文章目录
在前面两篇文章中,我们已经对ApplicationContext的大部分内容做了介绍,包括国际化,Spring中的运行环境,Spring中的资源,Spring中的事件监听机制,还剩唯一一个BeanFactory相关的内容没有介绍,这篇文章我们就来介绍BeanFactory,这篇文章结束,关于ApplicationContext相关的内容我们也总算可以告一段落了。本文对应官网中的
1.16及1.15小结
前面我们也提到了ApplicationContext继承了BeanFactory接口,其继承关系如下:
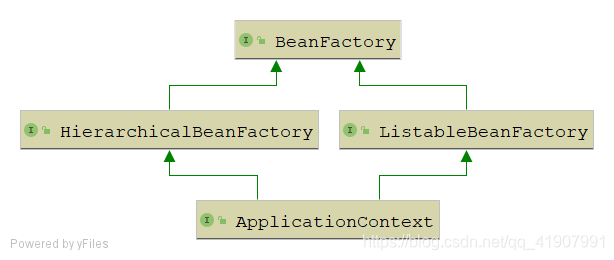
下面我们直接进入BeanFactory相关内容的学习
BeanFactory
接口定义
public interface BeanFactory {
// FactroyBean的前缀,如果getBean的时候BeanName有这个前缀,会去获取对应的FactroyBean
// 而不是获取FactroyBean的getObject返回的Bean
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
// 都是用于获取指定的Bean,根据名称获取指定类型获取
Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException;
// 获取指定的Bean的ObjectProvider,这个有个问题,ObjectProvider是什么?请参考我《Spring杂谈》相关文章
<T> ObjectProvider<T> getBeanProvider(Class<T> requiredType);
<T> ObjectProvider<T> getBeanProvider(ResolvableType requiredType);
// 检查容器中是否含有这个名称的Bean
boolean containsBean(String name);
// 判断指定的Bean是否为单例
boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
// 判断指定的Bean是否为原型
boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
// 判断指定的Bean类型是否匹配,关于ResolvableType我已经专门写文章介绍过了,请参考我《Spring杂谈》相关文章
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, Class<?> typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
// 返回指定Bean的类型
Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
// 返回指定Bean的别名
String[] getAliases(String name);
}
可以看到
BeanFactory接口主要提供了查找Bean,创建Bean(在getBean调用的时候也会去创建Bean),以及针对容器中的Bean做一些判断的方法(包括是否是原型,是否是单例,容器是否包含这个名称的Bean,是否类型匹配等等)
继承关系
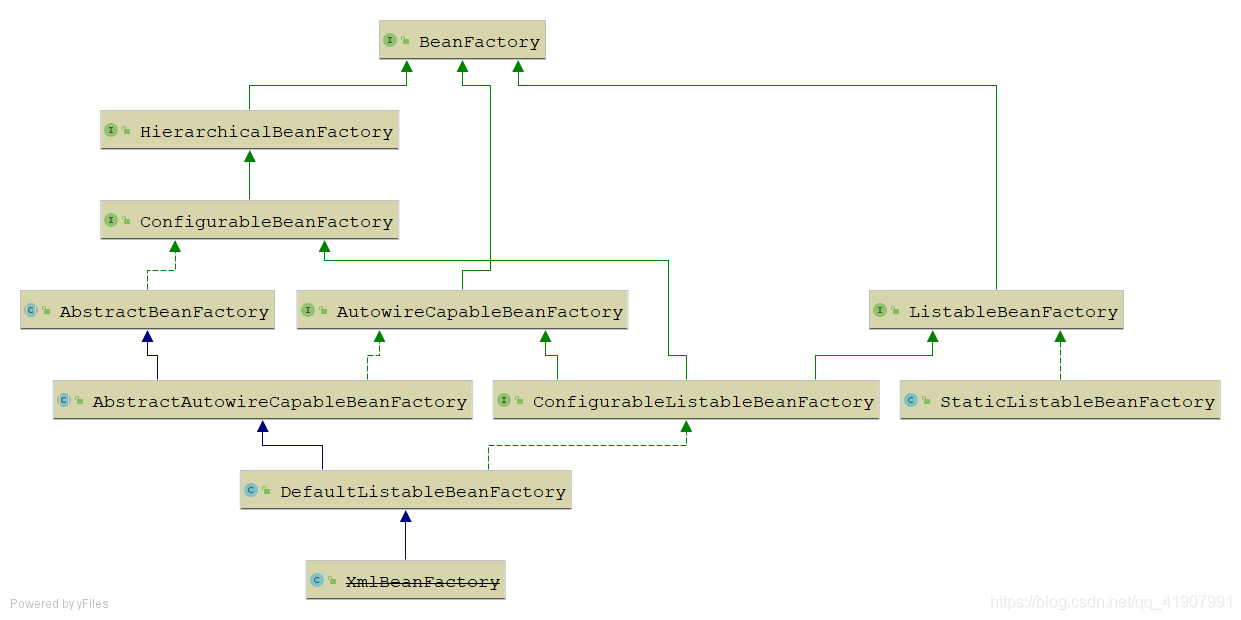
接口功能
作为BeanFactory的直接子接口的有三个,分别是HierarchicalBeanFactory,ListableBeanFactory,AutowireCapableBeanFactory。
1、HierarchicalBeanFactory
public interface HierarchicalBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
// 获取父容器
@Nullable
BeanFactory getParentBeanFactory();
// 获取父系容器,只在当前容器中判断是否包含这个名称的Bean
boolean containsLocalBean(String name);
}
HierarchicalBeanFactory对顶层的BeanFactory做了扩展,让其具有了父子层级关系
2、ListableBeanFactory
public interface ListableBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
// 1.查找容器中是否包含对应名称的BeanDefinition
// 2.忽略层级关系,只在当前容器中查找
boolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName);
// 1.查找容器中包含的BeanDefinition的数量
// 2.忽略层级关系,只在当前容器中查找
int getBeanDefinitionCount();
// 1.获取当前容器中所有的BeanDefinition的名称
// 2.忽略层级关系,只在当前容器中查找
String[] getBeanDefinitionNames();
// 根据指定类型获取容器中的对应的Bean的名称,可能会有多个
// 既会通过BeanDefinition做判断,也会通过FactoryBean的getObjectType方法判断
String[] getBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType type);
String[] getBeanNamesForType(@Nullable Class<?> type);
// 根据指定类型获取容器中的对应的Bean的名称,可能会有多个
// 既会通过BeanDefinition做判断,也会通过FactoryBean的getObjectType方法判断
// includeNonSingletons:是否能包含非单例的Bean
// allowEagerInit:是否允许对”懒加载"的Bean进行实例化,这里主要针对FactoryBean,因为FactoryBean
// 默认是懒加载的,为了推断它的类型可能会进行初始化。
String[] getBeanNamesForType(@Nullable Class<?> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit);
