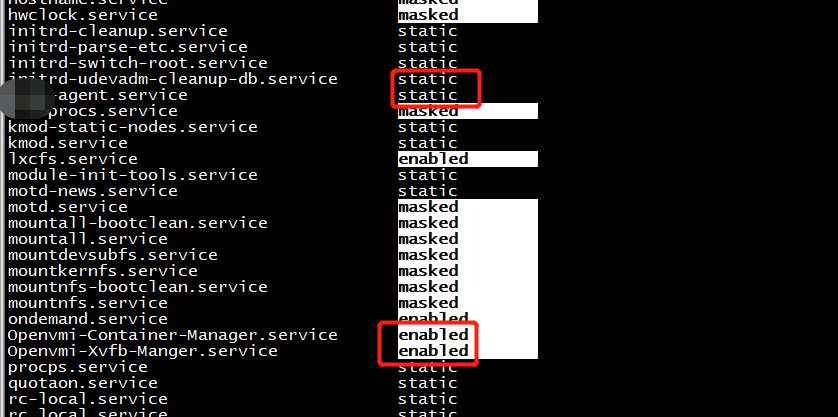
PS:使用命令 systemctl is-enabled postfix.service 得到的值可以是enable、disable或static,这里的 static 它是指对应的 Unit 文件中没有定义[Install]区域,因此无法配置为开机启动服务。
a template for multiple Xvfb services Simple xvfb.service systemd unit files for xvfb can be found at https://www.centos.org/forums/viewtopic.php?f=48&t=49080#p208363 and at https://askubuntu.com/a/621256/43344 . However, as I mentioned at the latter one can also take a templatized approach: [Unit] Description=virtual frame buffer X server for display %I After=network.target [Service] ExecStart=/usr/bin/Xvfb %I -screen 0 1280x1024x24 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target As a locally-written, non-system non-packaged, unit file for system-wide (as opposed to per-user) services this goes into /etc/systemd/system/xvfb@.service of course. controlling the services One instantiates the template, into an actual named service, with the display number that is desired. For display :99, therefore, there is an actual service instance named xvfb@:99.service. Set the service to auto-start on bootstrap with systemctl enable xvfb@:99.service . Unset auto-starting the service with systemctl disable xvfb@:99.service . Start the service manually with systemctl start xvfb@:99.service . Stop the service manually with systemctl stop xvfb@:99.service . Inspect the current service status in detail with systemctl status xvfb@:99.service .
场景 某些程序在启动时,会报出 (xxx 为你的程序名) xxx.service Failed to connect stdout to the journal socket, ignoring: Permission denied 说明: systemd 启动该程序期间,默认将标准输出和标准错误之类的定向输出给 journal。 如果权限不足,就会报出上述的错误。这个只是启动时的信息,并不是程序自身的日志机制。 一般来说等启动完成之后,程序自己的日志机制才会生效。在此之前都是由 systemd 在处理。 方法1 chmod 777 /run/systemd/journal/stdout systemctl stop xxx.service systemctl start xxx.service 方法2 在 /usr/lib/systemd/system/ 下打开 xxx.service 找到以下的代码,如果没有的,自行添加 StandardOutput=journal StandardError=journal 更改为你自定义的路径,也可以设置为 syslog StandardOutput=file:/path/to/your/custom.log StandardError=file:/path/to/your/custom.log 重启服务 (有多余步骤,主要防止修改不生效的问题) systemctl daemon-reload systemctl reset-failed systemctl stop xxx.service systemctl disable xxx.service systemctl enable xxx.service systemctl start xxx.service
[Unit] Description=customprocess After=network.target [Service] Type=forking ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/binary1 agent -config-dir /etc/sample.d/server StandardOutput=/var/log1.log StandardError=/var/log2.log Restart=always [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target