1. redis事务
redis是单线程来处理所有client请求的。
multi命令:将命令放入队列中,直到遇到exec命令,再开始执行队列中的命令。
- 结果打包返回。
- 事务中的写操作不能依赖事务中的读操作。
- 事务中的一个命令失败,并不回滚其他命令。
discard命令:来取消事务。
CAS(check and set):watch命令,被watch的key,在exec之前发生改变,则exec退出返回nil
2. pipeline
除了可以利用mget,mset之类的命令来一次处理多条key,来减少网络传输外,也可以使用pipeline。
pipeline方式打包命令发送,redis会缓存所有命令的执行结果,消耗内存直到最后一次返回,所以并非一次打包命令越多越好。
public static void usePipeline(){ try{ jedis = new Jedis(HOST, PORT); jedis.auth("password"); Pipeline pl = jedis.pipelined(); pl.rpush("nn", "my"); pl.rpush("nn", "name"); pl.rpush("nn", "is"); pl.rpush("nn", "chai"); pl.rpush("nn", "dorothy"); pl.lrange("nn", 0, 4); System.out.println(pl.syncAndReturnAll().toString()); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } }
3. 发布订阅pub/sub
如下是订阅者的代码:
@Test public void pubsubTest(){ String cmd = "auth password subscribe news.share news.blog "; try{ Socket socket = new Socket(HOST,PORT); InputStream in = socket.getInputStream(); OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream(); out.write(cmd.getBytes()); byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; while(true){ int readCount = in.read(buffer); System.out.write(buffer,0,readCount); System.out.println("-----------------"); } }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } }
客户端直接订阅方式如下:
redis> psubscribe news.* Reading messages... (press Ctrl-c to quit) 1. "psubscribe" 2. "news.*" 3. (integer) 1
客户端发布消息如下:(返回2表示有2个连接接收了此消息)
redis> publish news.share "share a link http://www.google.com" (integer) 2 redis> publish news.blog "I post a blog" (integer) 2
Java程序接收到的消息:
*3 $9 subscribe $10 news.share :1 *3 $9 subscribe $9 news.blog :2 -------------------------------------- *3 $7 message $10 news.share $34 share a link http://www.google.com -------------------------------------- *3 $7 message $9 news.blog $13 I post a blog --------------------------------------
- For Simple Strings the first byte of the reply is "+"
- For Errors the first byte of the reply is "-"
- For Integers the first byte of the reply is ":"
- For Bulk Strings the first byte of the reply is "$"
- For Arrays the first byte of the reply is "
*"
4. redis持久化
4.1 Snapshotting
快照是默认的持久化方式,默认文件名为dump.rdb,开启子进程完成快照保存。
可以在redis.conf修改配置定时完成快照。默认配置如下:
- save 900 1 #900 s内如果有1个key被修改
- save 300 10 #300s内如果有10个key被修改
- save 60 10000
也可以使用save和bgsave命令完成快照。save调用主线程完成快照保存,所以会阻塞client。
每次持久化都会将数据全部写入到磁盘一次,而不是增量的只同步脏数据。
4.2 Append-only file
比snapshotting有更好的持久化效果。将所有命令通过write函数追加到文件中(默认是appendonly.aof。
appendonly yes //启用aof # appendfsync always //性能差,但可以保证完全的持久化,不会丢失数据。 appendfsync everysec //每秒缓存一次 # appendfsync no //完全依赖os,持久化没保证。
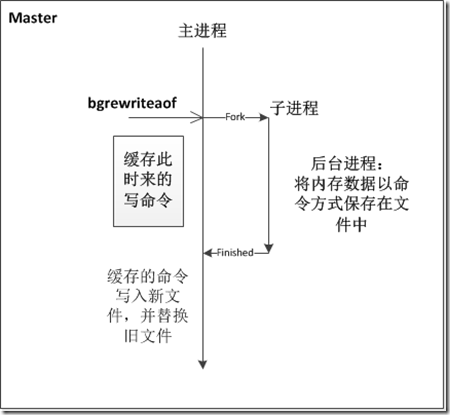
为了压缩aof文件,使用bgrewriteaof命令,开启子进程,将内存中的数据以命令的方式写入文件,并替换原来的文件。
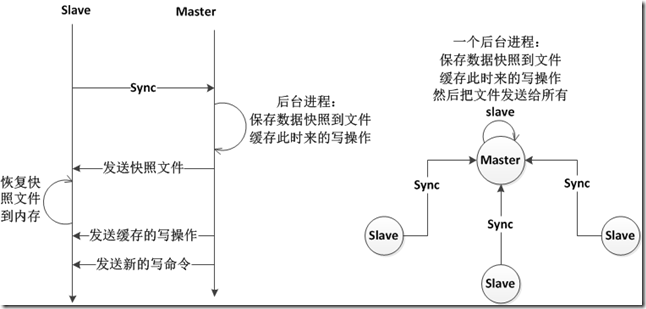
5. 主从复制Master/Slave
- master可有多个slave,slave直接可互连,成网状结构。
- 同步时,master不阻塞,slave阻塞不能处理client的请求。
- 注释掉save,禁用master的数据持久化,在slave上配置数据持久化。
- slave可以用作备份冗余,或者分担读请求。
配置slave很简单,只需要在slave的配置文件中加入如下:
slaveof 192.168.1.1 6379 #指定master的ip和端口
6. 虚拟内存
不使用os提供的虚拟内存的原因:http://antirez.com/post/redis-virtual-memory-story.html
- redis对象可能被分配到多个os页面上,一个对象被使用,会覆盖多个页面。
- redis可以把交换到磁盘的对象压缩。
配置如下:
vm-enabled yes #开启 vm-swap-file /tmp/redis.swap #交换出的对象保存的文件路径 vm-max-memory 1000000 #redis使用内存上限 vm-page-size 32 # 页面大小32字节 vm-pages 134217728 #交换文件大小 = vm-page-size * vm-pages vm-max-threads 4 #一般等于cpu核数
当vm-max-threads 为0时,master阻塞来处理对象的换入换出。
当vm-max-threads 不为0时,master不阻塞,只在换入时阻塞请求换入key的client。