// 获取指定类型的Bean,返回一个map,key为bean的名称,value为对应的Bean
<T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(@Nullable Class<T> type) throws BeansException;
// 获取指定类型的Bean,返回一个map,key为bean的名称,value为对应的Bean
// includeNonSingletons:是否能包含非单例的Bean
// allowEagerInit:是否允许对”懒加载"的Bean进行实例化,这里主要针对FactoryBean,因为FactoryBean
// 默认是懒加载的,为了推断它的类型可能会进行初始化。
<T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(@Nullable Class<T> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit)
throws BeansException;
// 获取添加了指定注解的Bean的名称
// 为了确定类型,会对FactoryBean所创建的Bean进行实例化
String[] getBeanNamesForAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType);
// 获取添加了指定注解的Bean的名称
// 为了确定类型,会对FactoryBean所创建的Bean进行实例化
// 返回一个map,key为bean的名称,value为对应的Bean
Map<String, Object> getBeansWithAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType) throws BeansException;
// 查询指定的Bean上的指定类型的注解,如果没有这个Bean会抛出NoSuchBeanDefinitionException
// 如果指定Bean上不存在这个注解,会从其父类上查找
@Nullable
<A extends Annotation> A findAnnotationOnBean(String beanName, Class<A> annotationType)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
}
从上面的方法中可以看出,相对于BeanFactory,ListableBeanFactory提供了批量获取Bean的方法。
3、AutowireCapableBeanFactory
public interface AutowireCapableBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
// 自动注入下的四种模型,如果有疑问请参考之前的文章《自动注入与精确注入》
int AUTOWIRE_NO = 0;
int AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME = 1;
int AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE = 2;
int AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR = 3;
// 已经过时了,不考虑
@Deprecated
int AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT = 4;
//该属性是一种约定俗成的用法:以类全限定名+.ORIGINAL 作为Bean Name,用于告诉Spring,在初始化的时候,需要返回原始给定实例,而别返回代理对象
String ORIGINAL_INSTANCE_SUFFIX = ".ORIGINAL";
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 下面这三个方法通常用于创建跟填充Bean(对Bean进行属性注入),但是请注意,直接采用下面这些方法创建或者装 // 配的Bean不被Spring容器所管理
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 用指定的class创建一个Bean,这个Bean会经过属性注入,并且会执行相关的后置处理器,但是并不会放入 // Spring容器中
<T> T createBean(Class<T> beanClass) throws BeansException;
// 为指定的一个对象完成属性注入,这个对象可以不被容器管理,可以是一个Spring容器外部的对象
// 主要调用populateBean
void autowireBean(Object existingBean) throws BeansException;
// 配置参数中指定的bean
// beanName表示在Bean定义中的名称。
// populateBean和initializeBean都会被调用
// existingBean:需要被配置的Bean
// beanName:对应的Bean的名称
Object configureBean(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 下面这一系列方法主要为了更细粒度的操纵Bean的生命周期
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 支持以给定的注入模型跟依赖检查级别创建,注入Bean。关于注入模型我这里就不想再说了
// 依赖检查的级别如下:
// 1.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE = 0,代表不进行依赖检查
// 2.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_SIMPLE = 2,代表对基本数据类的字段做检查。如果一个int类型的字段没有被赋值,那么会抛出异常
// 3.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_ALL = 3,对引用类型的字段做检查。如果一个Object类型的字段没有被赋值,那么会抛出异常
