在 android sqlite (上)中主要介绍了 sqlite的基础特性,及其如何利用SQLiteOpenHelper类来完成对sqlite数据靠的操作。
本次,主要将介绍下sqlite的事务、请求服务端,返回Json信息,最后解析入库。
关于事务,一言以概之就是批量操作数据库信息的时候,如果部分操作有异常,则回退之前所有的操作。可以保证本批次操作的一致性和完整性。
首先我们同样创建一个基础操作类来获取SQLiteDatabase

1 public class DataBaseHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper { 2 private final String SQL="create table if not exists t_user(id int primary key,name varchar2(100),password varchar2(100))"; 3 private String tag="DataBaseHelper"; 4 5 public DataBaseHelper(Context context, String name, CursorFactory factory, 6 int version) { 7 super(context, name, factory, version); 8 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 9 } 10 11 public DataBaseHelper(Context context, String name, int version) { 12 this(context, name, null, version); 13 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) { 18 Log.w(tag, "创建数据库"); 19 db.execSQL(SQL); 20 21 } 22 23 @Override 24 public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) { 25 26 Log.w(tag, "更新数据库版本"); 27 } 28 29 }
同时创建一张表
create table if not exists t_user(id int primary key,name varchar2(100),password varchar2(100))
现在我们要往上述的表中插入两条记录
1 2 ContentValues values=new ContentValues(); 3 values.put("name", "lwx"); 4 values.put("password", "123"); 5 database.insert("t_user", "name,password", values); 6 database.execSQL("insert into t_user(name,password)value('zy','520')"); 7 8 9
其中第二条记录故意将values写成了value.
执行后,发现第一条记录成功插入,而第二条记录不出意料的没有执行成功。
现在我们思考下,加入我们要执行一个操作,创建一个用户,同时给他赋权限。
明显要往用户表和权限表插入信息。因此我们就很有必要保证数据信息的一致性,要么一起成功,要么一起失败。
具体操作,看下面的代码
1 database.beginTransaction(); 2 try { 3 //设置事务成功 mInnerTransactionIsSuccessful=true 等效于jdbc commit;的封装 4 ContentValues values=new ContentValues(); 5 values.put("name", "lwx"); 6 values.put("password", "123"); 7 database.insert("t_user", "name,password", values); 8 database.execSQL("insert into t_user(name,password)value('zy','520')"); 9 database.setTransactionSuccessful(); 10 11 } catch (Exception e) { 12 Log.w(tag, "插入数据失败,进行回退操作.."); 13 }finally{ 14 database.endTransaction(); 15 }
与之前区别就在于多了
database.beginTransaction();
database.setTransactionSuccessful();
database.endTransaction();
这三句代码,第一句是打开事务,第二句保证我们操作正确执行后,顺利提交操作。最后一句则是关闭事务
关于JSON解析
1 public class JsonUtil { 2 private String jsonObjStr="{\"password\":cnblogs,\"name\":\"小猪\"}"; 3 public String getJsonValue(String key){ 4 //http://www.cnblogs.com/tt_mc/archive/2011/01/04/1925327.html 5 6 try { 7 JSONObject jsonObject=new JSONObject(jsonObjStr); 8 9 //jsonObject.opt("name");//不会爆异常 10 return (String)jsonObject.get(key); 11 } catch (JSONException e) { 12 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 return null; 16 17 } 18 }
将json数据写入数据库
JsonUtil jsonUtil=new JsonUtil(); ContentValues values=new ContentValues(); values.put("name", jsonUtil.getJsonValue("name")); values.put("password", jsonUtil.getJsonValue("password")); database.insert("t_user", "name,password", values);
这里为了方便,并没有指定json的出处。
最后,我们来通过apache的httpClient请求远程服务来获取json数据,最后解析入库
首先,我们定义一个httpUtil类,来完成我们的请求操作
1 public class HttpUtil { 2 private String url = "http://10.1.3.121:9003/httpServer/test"; 3 private String requestCode; 4 private String responseResult; 5 //需要android.permission.INTERNET 6 7 8 public HttpUtil(String requestCode) { 9 10 this.requestCode = requestCode; 11 } 12 13 //get方式 14 public String doGet() { 15 url += "?requestCode=" + requestCode; 16 Log.e("HttpRequest", url); 17 HttpGet get = new HttpGet(url); 18 19 HttpClient client = new DefaultHttpClient(); 20 21 try { 22 HttpResponse response = client.execute(get); 23 HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity(); 24 responseResult = EntityUtils.toString(entity); 25 26 } catch (ClientProtocolException e) { 27 Log.e("HttpRequest", "get请求服务地址出错"); 28 } catch (IOException e) { 29 Log.e("HttpRequest", "get请求服务地址出错"); 30 } 31 return responseResult; 32 33 } 34 35 public String doPost(){ 36 NameValuePair valuePair=new BasicNameValuePair("responseResult", responseResult); 37 List<NameValuePair> parameter=new ArrayList<NameValuePair>(); 38 try { 39 HttpEntity httpEntity= new UrlEncodedFormEntity(parameter); 40 HttpPost httpPost=new HttpPost(url); 41 httpPost.setEntity(httpEntity); 42 HttpClient client=new DefaultHttpClient(); 43 HttpResponse response =client.execute(httpPost); 44 HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity(); 45 responseResult = EntityUtils.toString(entity); 46 47 48 } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { 49 Log.e("HttpPost", "字符转换出错"); 50 } catch (ClientProtocolException e) { 51 Log.e("HttpRequest", "post请求服务地址出错"); 52 } catch (IOException e) { 53 Log.e("HttpRequest", "post请求服务地址出错"); 54 } 55 56 57 return responseResult; 58 } 59 60 61 }
接着,我们创建一个通过servlet来简单创建一个远程服务

