本篇体验LINQ的各种查询运算符。
先创建一个泛型方法,用来显示查询结果:
private static void DisplayQuery<T>(IEnumerable<T> query)
{
foreach (T item in query)
{
//Console.WriteLine(item.ToString());
Console.Write(item.ToString() + " ");
}
}
对一个集合进行操作
□ Where()对一个序列操作
● 使用Where<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> , Func<TSource, bool>):
List<int> list = new List<int>()
{
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8
};
IEnumerable<int> query = list.Where(x => x > 5);
DisplayQuery<int>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
结果:6 7 8
● 使用Where<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>,Func<TSource, int, bool>),根据数据源和元素索引返回值:
List<int> list = new List<int>()
{
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8
};
IEnumerable<int> query = list.Where((x,index) => index>=1 && x<=3);
DisplayQuery<int>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
结果:2 3
□ OfType()对一个序列操作
● OfType()是对非泛型IEnumerable的扩展,所以先确定集合类型后,才可以用该方法。
● OfType()的返回类型是IEnumerable<T>泛型,所以在使用OfType()之后,可以继续链式使用其它操作符。
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.Add(1);
list.Add(DateTime.Now);
list.Add("spriing is coming");
list.Add("enjoy your day");
var query = list.OfType<string>().Where(x => x.StartsWith("enjoy"));
DisplayQuery<string>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
结果: enjoy your day
□ Cast()将非泛型序列转换成泛型序列
● 对于一个非泛型集合,就不能使用LINQ操作符:
● 使用Cast()可以将非泛型集合转换成泛型集合:
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.Add("super star");
list.Add("good day");
var query = list.Cast<string>().Where(x => x.StartsWith("good"));
DisplayQuery<string>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
结果:good day
□ OrderBy(), ThenBy(),OrderByDescending(),ThenByDescending()
关于产品和分类:
public class Category
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
public class Product
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public Category Category { get; set; }
public DateTime BuyDate { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
public override string ToString()
{
return String.Format("编号:{0},名称:{1},类别:{2},购买时间:{3},价格:{4}", Id, Name, Category.Name, BuyDate, Price);
}
}
public static class ProductHelper
{
public static IEnumerable<Product> GetProducts()
{
Category category1 = new Category();
category1.Id = 1;
category1.Name = "数码电子";
Category category2 = new Category();
category2.Id = 2;
category2.Name = "服饰类";
return new List<Product>()
{
new Product(){Id = 1,BuyDate = new DateTime(2012,1,1),Category = category1,Name = "数码相机",Price = 800m},
new Product(){Id = 2,BuyDate = new DateTime(2012,1,3),Category = category1,Name = "录像机",Price = 900m},
new Product(){Id = 3,BuyDate = new DateTime(2012,1,2),Category = category2,Name = "体恤衫",Price = 300m},
new Product(){Id = 4,BuyDate = new DateTime(2012,1,8),Category = category2,Name = "茄克衫",Price = 600m}
};
}
}
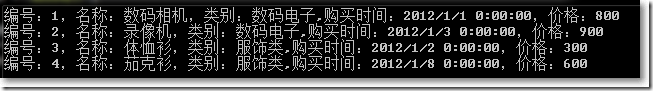
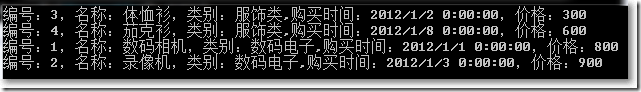
● OrderBy()对某个属性排序:
var query = ProductHelper.GetProducts().OrderBy(x => x.Id);
DisplayQuery<Product>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
● OrderBy()对属性的计算值排序:
var query = ProductHelper.GetProducts().OrderBy(x => x.BuyDate.Date);
DisplayQuery<Product>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
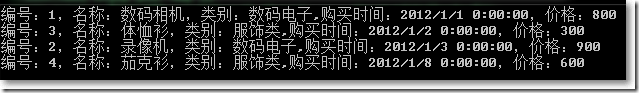
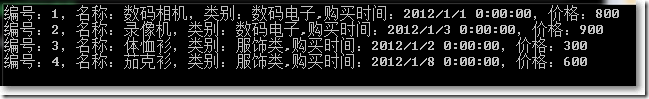
● OrderBy()组合ThenBy()链式排序:
var query = ProductHelper.GetProducts().OrderByDescending(x => x.Category.Id).ThenBy(x => x.Price);
DisplayQuery<Product>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
注意:ThenBy()是针对IOrderedEnumerable<T>的扩展,因此不能直接在IEnumerable<T>泛型集合使用ThenBy()。
● OrderyBy()接收IComparer<T>接口类型。
创建实现IComparer<T>接口的、针对Product的比较类:
public class ProductComparer : IComparer<Product>, IEqualityComparer<Product>
{
public int Compare(Product x, Product y)
{
if (x == y)//如果类别名称相同就比较产品价格