Object createBean(Class<?> beanClass, int autowireMode, boolean dependencyCheck) throws BeansException;
Object autowire(Class<?> beanClass, int autowireMode, boolean dependencyCheck) throws BeansException;
void autowireBeanProperties(Object existingBean, int autowireMode, boolean dependencyCheck)
throws BeansException;
//就是把Bean定义信息里面的一些东西,赋值到已经存在的Bean里面
void applyBeanPropertyValues(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
// 初始化Bean,执行初始化回调,及下面两个后置处理器中的方法
Object initializeBean(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
// 调用对应的两个后置处理器
Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException;
Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException;
// 执行销毁相关的回调方法
void destroyBean(Object existingBean);
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 关于注入点的相关方法
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 查找唯一符合指定类的实例,如果有,则返回实例的名字和实例本身
// 底层依赖于:BeanFactory中的getBean(Class)方法
<T> NamedBeanHolder<T> resolveNamedBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
// DependencyDescriptor:依赖名描述符,描述了依赖的相关情况,比如存在于哪个类,哪个字段,什么类型
// 查找指定名称,指定类型的Bean
// 底层依赖于:BeanFactory中的getBean(name,Class)方法
Object resolveBeanByName(String name, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) throws BeansException;
// 解析指定的依赖。就是根据依赖描述符的定义在容器中查找符合要求的Bean
@Nullable
Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName) throws BeansException;
//descriptor 依赖描述 (field/method/constructor)
//requestingBeanName 依赖描述所属的Bean
//autowiredBeanNames 与指定Bean有依赖关系的Bean的名称
//typeConverter 用以转换数组和连表的转换器
//备注:结果可能为null,毕竟容器中可能不存在这个依赖嘛~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
@Nullable
Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException;
}
可以看到这个类中的方法都跟装配Bean,配置Bean相关,另外还有一系列专门处理注入点的方法。可以看到接口有一个很大的作用就是对于一些不受Spring管理的Bean,也能为其提供依赖注入的功能。例如:
// DmzService没有被放入容器中
public class DmzService {
@Autowired
IndexService indexService;
public void test(){
System.out.println(indexService);
}
}
// 被容器所管理
@Component
public class IndexService {
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);
AutowireCapableBeanFactory beanFactory = ac.getBeanFactory();
DmzService bean = beanFactory.createBean(DmzService.class);
// 打印:com.dmz.official.beanfactory.IndexService@6ad5c04e
bean.test();
// 抛出NoSuchBeanDefinitionException
// ac.getBean(DmzService.class);
}
}
在上面的例子中,DmzService没有被容器管理,所以在调用ac.getBean(DmzService.class);会抛出NoSuchBeanDefinitionException,但是我们可以看到,indexService被注入到了DmzService中。
4、ConfigurableBeanFactory
public interface ConfigurableBeanFactory extends HierarchicalBeanFactory, SingletonBeanRegistry {
// 单例及原型的常量
String SCOPE_SINGLETON = "singleton";
String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = "prototype";
// 设置父容器,父容器一旦被设置,不可改变
void setParentBeanFactory(BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws IllegalStateException;
// 为Bean设置指定的类加载器
