一、tensorflow基础
1、安装
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple tensorflow
2、第一个tensorflow程序
import tensorflow as tf import os #屏蔽编译提醒警告 os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL']='2' a = tf.constant(10) b = tf.constant(12) c = tf.add(a,b) with tf.Session() as sess: print(sess.run(c))
二、tensorflow结构分析
1、图
1)获取默认图
tf.get_default_graph()
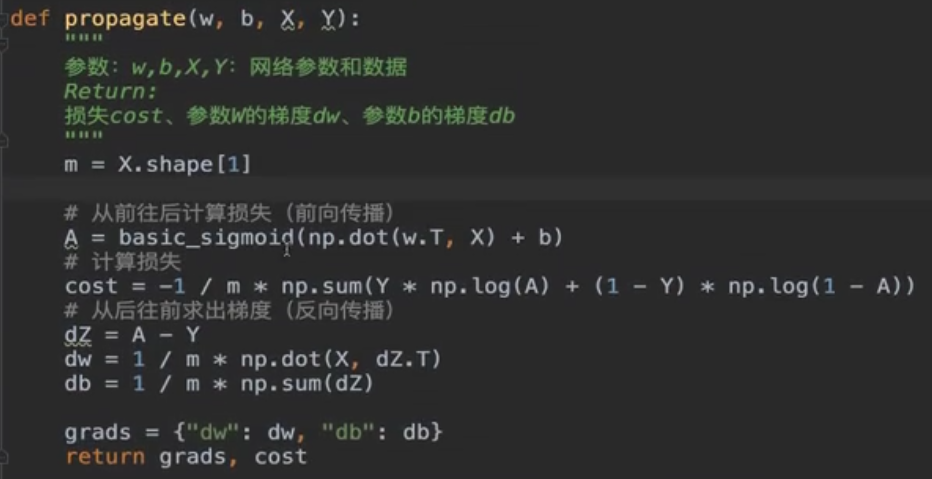
2)创建新图及使用

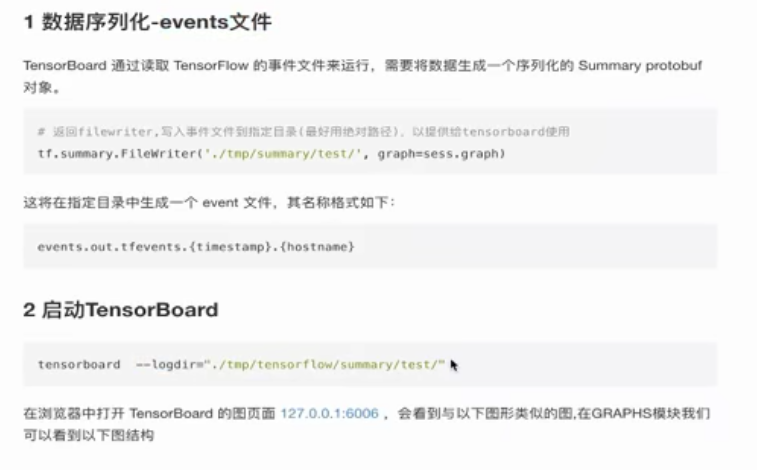
3)图可视化
2、OP
1)常用op

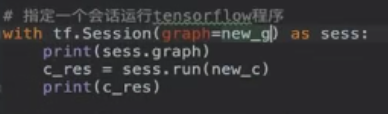
3、会话
1)开启会话

2)run

3)占位符与feed_dict使用

4、张量
1)创建张量
固定值张量

随机值张量

2)改变张量
类型改变

形状改变


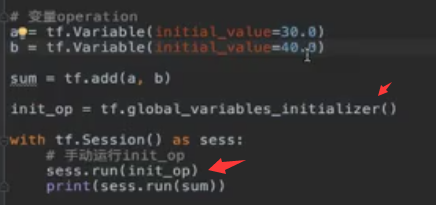
5、变量OP
1)创建使用变量

2)变量命名空间

三、回归算法实现
1、线性回归实现
import tensorflow as tf #命令行参数 tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer("max_step", 200, "训练的步数") #定义获取命令行参数变量 FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS def linearregressin(): """ 实现线性回归 :return: """ # 1、构造数据集 with tf.variable_scope("original_data"): x = tf.random_normal([100, 1], mean=0.0, stddev=1.0) y_true = tf.matmul(x, [[0.8]]) + [[0.7]] # 2、创建线性回归模型 with tf.variable_scope("linear_model"): weights = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal([1, 1])) # 随机权重 bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal([1, 1])) # 随机误差值 y_predict = tf.matmul(x, weights) + bias # 3、确定损失率:均方误差 (y_predict - y_true)^2 / m with tf.variable_scope("loss"): loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict - y_true)) # 4、使用梯度下降优化 # w2 = w1 - 学习率*方向 b2 = b1 - 学习率*方向 with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"): optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(loss) # 5、收集观察变量 零纬度scalar 高纬度histogram losses = tf.summary.scalar("loss", loss) weightses = tf.summary.histogram("weights", weights) biases = tf.summary.histogram("bias", bias) merge_op = tf.summary.merge_all() # 初始化变量 init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer() #创建一个saver saver = tf.train.Saver() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init_op) filewriter = tf.summary.FileWriter("./tmp/summary/", graph=sess.graph) #---------测试保存的模型----------- # print("weight:",weights.eval(),"bias:",bias.eval()) # saver.restore(sess, "./tmp/ckpt/linearregressin") # print("weight:", weights.eval(), "bias:", bias.eval()) for i in range(FLAGS.max_step): sess.run(optimizer) summary = sess.run(merge_op) filewriter.add_summary(summary, i) saver.save(sess, "./tmp/ckpt/linearregressin") return None if __name__ == "__main__": linearregressin()
2、逻辑回归梯度下降原理
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/44591359