1、The Nomenclature of Selection Models
Diversifying selection(disruptive selection):a type of selection where two or more extreme phenotypic values are favoured simultaneously.This type of selection will often increase variability, and diversifying selection has, therefore, in the molecular evolution literature recently been used more generically to describe any type of selection that increases variability
neutrality test:A statistical method aimed at rejecting a model of neutral evolution is called a neutrality test.
SNP: single nucleotide polymorphism
Balancing selection: selection that increases variability within a population
Positive selection:selection acting upon new advantageous mutations
Negative selection: selection acting upon new deleterious mutation
Frequency spectrum: the allelic sample distribution in independent nucleotide sites
LD: linkage disequilibrium
Variance(方差):A measure of the amount of variation around a mean value
Genetic drift:The random fluctuations in allele frequencies over time that are due to chance alone.
Selective sweep:the process by which a new advantageous mutation eliminates or reduces variation in linked neutral sites as it increases in frequency in the population
In particular,we should be able to detect the molecular signatures of new, strongly selected advantageous mutations that have recently become fixed(reached a
frequency of one in the population).As these mutations increase in frequency, they tend to reduce variation in the neighboring region where neutral variants
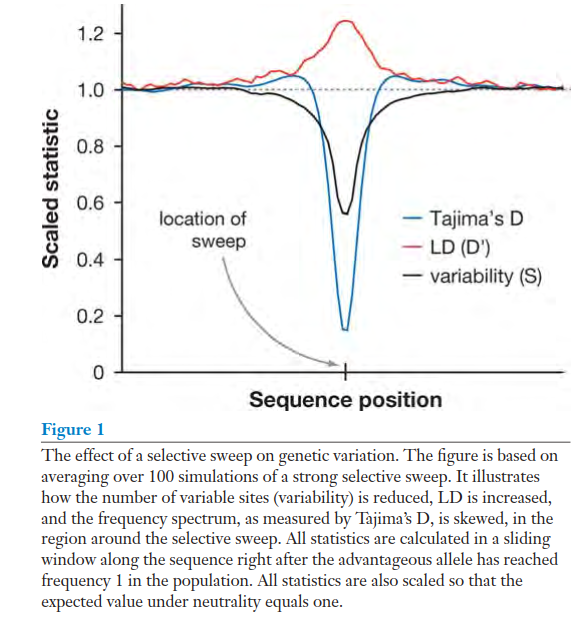
are segregating . This process, by which a selected mutation reduces variability in linked sites as it goes to fixation, is known as a selective sweep (Figure 1)。
The hope is that by analysis of large comparative genomic data sets and large SNP data sets we will be able to determine how and where both positive and
negative selective has affected variation in humans and other organisms.
2、population genetic signatures of selection
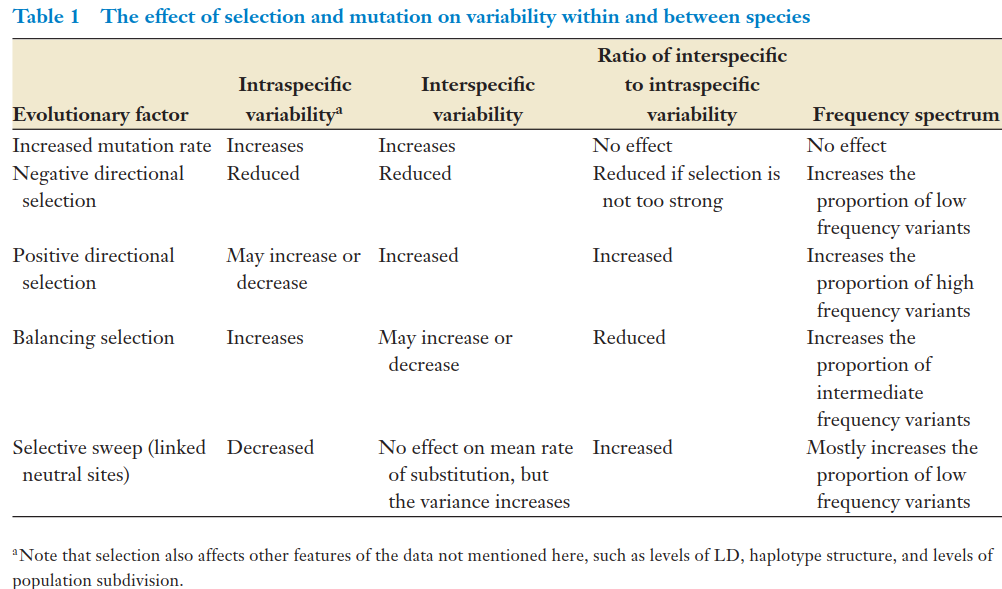
One of the main effects of selection is to modify the levels of variability within and between species(选择的主要影响是修饰了种内或种间的变异水平)。
selective sweep:tends to drastically reduce variation within a population, but will not lead to a reduction in species-specific differences.
Conversely, negative selection acting on multiple loci will tend to reduce variability between species more drastically then variability within species.
Note that changes in the mutation rate alone will have the same effect on interspecific (between-species) and intraspecific (within-species) variability.
However, selection affects intraspecific and interspecific variability differently. Many of the common population genetic methods for detecting selection
are therefore based on comparing variation with and between species, most famously the HKA test.
3、Population Differentiation
Selection may in many cases increase the degree of differentiation among populations. In particular, recent theory shows that a selective sweep can have a dramatic impact on the level of population subdivision, particularly when the sweep has not yet spread to all populations within a species 【1,2, 3】. When a locus shows extraordinary levels of genetic population differentiation, compared with other loci,this may then be interpreted as evidence for positive selection.
4、The Frequency Spectrum
1、The effects of local selection, balanced polymorphism and background selection on equilibrium patterns of genetic diversity in subdivided populations
2、Adapt globally, act locally: the effect of selective sweeps on bacterial sequence diversity
3、Genetic hitch-hiking in a subdivided population