void setBeanClassLoader(@Nullable ClassLoader beanClassLoader);
// 获取类型加载器,可能返回null,代表系统类加载器不可访问
@Nullable
ClassLoader getBeanClassLoader();
// 设置临时的类加载器,在进行类加载时期织入时会用到(loadTimeWeaver)
void setTempClassLoader(@Nullable ClassLoader tempClassLoader);
@Nullable
ClassLoader getTempClassLoader();
// 是否缓存Bean的元数据,默认是开启的
void setCacheBeanMetadata(boolean cacheBeanMetadata);
boolean isCacheBeanMetadata();
// 定义用于解析bean definition的表达式解析器
void setBeanExpressionResolver(@Nullable BeanExpressionResolver resolver);
@Nullable
BeanExpressionResolver getBeanExpressionResolver();
// 数据类型转换相关
void setConversionService(@Nullable ConversionService conversionService);
@Nullable
ConversionService getConversionService();
void addPropertyEditorRegistrar(PropertyEditorRegistrar registrar);
void registerCustomEditor(Class<?> requiredType, Class<? extends PropertyEditor> propertyEditorClass);
void copyRegisteredEditorsTo(PropertyEditorRegistry registry);
void setTypeConverter(TypeConverter typeConverter);
TypeConverter getTypeConverter();
// 值解析器,例如可以使用它来处理占位符
void addEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver valueResolver);
boolean hasEmbeddedValueResolver();
@Nullable
String resolveEmbeddedValue(String value);
// 添加后置处理器
void addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor);
int getBeanPostProcessorCount();
// 注册指定名称的Scope
void registerScope(String scopeName, Scope scope);
// 返回所有的注册的scope的名称
String[] getRegisteredScopeNames();
// 返回指定名称的已注册的scope
@Nullable
Scope getRegisteredScope(String scopeName);
AccessControlContext getAccessControlContext();
// 从另外一个容器中拷贝配置,不包含具体的bean的定义
void copyConfigurationFrom(ConfigurableBeanFactory otherFactory);
// 为Bean注册别名
void registerAlias(String beanName, String alias) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
// 解析别名
void resolveAliases(StringValueResolver valueResolver);
// 合并BeanDefinition,参考我之前的文章,《BeanDefinition下》
BeanDefinition getMergedBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
// 是否是一个FactoryBean
boolean isFactoryBean(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
// 循环依赖相关,标志一个Bean是否在创建中
void setCurrentlyInCreation(String beanName, boolean inCreation);
boolean isCurrentlyInCreation(String beanName);
//处理bean依赖问题
//注册一个依赖于指定bean的Bean
void registerDependentBean(String beanName, String dependentBeanName);
// 返回所有指定的Bean从属于哪些Bean
String[] getDependentBeans(String beanName);
// 返回指定名称的bean的所有依赖
String[] getDependenciesForBean(String beanName);
// 销毁Bean
void destroyBean(String beanName, Object beanInstance);
// 先从域中移除,然后再销毁
void destroyScopedBean(String beanName);
// 销毁所有单例
void destroySingletons();
}
可以看到这个接口继承了HierarchicalBeanFactory,并基于它扩展了非常多的方法。除了继承了HierarchicalBeanFactory,还继承了一个SingletonBeanRegistry,其接口定义如下:
public interface SingletonBeanRegistry {
//以指定的名字将给定Object注册到BeanFactory中。
//此接口相当于直接把Bean注册,所以都是准备好了的Bean。(动态的向容器里直接放置一个Bean)
