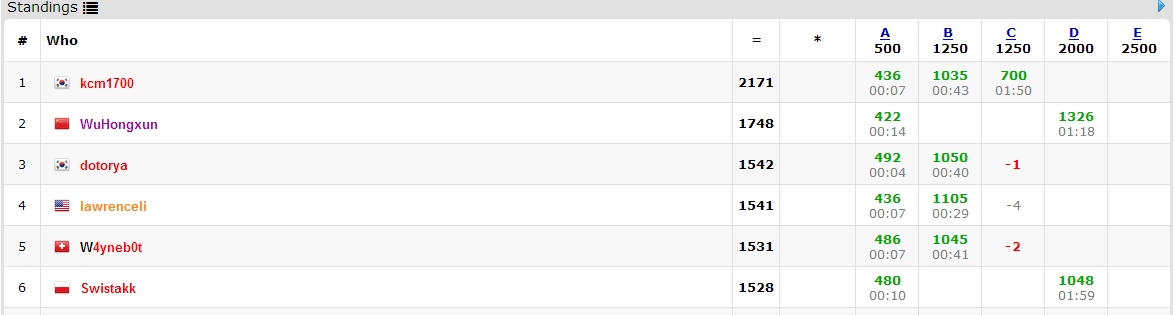
这次出的题貌似有点难啊,Div.1的Standing是这样的,可以看到这位全站排名前10的W4大神也只过了AB两道题。
A:http://codeforces.com/contest/705/problem/A
题意:输出形如I hate that I love that I hate ......it的句子,输入N表示形容词的个数

#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <bitset>
#include <math.h>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x;
printf ( "I hate" );
scanf ( "%d", &x );
x--;
int p = 1;
while ( x )
{
if ( p == 1 ) printf ( " that I love" );
else printf ( " that I hate" );
x--;
p = 1 - p;
}
printf ( " it
" );
return 0;
}
B:http://codeforces.com/contest/705/problem/B
题意:对于一系列由若干个点组成的环进行游戏,规则如下:若所有环的结点数都为1,则游戏结束;否则选择一个节点数大于1的环拆成两个环,无法进行操作者失败。输入一个序列,对于序列的每个前缀,依次求当初始各环的结点数分别为序列中的数字时先手必胜还是必败。
首先只考虑一个环的情况,若环中节点数个数为偶数,显然先手必胜,只需将环分成两个节点数相同的环即可。若节点数为奇数,先手划分只能得到一个偶数环和一个奇数环,若奇数环大小为1,则同上一种情况,此时先手必败;若奇数环大于1,则先手者首先在偶数环的子游戏上失败,被迫继续先手奇数环子游戏,直到奇数为1时失败。可见,先手能否获胜只与奇偶性有关。此游戏是SG游戏,多个游戏的结果为各个子游戏结果的异或和,只要用当前前缀的异或和与下一个子游戏环的胜负情况进行异或即为新的游戏的胜负情况。

#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <bitset>
#include <math.h>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[110000];
int main()
{
int N, tmp;
scanf ( "%d", &N );
for ( int i = 1; i <= N; i++ ) scanf ( "%d", &a[i] );
if ( a[1] % 2 == 1 )
{
printf ( "2
" );
tmp = 2;
}
else
{
printf ( "1
" );
tmp = 1;
}
for ( int i = 2; i <= N; i++ )
{
int x;
if ( a[i] % 2 == 1 ) x = 2;
else x = 1;
if ( tmp != x ) printf ( "1
" );
else printf ( "2
" );
if ( tmp != x ) tmp = 1;
else tmp = 2;
}
return 0;
}
C:http://codeforces.com/contest/705/problem/C
题意:一个手机上有N个APP,定义3种操作:1)某个APP产生了1条消息。2)查看某个APP目前产生的所有消息。3)查看所有消息中的前若干条。要求输出每步操作后未读消息的数量。
可以用队列实现。cnt[i]表示第i个APP产生的消息总数,re1[i]和re2[i]表示第i个APP的已读消息数量,1和2分别对应两种阅读方式。当进行操作1时,只需将相应的cnt加1,并将新消息加入队列;当进行操作2时,只需将未读消息的数量减去(cnt-re1)即可;当进行操作3时,先比较本次读的前缀长度与之前进行操作3时的最大长度进行比较,只对其中的未读部分进行操作,首先取出队首元素,将其所属的APP的re2加1。若re2>re1,则更新re1并将未读消息数减1。

#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <bitset>
#include <math.h>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
queue<int> q;
int cnt[310000], re1[310000], re2[310000], r;
int main()
{
int N, M, ans = 0;
scanf ( "%d%d", &N, &M );
while ( !q.empty() ) q.pop();
for ( int i = 1; i <= M; i++ )
{
int a, b;
scanf ( "%d%d", &a, &b );
if ( a == 1 )
{
q.push ( b );
cnt[b]++;
ans++;
}
if ( a == 2 )
{
ans -= cnt[b] - re1[b];
re1[b] = cnt[b];
}
if ( a == 3 )
{
if ( b > r )
{
for ( int i = r + 1; i <= b; i++ )
{
int x = q.front();
re2[x]++;
if ( re2[x] > re1[x] )
{
ans -= re2[x] - re1[x];
re1[x] = re2[x];
}
q.pop();
}
r = b;
}
}
printf ( "%d
", ans );
}
return 0;
}
D:http://codeforces.com/contest/705/problem/D
题意:N个点排成一排,S为起点,E为重点。在两个点x,y之前转移的代价定义为x与y的横坐标之差的绝对值加上此运动中的变大/变小状态下对应的在x点的起飞时间和y点的降落时间。若x点在y点左边,则以变大状态运动,反之以变小状态运动。一个点在变大和变小两种状态下的起飞与降落的时间不同。要求在每个点都经过且仅经过一次的情况下,求出从S转移到E的最小代价。
可以用贪心来解,至于为什么能贪心还没想明白。首先序列里只有S和E两个点,之后按从1到N的顺序依次把每个点插入,插入点的时候选择使总代价增加最少的位置。

#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
long long x[5005], a[5005], b[5005], c[5005], d[5005];
int nex[5005];
long long cost ( int i, int j )
{
if ( j > i ) return abs ( x[i] - x[j] ) + d[i] + a[j];
return abs ( x[i] - x[j] ) + c[i] + b[j];
}
int main()
{
int N, S, E;
scanf ( "%d%d%d", &N, &S, &E );
for ( int i = 1; i <= N; i++ ) scanf ( "%d", &x[i] );
for ( int i = 1; i <= N; i++ ) scanf ( "%d", &a[i] );
for ( int i = 1; i <= N; i++ ) scanf ( "%d", &b[i] );
for ( int i = 1; i <= N; i++ ) scanf ( "%d", &c[i] );
for ( int i = 1; i <= N; i++ ) scanf ( "%d", &d[i] );
nex[S] = E;
long long ans = cost ( S, E );
for ( int i = 1; i <= N; i++ )
{
if ( i == S || i == E ) continue;
int u = S, v;
long long MIN = 1e18;
while ( u != E )
{
long long tmp = cost ( u, i ) + cost ( i, nex[u] ) - cost ( u, nex[u] );
if ( tmp < MIN )
{
MIN = tmp;
v = u;
}
u = nex[u];
}
ans += MIN;
nex[i] = nex[v];
nex[v] = i;
}
printf ( "%I64d
", ans );
return 0;
}
