分层图实际上就是把一个图复制好几份,分别代表每一层图,相邻的层之间的节点如果在原图有边就可以连边,同一层节点之间在原图有边也连边。
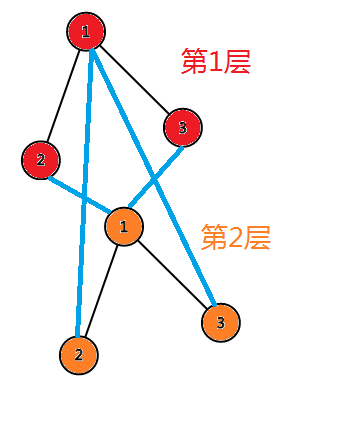
这里蓝边就是相邻层的边,黑边就是同一层之间的边。原图就是 ((1,2),(1,3)) 两条边。
Luogu P4568 [JLOI2011]飞行路线
给定一个图,每个图之间有边权,可以将 (k) 个边的边权改为 (0) ,求 (S) 到 (T) 的最短路。
其中 (2leq nleq 10^4,1leq mleq 5 imes 10^4,0leq kleq 10)
可以把这个图分成 (k) 层的分层图,那么现在每个点和每条边代表什么意思呢?定义在第 (i) 层的节点为用了 (i) 次边权取 (0) 的节点,那么每个黑边在同一层图内走代表的就是没有使用边权取 (0), 而走蓝边就是代表把边权取 (0),然后走到下一层图(也就是代表使用了一次边权取 (0) 的操作)。
这个时候以第 (0) 层图的 (s) 为起点跑最短路,答案为每一层 (t) 的最短路的最小值。
(mathcal{Code})
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#define pp std::pair<int, int>
#define mp std::make_pair
#define fir first
#define sec second
const int N = 10010;
const int M = 50010;
const int K = 21;
const int INF = 0x7fffffff;
inline int Min(int x, int y) { return x < y ? x : y; }
inline int read() {
int r = 0; bool w = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-') w = 1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
r = (r << 3) + (r << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return w ? ~r + 1 : r;
}
int n, m, k, s, t, ans = INF;
int dis[N * K];
bool vis[N * K];
//Edge
int head[N * K], ent;
struct Node {
int next, to, val;
}e[2 * ((2 + K) * M + K)];
inline void add(int x, int y, int z) {
e[++ent].to = y; e[ent].val = z; e[ent].next = head[x]; head[x] = ent;
}
std::priority_queue<pp>q;
void Dij() {
dis[s] = 0;
q.push(mp(-dis[s], s));
while(!q.empty()) {
int x = q.top().sec;
q.pop();
if(vis[x]) continue;
vis[x] = 1;
for(int i = head[x] ; i; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].to;
if(dis[v] > dis[x] + e[i].val) {
dis[v] = dis[x] + e[i].val;
if(!vis[v]) q.push(mp(-dis[v], v));
}
}
}
}
signed main() {
n = read(); m = read(); k = read(); s = read(); t = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
int x = read(), y = read(), z = read();
add(x, y, z); add(y, x, z);
for(int j = 1; j <= k; ++j) {
add(x + (j - 1) * n, y + j * n, 0);
add(y + (j - 1) * n, x + j * n, 0);
add(x + j * n, y + j * n, z);
add(y + j * n, x + j * n, z);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j <= k; ++j)
dis[i + j * n] = INF;
Dij();
for(int i = 0; i <= k; ++i) ans = Min(ans, dis[t + i * n]);
printf("%d
", ans);
return 0;
}
练习题目:
Luogu P2939[USACO09FEB]Revamping Trails G
Luogu P4822 [BJWC2012]冻结 参考代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#define pp std::pair<int, int>
#define mp std::make_pair
#define frist fsr
#define sec second
const int N = 501000;
int n, m, k;
inline int Min(int x, int y) { return x < y ? x : y; }
inline int read() {
int r = 0; bool w = 0; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-') w = 1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
r = (r << 3) + (r << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return w ? ~r + 1 : r;
}
int head[N], ent, dis[N];
bool vis[N];
struct Node {
int next, to, val;
}e[N << 1];
inline void add(int x, int y, int z) {
e[++ent].to = y; e[ent].next = head[x]; e[ent].val = z; head[x] = ent;
}
std::priority_queue<pp>q;
signed main() {
n = read(); m = read(); k = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
int x = read(), y = read(), z = read();
add(x, y, z); add(y, x, z);
for(int j = 1; j <= k; ++j) {
add(x + j * n, y + j * n, z);
add(y + j * n, x + j * n, z);
add(x + (j - 1) * n, y + j * n, z / 2);
add(y + (j - 1) * n, x + j * n, z / 2);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j <= k; ++j)
dis[i + j * n] = 0x7fffffff;
dis[1] = 0;
q.push(mp(0,1));
while(!q.empty()) {
int x = q.top().sec;q.pop();
if(vis[x]) continue;
vis[x] = 1;
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].to;
if(dis[v] > dis[x] + e[i].val) {
dis[v] = dis[x] + e[i].val;
if(!vis[v])
q.push(mp(-dis[v], v));
}
}
}
int ans = 0x7fffffff;
for(int i = 0; i <= k; ++i)
ans = Min(ans, dis[i * n + n]);
printf("%d
", ans);
return 0;
}