//什么BeanPostProcessor、InitializingBean、afterPropertiesSet等都不会被执行的,销毁的时候也不会收到destroy的信息
void registerSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject);
//以Object的形式返回指定名字的Bean,如果仅仅还是只有Bean定义信息,这里不会反悔
// 需要注意的是:此方法不能直接通过别名获取Bean。若是别名,请通过BeanFactory的方法先获取到id
@Nullable
Object getSingleton(String beanName);
//是否包含此单例Bean(不支持通过别名查找)
boolean containsSingleton(String beanName);
// 得到容器内所有的单例Bean的名字们
String[] getSingletonNames();
int getSingletonCount();
// 获取当前这个注册表的互斥量(mutex),使用者通过该互斥量协同访问当前注册表
Object getSingletonMutex();
}
从上面可以看到,SingletonBeanRegistry主要是实现了对容器中单例池的管理。
5、ConfigurableListableBeanFactory
// 所有接口的集大成者,拥有上面所有接口的功能
public interface ConfigurableListableBeanFactory
extends ListableBeanFactory, AutowireCapableBeanFactory, ConfigurableBeanFactory {
// 自动装配的模式下,忽略这个类型的依赖
void ignoreDependencyType(Class<?> type);
//自动装配的模式下,忽略这个接口类型的依赖
void ignoreDependencyInterface(Class<?> ifc);
// 注入一个指定类型的依赖。这个方法设计的目的主要是为了让容器中的Bean能依赖一个不被容器管理的Bean
void registerResolvableDependency(Class<?> dependencyType, @Nullable Object autowiredValue);
// 判断指定名称的Bean能否被注入到指定的依赖中
boolean isAutowireCandidate(String beanName, DependencyDescriptor descriptor)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
// 获取指定的BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
// 获取包含了所有的Bean的名称的迭代器
Iterator<String> getBeanNamesIterator();
// 清理元数据的缓存
void clearMetadataCache();
// 冻结所有的Bean配置
void freezeConfiguration();
boolean isConfigurationFrozen();
// 实例化当前所有的剩下的单实例
void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException;
}
6、AbstractBeanFactory
public abstract class AbstractBeanFactory extends FactoryBeanRegistrySupport implements ConfigurableBeanFactory {
//... 实现了大部分的方法,其中最终的实现为getBean()/doGetBean()方法的实现,提供了模版。其实createBean抽象方法,还是子类去实现的
//... isSingleton(String name) / isPrototype(String name) / containsBean(String name) 也能实现精准的判断了
// ===其中,它自己提供了三个抽象方法,子类必要去实现的===
// 效果同:ListableBeanFactory#containsBeanDefinition 实现类:DefaultListableBeanFactory
protected abstract boolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName);
// 效果同:ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#getBeanDefinition 实现类:DefaultListableBeanFactory
protected abstract BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws BeansException;
// 创建Bean的复杂逻辑,子类去实现。(子类:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory)
protected abstract Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException;
}
7、AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
public abstract class AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory extends AbstractBeanFactory
implements AutowireCapableBeanFactory {
......
// 1.实现了AbstractBeanFactory中的createBean方法,能够创建一个完全的Bean
// 2.实现了AutowireCapableBeanFactory,能对Bean进行实例化,属性注入,已经细粒度的生命周期管理
}
8、DefaultListableBeanFactory
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable {
.....
