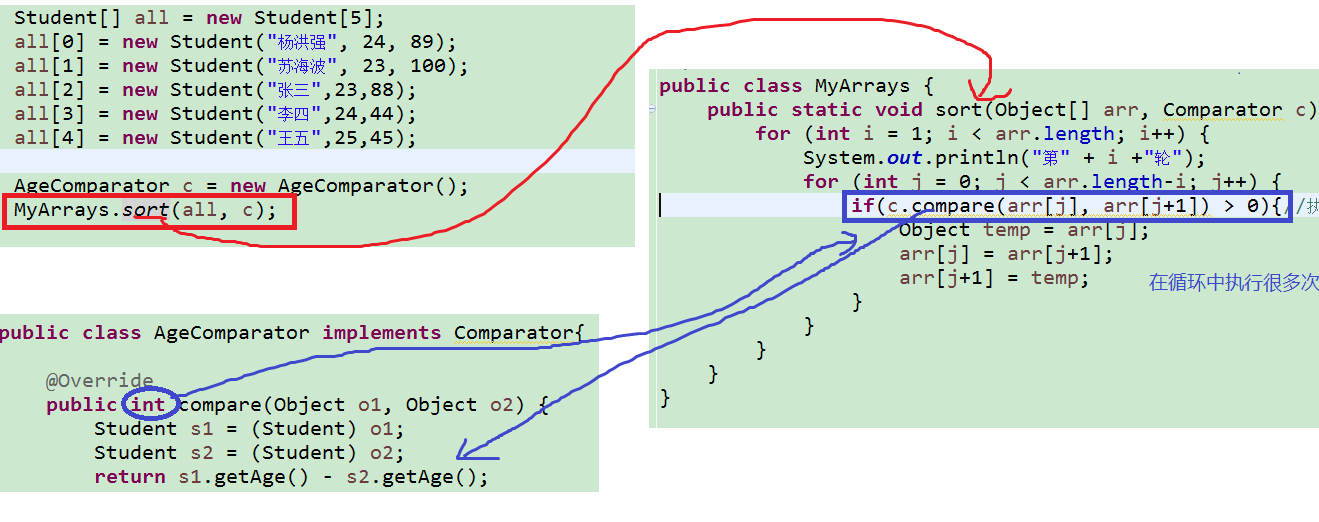
package test04; public class TestComparator2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Student[] all = new Student[5]; all[0] = new Student("杨洪强", 24, 89); all[1] = new Student("苏海波", 23, 100); all[2] = new Student("张三",23,88); all[3] = new Student("李四",24,44); all[4] = new Student("王五",25,45); AgeComparator c = new AgeComparator(); MyArrays.sort(all, c); for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++) { System.out.println(all[i]); } } }
package test04; public class Student { String name; int age; int score; public Student(String name, int age, int score) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; this.score = score; } public Student() { super(); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public int getScore() { return score; } public void setScore(int score) { this.score = score; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", score=" + score + "]"; } }
package test04; import java.util.Comparator; /* * 需求:编写一个MyArrays的数组工具类,这个工具类,想要为任意的对象数组,进行升序排序 */ public class MyArrays { public static void sort(Object[] arr,Comparator c){ for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < arr.length-1; j++) { // System.out.println("比较:arr["+j+"]和arr["+(j+1)+"]"); // System.out.println(arr[j]); // System.out.println(arr[j+1]); // System.out.println(); if(c.compare(arr[j], arr[j+1])>0){ Object temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j+1]; arr[j+1] = temp; } } } } }
package test04; import java.util.Comparator; public class AgeComparator implements Comparator { @Override public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { Student s1 = (Student) o1; Student s2 = (Student) o2; return s1.getAge() - s2.getAge(); } }
定制比较器的使用图解
自然比较器
package com.atguigu.test05; import java.util.Arrays; /* * 总结: * Arrays的sort方法有两种: * (1)void sort(Object[] arr): * 根据元素的自然顺序对指定对象数组按升序进行排序。数组中的所有元素都必须实现 Comparable 接口。 * (2)void sort(Object[] arr, Comparator c): * 根据“指定比较器”产生的顺序对指定对象数组进行排序。数组中的所有元素都必须是通过“指定比较器”可相互比较的 */ public class TestArrays { public static void main(String[] args) { Student[] all = new Student[5]; all[0] = new Student("杨洪强", 24, 89); all[1] = new Student("苏海波", 23, 100); all[2] = new Student("张三",23,88); all[3] = new Student("李四",24,44); all[4] = new Student("王五",25,45); //如果我们的学生类Student,实现了java.lang.Comparable接口, //能不能按照自然排序的规则进行排序呢 //Arrays中有这样的方法 //public static void sort(Object[] a) Arrays.sort(all);//这里面排序过程中,调用了元素本身的compareTo()方法 //因为元素本身是Student类型,它实现了java.lang.Comparable接口 //本身就具备比较大小的能力,即拥有compareTo()方法 for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++) { System.out.println(all[i]); } } }
package com.atguigu.test05; /* * java.util.Comparator:定制比较,定制顺序 * int compare(Object o1, Object o2): * o1与o2比较,o1>o2,返回正整数 * o1与o2比较,o1<o2,返回负整数 * o1与o2比较,o1=o2,返回0 * java.lang.Comparable:自然比较,自然顺序 * int compareTo(Object obj) * this与obj对象比较,this > obj,返回正整数 * this与obj对象比较,this < obj,返回负整数 * this与obj对象比较,this = obj,返回0 * * 上午讲的定制比较器,用定制比较器的对象,比较两个学生对象: * AgeComparator c = new AgeComparator(); * if(c.compare(s1, s2) > 0){...} * * 希望学生对象本身就具备比较大小的能力。 */ public class TestComparable { public static void main(String[] args) { Student s1 = new Student("杨洪强", 24, 89); Student s2 = new Student("苏海波", 23, 100); //按成绩比较 if(s1.compareTo(s2)>0){ System.out.println("s1 > s2成绩"); }else if(s1.compareTo(s2)<0){ System.out.println("s1 < s2成绩"); }else{ System.out.println("s1 = s2成绩"); } //按年龄比较,只能再用定制比较,补充完成这个功能 } } class Student implements Comparable{ private String name; private int age; private int score; public Student(String name, int age, int score) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; this.score = score; } public Student() { super(); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public int getScore() { return score; } public void setScore(int score) { this.score = score; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", score=" + score + "]"; } @Override public int compareTo(Object obj) { //this与obj比较,this和obj都是学生对象 Student other = (Student) obj; //例如:对于学生对象来说,最常用的是按成绩排名,那么我就可以把自然顺序定位成绩升序 /* if(this.score > other.score){ return 1; }else if(this.score < other.score){ return -1; } return 0;*/ return this.score - other.score; } }