题目链接 & 题面
AcWing:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/111/
ContestHunter 挂了,只有 AcWing 上能找到这题了。。
题目描述
给定一个整数 M,对于任意一个整数集合 S,定义“校验值”如下:
从集合 S 中取出 M 对数(即 2∗M个数,不能重复使用集合中的数,如果 S 中的整数不够 M 对,则取到不能取为止),使得“每对数的差的平方”之和最大,这个最大值就称为集合 S 的“校验值”。
现在给定一个长度为 N 的数列 A 以及一个整数 T。
我们要把 A 分成若干段,使得每一段的“校验值”都不超过 T。
求最少需要分成几段。
输入格式
第一行输入整数 K,代表有 K 组测试数据。
对于每组测试数据,第一行包含三个整数 N,M,T 。
第二行包含 N 个整数,表示数列A1,A2…AN。
输出格式
对于每组测试数据,输出其答案,每个答案占一行。
数据范围
1≤K≤12,
1≤N,M≤500000,
0≤T≤10^18,
0≤Ai≤2^20
基本思路
朴素算法——暴力
从这个集合的开头开始,确定每一个划分点。
采用类似贪心的方法,不考虑后面的数, 一个个向后枚举划分点。
拿样例数据举例:
2
5 1 49
8 2 1 7 9
5 1 64
8 2 1 7 9
先规定起始点 l 为 0,然后枚举:
{8} -> {8, 2} -> {8, 2, 1} -> {8, 2, 1, 7} -> {8, 2, 1, 7, 9} ->{8, 2, 1, 7}, {9}
每次枚举还需要 O(n lg n) 的时间来排序,时间复杂度为 O(n^2 lg n)
倍增(其实有点像二分)
把枚举改成倍增
显而易见,对于相同的左端 l,右端 r 越大,校验值越大(也有可能相等)。
所以,校验值可以看成是具有单调性的,可以通过倍增求解。
具体来说,可以确定一个右端 R 和右端增加长度 p,如果这个序列的校验值小于等于上限,那么将 p 乘以 2,并且将右端更新(R+=p),如果大于上限,就将 p 除以 2。
这样,我们可以将时间复杂度降低到 O(n^2)
关于排序
每次求校验值时都需要排序,其实没有必要使用快速排序,可以采用归并排序,把新增的序列排好序然后再归并。时间复杂度 O(n lg n)
然而我用了时间复杂度相同的二分插入排序,但是后面 TLE 了,时间限制是10s,我的程序运行了600s
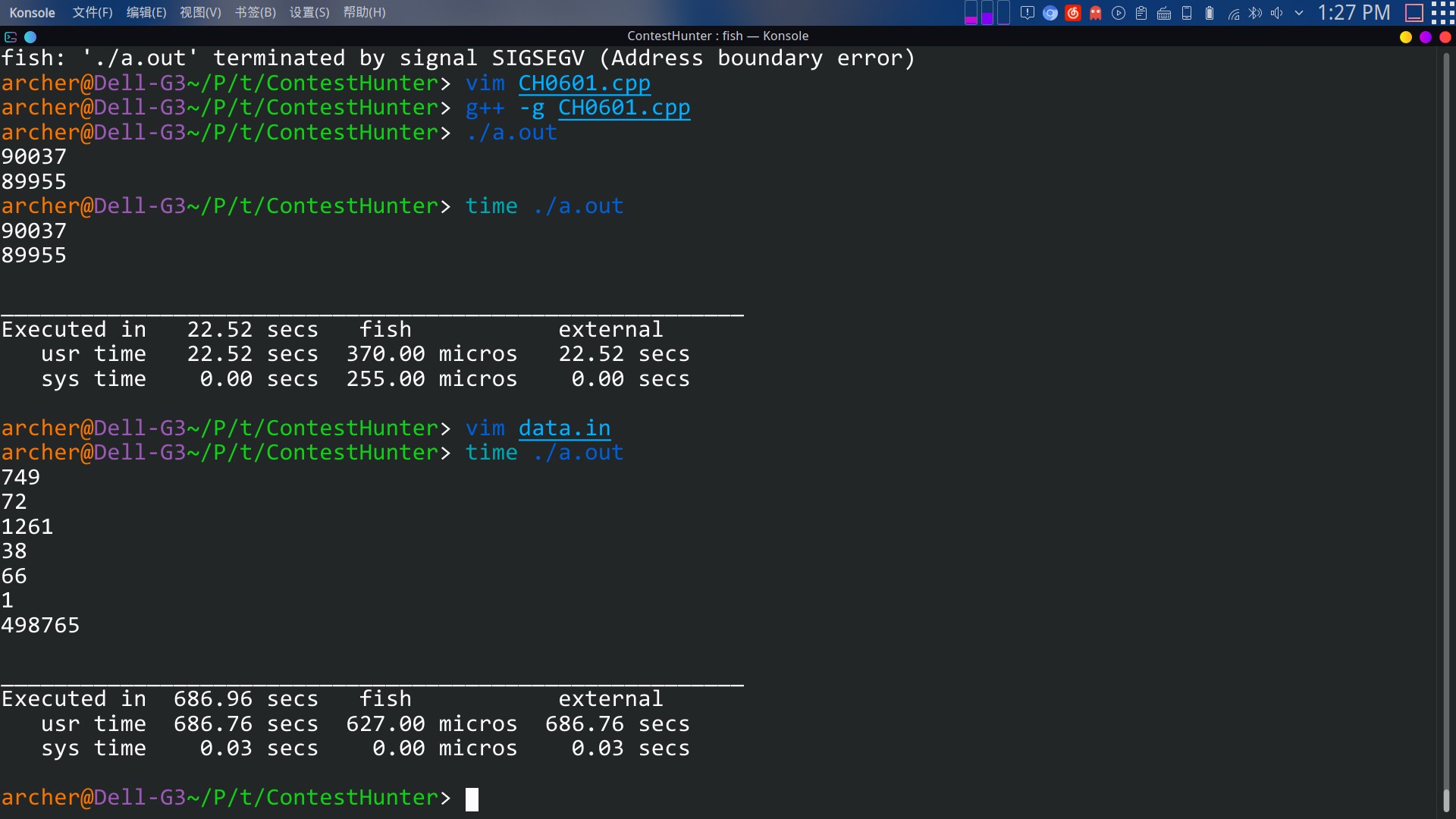