// 没什么好说的了,最牛逼的一个BeanFactory,拥有上面的一切功能,额外的它实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,具备注册管理BeanDefinition的功能
}
ApplicationContext体系汇总
ApplicationContext整体可以分为两个体系,一个就是web体系,另外一个就是非web体系。
非web体系
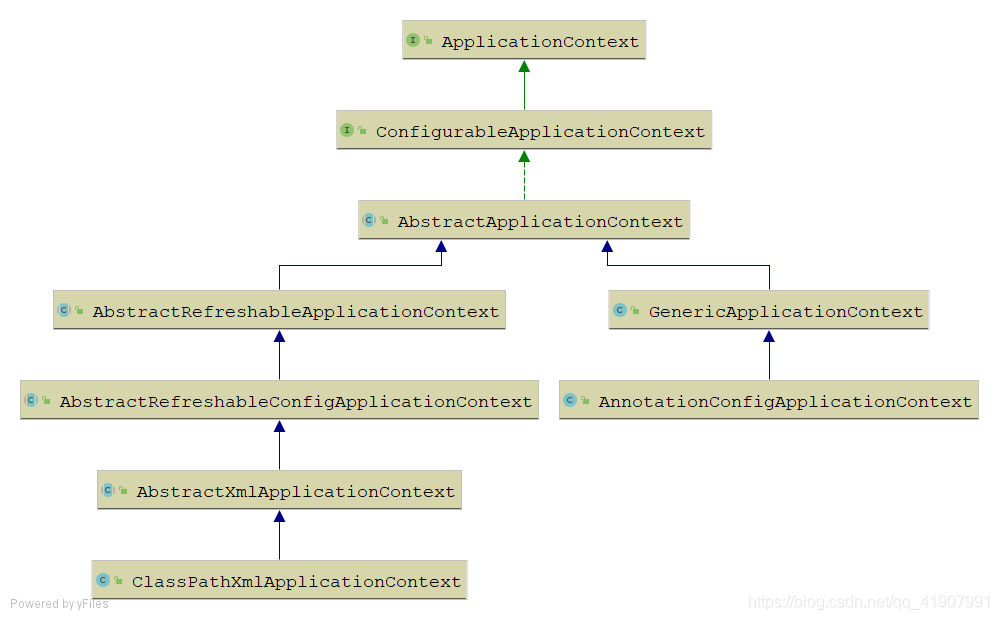
1、ConfigurableApplicationContext
ApplicationContext接口中的方法比较简单,之前我们也一一分析它继承的接口以及它所具有的功能。并且ApplicationContext接口的方法都是只读的,不能对当前的容器做任何改变。而ConfigurableApplicationContext接口在ApplicationContext的基础上增加了很多进行配置的方法,比如添加事件监听器,添加后置处理器等等。
public interface ConfigurableApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext, Lifecycle, Closeable {
// 配置路径的分隔符
String CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS = ",;
";
String CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME = "conversionService";
String LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME = "loadTimeWeaver";
String ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME = "environment";
String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME = "systemProperties";
String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
//设置此应用程序上下文的唯一ID。
void setId(String id);
//设置父容器,设置后不能再改了
void setParent(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent);
//设置environment 此处为ConfigurableEnvironment 也是可以配置的应用上下文
void setEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment);
// 此处修改父类返回值为ConfigurableEnvironment
@Override
ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment();
//添加一个新的BeanFactoryPostProcessor(refresh()的时候会调用的)
void addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor);
// 添加一个事件监听器
void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener);
// 注册协议处理器 允许处理额外的资源协议
void addProtocolResolver(ProtocolResolver resolver);
//加载或刷新配置的持久表示 最最最重要的一个方法
//表示可以是xml、可以是注解、可以是外部资源文件等等。。。。
// 这个方法执行完成后,所有的单例Bean都已经被实例化,Bean工厂肯定也就被创建好了
void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
//JVM运行时注册一个关闭挂钩,在关闭JVM时关闭此上下文,除非此时已经关闭
void registerShutdownHook();
//关闭此应用程序上下文,释放实现可能持有的所有资源和锁 包括一些销毁、释放资源操作
@Override
void close();
//标识上下文是否激活 refresh()后就会激活
boolean isActive();
// 返回此上下文内部的Bean工厂,可以用来访问底层工厂的特定功能。通过此工厂可以设置和验证所需的属性、自定义转换服务
// 备注:父类方法为获得AutowireCapableBeanFactory接口,而此处的ConfigurableListableBeanFactory可配置、可列出Bean的工厂是它的子类
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}
2、AbstractApplicationContext
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
// 这个类实现了ConfigurableApplicationContext,具备了上面接口大部分功能,
// 但是他没有实现getBeanFactory()方法,这个方法留待子类实现,所以它自己没有实际的管理Bean的能力,只是定义了一系列规范
}
3、AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {
// 碰到重复的Bean时,是否允许覆盖原先的BeanDefinition
@Nullable
private Boolean allowBeanDefinitionOverriding;
// 是否允许循环引用
@Nullable
private Boolean allowCircularReferences;
// 默认持有一个DefaultListableBeanFactory
@Nullable
private DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
// 对内部工厂进行操作时所采用的锁
private final Object beanFactoryMonitor = new Object();
public AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext() {
}
public AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
super(parent);
}
public void setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(boolean allowBeanDefinitionOverriding) {
this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding = allowBeanDefinitionOverriding;
}
public void setAllowCircularReferences(boolean allowCircularReferences) {
this.allowCircularReferences = allowCircularReferences;
}
// 刷新Bean工厂,如果当前上下文中已经存在一个容器的话,会先销毁容器中的所有Bean,然后关闭Bean工厂
// 之后在重新创建一个DefaultListableBeanFactory
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
@Override
protected void cancelRefresh(BeansException ex) {
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
if (this.beanFactory != null) {
this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(null);
}
}
super.cancelRefresh(ex);
}
@Override
protected final void closeBeanFactory() {
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
if (this.beanFactory != null) {
this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(null);
this.beanFactory = null;
}
}
}
protected final boolean hasBeanFactory() {
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
return (this.beanFactory != null);
}
}
// 复写了getBeanFactory,默认返回的是通过createBeanFactory创建的一个DefaultListableBeanFactory
@Override
public final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
if (this.beanFactory == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("BeanFactory not initialized or already closed - " +
"call 'refresh' before accessing beans via the ApplicationContext");
}
return this.beanFactory;
}
}
protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() {
return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory());
}
.......
// 提供了一个抽象的加载BeanDefinition的方法,这个方法没有具体实现,不同的配置方式需要进行不同的实现,
// 到这里,配置的方式不能确定,既可能是以XML的方式,也可能是以java config的方式
// 另外配置文件的加载方式也不能确定
protected abstract void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
throws BeansException, IOException;
}
可以看到这个类可以进一步对上下文进行配置,例如进行是否开启循环引用,是否允许进行BeanDefinition的覆盖等等。另外它所提供的一个重要的功能就是使容器具备刷新的功能,换言之凡是需要刷新功能的容器都需要继承这个类。
4、AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext
implements BeanNameAware, InitializingBean {
// 这个变量代表了配置文件的路径,到这里配置的信息相比于其父类AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext做了进一步的明确,但是仍然不能确定是XML还是javaconfig,只能确定配置在configLocations里面
@Nullable
private String[] configLocations;
.....
}
5、AbstractXmlApplicationContext
public abstract class AbstractXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext {
// 是否进行XML类型的校验,默认为true
private boolean validating = true;
// .....