public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doPost(request, response); } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { String requestCode =request.getParameter("requestCode"); String jsonObjStr; response.setCharacterEncoding("GBK"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); if(requestCode.equals("1")){ jsonObjStr="{\"password\":eoe,\"name\":\"yiyou\"}"; }else{ jsonObjStr="{\"password\":csdn,\"name\":\"itstart\"}"; } out.print(jsonObjStr); out.flush(); out.close(); }
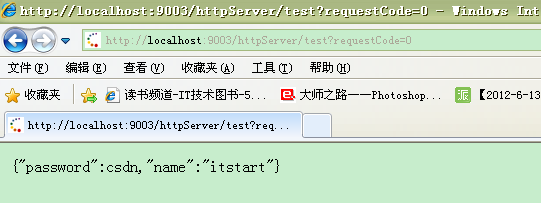
对于之前的JosnUtil类我做了点改动
public JsonUtil(){} public JsonUtil(String jsonObjStr){ this.jsonObjStr=jsonObjStr; }
最后是android中activity的处理方式了
baseHelper=new DataBaseHelper(SqliteActivity.this, "user.db", 1); database= baseHelper.getWritableDatabase(); int ramNum=(int)(Math.random()*1); String requestCode[]=new String[]{"1","0"}; Log.w(tag, "产生的随机数:"+ramNum); HttpUtil httpUtil=new HttpUtil(requestCode[ramNum]); String result=httpUtil.doGet(); JsonUtil jsonUtil2=new JsonUtil(result); insertData(jsonUtil2);
insertData方法代码

1 public void insertData(JsonUtil jsonUtil){ 2 Cursor cursor=null; 3 ContentValues values=new ContentValues(); 4 values.put("name", jsonUtil.getJsonValue("name")); 5 values.put("password", jsonUtil.getJsonValue("password")); 6 database.insert("t_user", "name,password", values); 7 //database.execSQL("insert into t_user(name,password)values('zy','520')"); 8 // cursor=database.rawQuery("select name from t_user where name=?", new String[]{"zy"}); 9 cursor= database.rawQuery("select name from t_user ", null); 10 11 while(cursor.moveToNext()){ 12 if(cursor.moveToLast()!=true) 13 continue; 14 String name= cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("name")); 15 Log.w(tag, name); 16 Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), name, 1).show(); 17 } 18 19 }

总结:当我们需要的时候,尽量多结合一些常用的或则自己不熟悉的模块,进行整合。
这样既达到了复习的效果,又可以学习新的知识。:)
