1.什么是EL表达式
EL(Expression Language) 是为了使JSP写起来更加简单。表达式语言的灵感来自于 ECMAScript 和 XPath 表达式语言,它提供了在 JSP 中简化表达式的方法,让Jsp的代码更加简化。
2.语法:
${表达式}
其中, EL 表达式在输出 null 值的时候,输出的是空串。jsp 表达式脚本输出 null 值的时候,输出的是 null, 例如下面的例子

3.EL 表达式搜索域数据的顺序
EL 表达式主要是在 jsp 页面中输出域对象中的数据,当四个域中都有相同的 key 的数据的时候,EL 表达式会按照四个域从小到大去搜索,找到哪个就输出哪个,即按照PageContext、Request、Session 、application的顺序搜索
<body> <%
//往四个域中都保存了相同的 key 的数据。
request.setAttribute("key", "request"); session.setAttribute("key", "session"); application.setAttribute("key", "application"); pageContext.setAttribute("key", "pageContext"); %> ${ key } </body>
4.EL 表达式输出 Bean 的普通属性,数组属性。List 集合属性,map 集合属性
public Person(String name, int age, String[] hobby, List<String> nickname, Map<String, Integer> scores) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.hobby = hobby; this.nickname = nickname; this.scores = scores; }
<body> <% HashMap<String, Integer> score = new HashMap<>(); score.put("math", 100); score.put("english", 140); ArrayList<String> nickname = new ArrayList<>(); nickname.add("狗蛋"); nickname.add("狗剩"); String[] hobby = new String[]{"吃饭", "学习"}; Person person = new Person("小明", 25, hobby, nickname, score); pageContext.setAttribute("p", person); %> <h1>注意:本质是找bean类的get方法</h1> 输出 Person:${ p }<br/> 输出 Person 的 name 属性:${p.name} <br/> 输出 Person 的 age 属性:${p.age} <br/> 输出 Person 的 hobby 数组个别元素值(这里输出索引为1):${p.hobby[1]} <br/> 输出 Person 的 nickname 集合中的元素值:${p.nickname} <br/> 输出 Person 的 List 集合中个别元素值(这里输出索引为1):${p.nickname[1]} <br/> 输出 Person 的 Map 集合: ${p.scores} <br/> 输出 Person 的 Map 集合中某个key的值(这里输出key是english): ${p.scores.english} <br/> </body>
运行效果, 如下图所示:

5.EL 表达式——运算
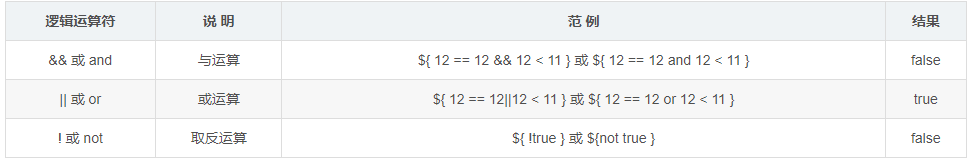
语法:${ 运算表达式 } , EL 表达式支持如下运算符:
(1)关系运算

