原文 from https://www.cnblogs.com/zhengAloha/p/8665719.html
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <pthread.h>
pthread_t ntid;
char buf[100] = {0};
int flag = 0;
sem_t sem;
void* func(void* arg)
{
printf("please input the str first:
");
while(flag == 0)
{
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
sem_wait(&sem);
printf("please input the str.
");
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main()
{
int err;
sem_init(&sem,0,0);
err = pthread_create(&ntid,NULL,func,NULL);
if(err != 0)
{
printf("can not create thread : %s
",strerror(err));
return -1;
}
while(scanf("%s",buf))
{
printf("输入的字符串为:%s
",buf);
if(!strncmp(buf,"end",3))
{
flag = 1;
sem_post(&sem);
break;
}
else
{
sem_post(&sem);
}
}
printf("等待回收子线程
");
err = pthread_join(ntid, NULL);
if (err != 0)
{
printf("pthread_join error.
");
exit(-1);
}
printf("子线程回收成功
");
sem_destroy(&sem);
sleep(1);
exit(0);
}
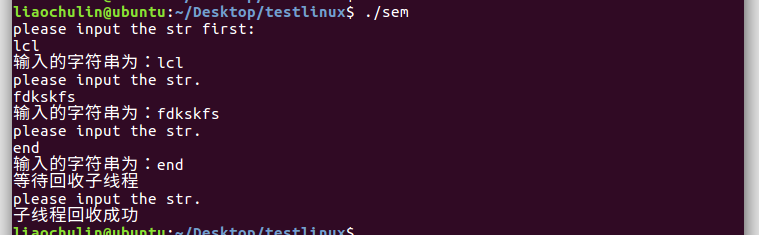
copy了一份代码,稍微修改使其能显示其同步性,mainThread 输出之后,阻塞住的sub Thread 随后输出
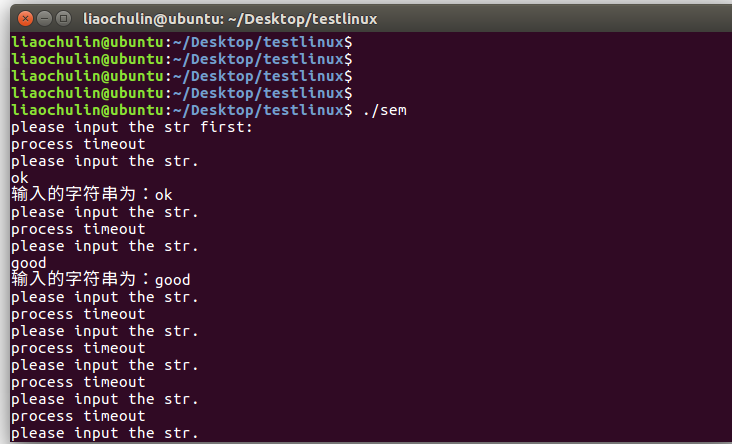
2.另外关于等待超时返回的函数,sem_timedwait(sem_t*sem,const struct timespec*timeout),有时候我们不需要线程一直阻塞,需要一个超时机制,以下为5s超时后wait 返回示例。
void* func(void* arg)
{
printf("please input the str first:
");
while(flag == 0)
{
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
wait(5000);
printf("please input the str.
");
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int wait(int milliseconds)
{
int ret = true;
if(milliseconds > 0)
{
int s;
struct timespec ts;
if(clock_gettime(CLOCK_REALTIME,&ts)== -1)
{
ret = false;
}
ts.tv_sec += milliseconds/1000;
ts.tv_nsec+= (milliseconds%1000)*1000000;
if (ts.tv_nsec >= 1000000000) //ns增加后超过1s则进位
{
ts.tv_nsec -= 1000000000;
ts.tv_sec++;
}
while((s = sem_timedwait(&sem, &ts)) == -1 && errno == EINTR) //当阻塞于某个慢系统调用的一个进程捕获某个信号且相应信号处理函数返回时,该系统调用可能返回一个EINTR错误
{
continue;
}
if(s == -1)
{
if (errno == ETIMEDOUT) //正常超时
{
printf("process timeout
");
}
else
{
printf("process sem_timedwait error");
}
ret = false;
}
}
else
{
ret= !sem_wait(&sem);
}
return ret;
}