{
return x.Price.CompareTo(y.Price);
}
else //如果类别名称不同,比较类别的编号
{
return x.Category.Id.CompareTo(y.Category.Id);
}
}
public bool Equals(Product x, Product y)
{
if (x.Category.Name == y.Category.Name)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
public int GetHashCode(Product obj)
{
return obj.GetHashCode();
}
}
主程序:
var query = ProductHelper.GetProducts().OrderBy(x => x, new ProductComparer());
DisplayQuery<Product>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
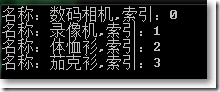
□ Select()投影
var query = ProductHelper.GetProducts().Select((x, index) => new {Name = x.Name, Index = index});
foreach (var item in query)
{
Console.WriteLine("名称:{0},索引:{1}",item.Name,item.Index);
}
Console.ReadKey();
在ASP.NET MVC中,经常需要填充下拉框,可以用Select()投影出IEnumerable<SelectListItem>集合:
list.Select(x => new SelectListItem{Text = x.Name, Value = x.Code});
□ Take()和Skip()
List<int> list = new List<int>()
{
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8
};
var query = list.Skip(7).Take(1);
DisplayQuery<int>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
结果:8
□ TakeWhile()和SkipWhile()
● TakeWhile()在遇到不符合条件的元素时,就停止在集合中的遍历,而Where在遇到不符合条件的元素时,会继续遍历直到结束。
int[] array = {1, 2, 10, 5, 6};
var query = array.TakeWhile(x => x <= 5);
DisplayQuery<int>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
结果: 1 2
● SkipWhile()会跳过符合条件的元素,直到遇到第一个不符合条件的元素,把该元素以及后面的元素返回。
int[] array = {1, 2, 10, 5, 6};
var query = array.SkipWhile(x => x <= 5);
DisplayQuery<int>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
结果: 10 5 6
□ Reverse()反转元素排列
int[] arr = {1, 2};
var query = arr.Reverse();
DisplayQuery<int>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
结果: 2 1
□ DefaultIfEmpty()针对集合为空的处理
● 如果是空的整型集合,默认返回0
int[] array = {};
var query = array.DefaultIfEmpty();
DisplayQuery<int>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
结果: 0
● 为空的整型指定默认值
int[] array = { };
var query = array.DefaultIfEmpty(100);
DisplayQuery<int>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
结果: 100
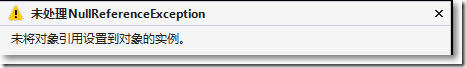
● 如果是空的类类型,默认值是null,不指定默认值会抛异常
Product[] arraryProducts = {};
var query = arraryProducts.DefaultIfEmpty();
DisplayQuery<Product>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
● 为空的类类型指定默认值
Product[] arraryProducts = { };
Category category = new Category();
category.Id = 1;
category.Name = "酒类";
var query = arraryProducts.DefaultIfEmpty(new Product(){Id = 1,BuyDate = DateTime.Now,Category = category,Name = "贵州茅台",Price = 200m});
DisplayQuery<Product>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
□ Distinct()剔除重复元素
● 剔除重复的整型
int[] array = {1, 2, 2};
var query = array.Distinct();
DisplayQuery<int>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
结果:1 2
● 自定义剔除规则
public class Category
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public override string ToString()
{
return String.Format("编号:{0},名称:{1}", Id, Name);
}
}
public static class CategoryHelper
{
public static IEnumerable<Category> GetCategories()
{
return new List<Category>()
{
new Category(){Id = 1,Name = "烟类"},
new Category(){Id = 2,Name = "烟类"},
new Category(){Id = 3,Name = "酒类"}
};
}
}
public class CategoryComparer : IEqualityComparer<Category>
{
public bool Equals(Category x, Category y)
{
return x.Name == y.Name;
}
public int GetHashCode(Category obj)
{
return obj.Name.GetHashCode();
}
}
主程序:
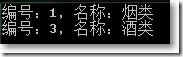
IEqualityComparer<Category> customComparer = new CategoryComparer();
var query = CategoryHelper.GetCategories().Distinct(customComparer);
DisplayQuery<Category>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
注意:
public int GetHashCode(Category obj)方法中,一定要返回所比较属性的哈希值。
● 写一个适合于任何类、任何属性的泛型方法
public class PropertyComparer<T> : IEqualityComparer<T>
{
//需要比较的属性的PropertyInfo