(2)逻辑运算
(3)算数运算

(4) empty 运算
empty 运算可以判断一个数据是否为空,如果为空,则输出 true,不为空输出 false。
以下几种情况为空:
值为 null 值的时候,为空 值为空串的时候,为空 值是 Object 类型数组,长度为零的时候 list 集合,元素个数为零 map 集合,元素个数为零
<body> <% // 1、值为 null 值的时候,为空 request.setAttribute("emptyNull", null); // 2、值为空串的时候,为空 request.setAttribute("emptyStr", ""); // 3、值是 Object 类型数组,长度为零的时候 request.setAttribute("emptyArr", new Object[]{}); // 4、list 集合,元素个数为零 List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); // list.add("abc"); request.setAttribute("emptyList", list); // 5、map 集合,元素个数为零 Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); // map.put("key1", "value1"); request.setAttribute("emptyMap", map); %> ${ empty emptyNull } <br/> ${ empty emptyStr } <br/> ${ empty emptyArr } <br/> ${ empty emptyList } <br/> ${ empty emptyMap } <br/> </body>
(5)三元运算
表达式 1?表达式 2:表达式 3
如果表达式 1 的值为真,返回表达式 2 的值,如果表达式 1 的值为假,返回表达式 3 的值
${ 12 != 12 ? "哈哈":"哦哦" }
(6) “ . ”点运算 和 [ ] 中括号运算符
. 点运算,可以输出 Bean 对象中某个属性的值。
[ ]中括号运算,可以输出有序集合中某个元素的值。
并且[]中括号运算,还可以输出 map 集合中 key 里含有特殊字符的 key 的值。
<body> <% Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("a.a.a", "aaaValue"); map.put("b+b+b", "bbbValue"); map.put("c-c-c", "cccValue"); request.setAttribute("map", map); %> ${ map['a.a.a'] } <br> ${ map["b+b+b"] } <br> ${ map['c-c-c'] } <br> </body>
此处[" "]和[’ ']都可以
6.EL 表达式的 11 个隐含对象 (此处是重中之重)
(1)EL 个达式中 11 个隐含对象,是 EL 表达式中自己定义的,可以直接使用。
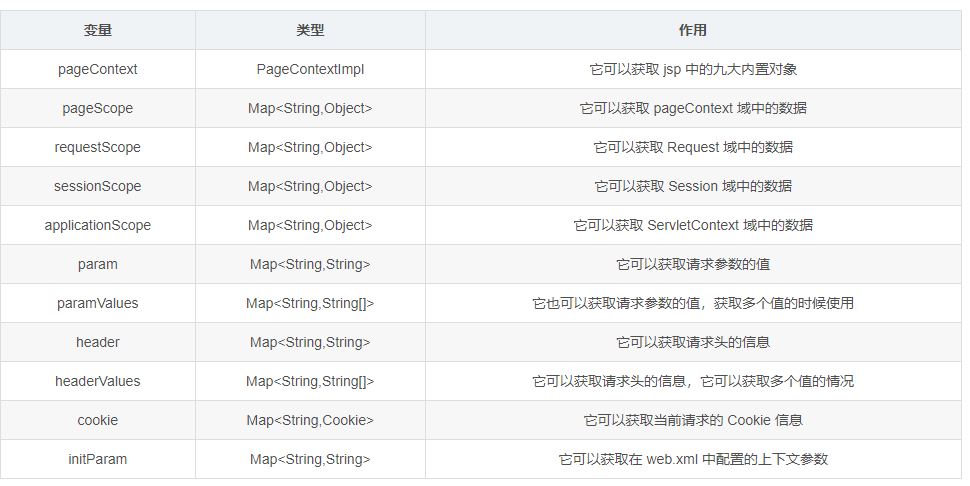
(2)EL 获取四个特定域中的属性
pageScope ====== pageContext 域
requestScope ====== Request 域
sessionScope ====== Session 域
applicationScope ====== ServletContext 域
<body> <% pageContext.setAttribute("key1", "pageContext1"); pageContext.setAttribute("key2", "pageContext2"); request.setAttribute("key2", "request"); session.setAttribute("key2", "session"); application.setAttribute("key2", "application"); %> ${ applicationScope.key2 } </body>
(3) pageContext 对象的使用
1 协议:request.getScheme() 2 服务器 ip:request.getServerName() 3 服务器端口:request.getServerPort() 4 获取工程路径:getContextPath() (常用) 5 获取请求方式:request.getMethod() 6 获取客户端 ip 地址:request.getRemoteHost() 7 获取会话的 id 编号:session.getId()
(4)EL 表达式其他隐含对象的使用
param Map<String,String> 它可以获取请求参数的值
paramValues Map<String,String[]> 它也可以获取请求参数的值,获取多个值的时候使用
1 输出请求参数 username 的值:${ param.username } <br> 2 输出请求参数 password 的值:${ param.password } <br/> 3 输出请求参数 username 的值:${ paramValues.username[0] } <br/> 4 输出请求参数 hobby 的值:${ paramValues.hobby[0] } <br> 5 输出请求参数 hobby 的值:${ paramValues.hobby[1] } <br/>
header Map<String,String> 它可以获取请求头的信息
headerValues Map<String,String[]> 它可以获取请求头的信息,它可以获取多个值的情况
1 输出请求头【User-Agent】的值(如上5.6所写,key中含有特殊符号,需要使用['']或[""]包起来,下同):${ header['User-Agent'] } <br> 2 输出请求头【Connection】的值:${ header.Connection } <br> 3 输出请求头【User-Agent】的值:${ headerValues['User-Agent'][0] } <br
cookie Map<String,Cookie> 它可以获取当前请求的 Cookie 信息
获取 Cookie 的名称:${ cookie.JSESSIONID.name } <br>
获取 Cookie 的值:${ cookie.JSESSIONID.value } <br
initParam Map<String,String> 它可以获取在 web.xml 中配置的上下文参数
web.xml 中的配置:
<context-param> <param-name>username</param-name> <param-value>root</param-value> </context-param> <context-param> <param-name>url</param-name> <param-value>jdbc:mysql:///test</param-value> </context-param>
示例代码:
输出: Context-param;username 的值:${ initParam.username } <br>
输出: Context-param;url 的值:${ initParam.url } <br/>
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------分割线-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
servlet中的三大作用域对象 、 jsp中的四大作用域对象和九大内置对象 、 el表达式中的三大作用域对象对比: (别记混了)



