1、冒泡排序
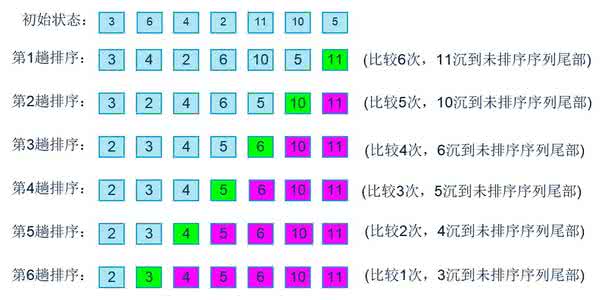
//第一层循环与i的初始值无关,而只与循环了多少次有关
//第一层循环含义为:需要遍历arr.length-1次数组,才能将数组排好序
//第二层循环要解决的问题便是:待排序区域的起始和结尾位置,在进行这个循环时,数组已经排好了几个值
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {3,1,4,9,2,5,6};
int temp=0;
for(int i=0;i<a.length-1;i++){ //i是用来判断
for(int j=0;j<a.length-1-i;j++){
if(a[j]>a[j+1]){
temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
}
}
2、直接选择排序
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = { 63, 4, 24, 1, 3, 15 };
int index;
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
index = 0;
//找出待排序序列中的最大值的位置
for (int j = 1; j <= array.length - i; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[index]) {
index = j;
}
}
// 交换最大值和此序列的最后一位
int temp = array[array.length - i];// 把最后一位元素值保持到临时变量中
array[array.length - i] = array[index];// 把最大值值保存到最后一位元素单元中
array[index] = temp;// 把最后一位原值保存到最大值所在元素中
}
// 输出直接选择排序后的数组值
for (int i : array) {
System.out.print(" >" + i);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
3、反转排序
//将原序列反序排列
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = { 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 };
int temp;
int len = a.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len / 2; i++) {
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[len-1-i];
a[len-1-i] = temp;
}
for (int m : a) {
System.out.print(m+" ");
}
}
}