private PropertyInfo _PropertyInfo;
//通过构造函数把需要比较的属性传进来
public PropertyComparer(string propertyName)
{
_PropertyInfo = typeof (T).GetProperty(propertyName,
BindingFlags.GetProperty | BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public);
if (_PropertyInfo == null)
{
throw new ArgumentException(string.Format("{0} 不是{1}的属性",propertyName,typeof(T)));
}
}
public bool Equals(T x, T y)
{
object xValue = _PropertyInfo.GetValue(x, null);
object yValue = _PropertyInfo.GetValue(y, null);
//如果xValue的属性值为null,那yValue的属性值也必须是null,才返回true
if (xValue == null)
return yValue == null;
return xValue.Equals(yValue);
}
public int GetHashCode(T obj)
{
object propertyValue = _PropertyInfo.GetValue(obj, null);
if (propertyValue == null)
return 0;
else
{
return propertyValue.GetHashCode();
}
}
}
主程序:
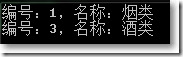
IEqualityComparer<Category> customComparer = new PropertyComparer<Category>("Name");
var query = CategoryHelper.GetCategories().Distinct(customComparer);
DisplayQuery<Category>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
□ GroupBy()
public class Category
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public override string ToString()
{
return String.Format("编号:{0},名称:{1}", Id, Name);
}
}
public static class CategoryHelper
{
public static IEnumerable<Category> GetCategories()
{
return new List<Category>()
{
new Category(){Id = 1,Name = "烟类"},
new Category(){Id = 2,Name = "烟类"},
new Category(){Id = 3,Name = "酒类"}
};
}
}
● 通常用法
主程序:
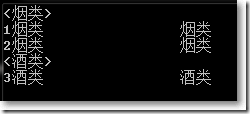
IEnumerable<IGrouping<string,Category>> query = CategoryHelper.GetCategories().GroupBy(x => x.Name);
foreach (var item in query)
{
Console.WriteLine("<{0}>",item.Key);
foreach (var p in item)
{
Console.WriteLine(p.ToString());
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
GroupBy()的返回类型是IGrouping<TKey,TSource>的集合,该接口只提供了一个Key属性,也就是用来分组的属性值。
public interface IGrouping<out TKey,out TElement>
{
TKey Key { get; }
}
● 投影
var query = CategoryHelper.GetCategories()
.GroupBy(x => x.Name, x => new {Text = x.Id + x.Name, Value = x.Name});
foreach (var item in query)
{
Console.WriteLine("<{0}>", item.Key);
foreach (var p in item)
{
Console.WriteLine(p.Text.PadRight(20) + p.Value);
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
对多个集合进行操作
□ Intersect()获取2个集合的交集
int[] arr1 = {0, 1, 2,3};
int[] arr2 = {2, 3, 4};
var query = arr1.Intersect(arr2);
DisplayQuery<int>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
结果: 2 3
□ Except()获取第一个集合中有,而第二个集合中没有的元素
int[] arr1 = {0, 1, 2,3};
int[] arr2 = {2, 3, 4};
var query = arr1.Except(arr2);
DisplayQuery<int>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
结果:0 1
□ Concat()将2个集合串联起来,不剔除重复元素
int[] arr1 = { 1, 2 };
int[] arr2 = { 2, 3 };
var query = arr1.Concat(arr2);
DisplayQuery<int>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
结果:1 2 2 3
□ Union()将2个集合串联起来,剔除重复元素
int[] arr1 = { 1, 2 };
int[] arr2 = { 2, 3 };
var query = arr1.Union(arr2);
DisplayQuery<int>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
结果:1 2 3
□ Zip()合并2个集合中位置相同的元素,将2个元素的操作结果返回一个新的元素。如果两个集合的长度不相等,以长度短的为准。
int[] arr1 = {1, 2};
string[] arr2 = {"星期一", "星期二", "星期三"};
var query = arr1.Zip(arr2, (x, y) => String.Format("{0},{1}", x, y));
DisplayQuery<string>(query);
Console.ReadKey();
总结
● 一般性的条件筛选:Where()
● 返回具体的集合类型再进行链式操作:OfType()
● 非泛型集合转换成泛型集合后再使用LINQ操作符:Cast()
● 排序、链式排序:OrderBy(), ThenBy(),实现IComparer<T>接口可以自定义排序规则
● 投影:Select()
● 返回前N个,跳过N个,分页:Take()和Skip()
● 返回符合/不符合条件,但不执行完遍历:TakeWhile()和SkipWhile()
● 反转集合元素:Reverse()
● 空集合处理:DefaultIfEmpty()
● 剔除集合中的重复元素:Distinct(),实现IEqualityComparer<Category>可自定义相等规则,针对某具体类或写一个泛型方法
● 分组以及分组后投影:GroupBy()
● 2个集合的交集:Intersect()
● 2个集合的查集:Except()
● 2个集合的串联:Concat()和Union()
● 2个集合的合并:Zip()
参考资料:
※ 《.NET之美》--张子阳,感谢写了这么好的书!
※ A Generic IEqualityComparer for Linq Distinct()