应该是 vector 常数太大了吧
代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
using std::min;
const int MAX=500005;
int k, n, m;
vector<long long> o, ne;
long long t, a[MAX];
int genius(void);
long long check(int, int);
int main(){
freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
scanf("%d", &k);
for(int i=0; i<k; i++){
scanf("%d%d%lld", &n, &m, &t);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
scanf("%lld", &a[i]);
}
printf("%d
", genius());
}
return 0;
}
int genius(){
int r=0, ans=0, l, p;
long long ch;
while(r<n){
if(r==n-1){
ans++; break;
}
l=r; p=1;
ne.clear(); o.clear();
while(p!=0 && r<n){
ch = check(r, p);
if(ch<=t){
r+=p; p*=2;
o=ne;
}
else p/=2;
}
ans++;
}
return ans;
}
long long check(int r, int p){
ne=o;
int l, r1, mid;
for(int i=r; i<min(r+p, n); i++){
l=0; r1=ne.size();
while(l<r1){
mid=(l+r1)>>1;
if(ne[mid]>=a[i]) r1=mid;
else l=mid+1;
}
ne.insert(ne.begin()+l, a[i]);
}
int s=ne.size();
long long ans=0;
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
if(s>=(i+1)*2){
ans+=(ne[i]-ne[s-i-1])*(ne[i]-ne[s-i-1]);
}
}
return ans;
}