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
protected void initBeanDefinitionReader(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) {
reader.setValidating(this.validating);
}
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
@Nullable
protected Resource[] getConfigResources() {
return null;
}
}
可以看到这个类进一步对配置的加载做了进一步的明确,首先明确了配置的类型为XML,第二明确了要通过getConfigResources方法来加载需要的配置资源,但是并没有对这个方法做具体实现,因为对于Resource的定义,可能是通过classpath的方式,也可能是通过URL的方式,基于此又多了两个子类
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,从classPath下加载配置文件FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,基于URL的格式加载配置文件
6、GenericApplicationContext
这个类已经不是抽象类了,我们可以直接使用它。但是这个类有一个很大的缺点,它不能读取配置,需要我们手动去指定读取的方式及位置。其实从上文中的分析我们可以看出,从AbstractApplicationContext到AbstractXmlApplicationContext一步步明确了配置的加载方式,Spring通过这种类的继承将配置的加载分了很多层,我们可以从AbstractXmlApplicationContext的子类开始从任意以及进行扩展。
而GenericApplicationContext只实现了上下文的基本功能,并没有对配置做任何约束,所以在使用它的我们需要手动往其中注册BeanDefinition。这样虽然很灵活,但是也很麻烦,如果我们使用GenericApplicationContext可能需要进行下面这样的操作
GenericApplicationContext ctx = new GenericApplicationContext();
//使用XmlBeanDefinitionReader,这个地方我们甚至可以自己定义解析器,不使用Spring容器内部的
XmlBeanDefinitionReader xmlReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(ctx);
//加载ClassPathResource
xmlReader.loadBeanDefinitions(new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml"));
PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader propReader = new PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader(ctx);
propReader.loadBeanDefinitions(new ClassPathResource("otherBeans.properties"));
//调用Refresh方法
ctx.refresh();
//和其他ApplicationContext方法一样的使用方式
MyBean myBean = (MyBean) ctx.getBean("myBean");
平常开发中我们基本用不到这个东西
7、AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
public class AnnotationConfigApplicationContext extends GenericApplicationContext implements AnnotationConfigRegistry {
private final AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader;
private final ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner;
.......
}
通过AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader注册配置类,用ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner扫描配置类上申明的路径,得到所有的BeanDefinition。然后其余的没啥了。这个我们经常使用,因为不用再需要xml文件了,使用@Configuration配置类即可,更加的方便。
web体系
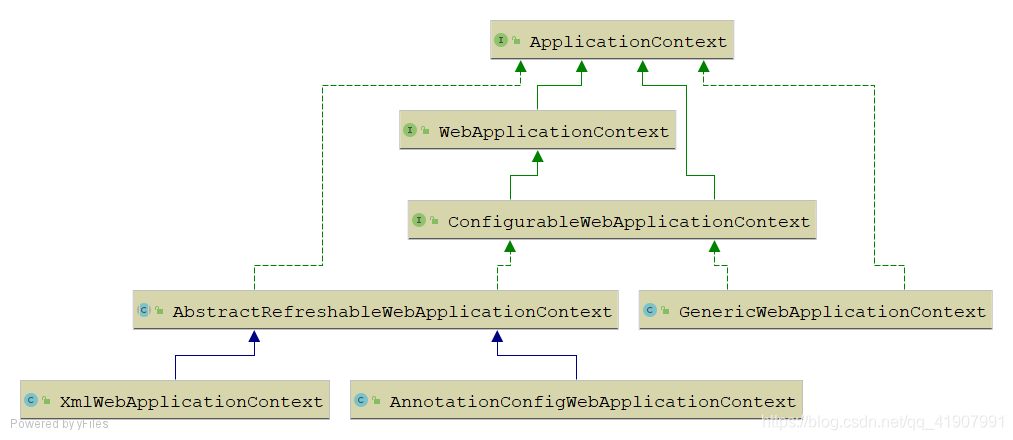
1、WebApplicationContext
public interface WebApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext {
String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
String SCOPE_REQUEST = "request";
String SCOPE_SESSION = "session";
String SCOPE_APPLICATION = "application";
String SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME = "servletContext";
String CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME = "contextParameters";
String CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME = "contextAttributes";
@Nullable
ServletContext getServletContext();
}
定义了一堆常量,以及一个方法,约束了所有的web容器必须能返回一个Servlet的上下文(ServletContext)
2、ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
public interface ConfigurableWebApplicationContext extends WebApplicationContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext {
String APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ":";
String SERVLET_CONFIG_BEAN_NAME = "servletConfig";
void setServletContext(@Nullable ServletContext servletContext);
void setServletConfig(@Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig);
@Nullable
ServletConfig getServletConfig();
// 设置及获取当前上下文的命名空间,命名空间用于区分不同的web容器的配置,在查找配置时会根据命名空间查找
// 默认不进行命名空间配置,配置会在/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml下查找
// 如果配置了,会在/WEB-INF+"namespace"+/applicationContext.xml下查找
// 根容器没有Namespace
void setNamespace(@Nullable String namespace);
@Nullable
String getNamespace();
void setConfigLocation(String configLocation);
void setConfigLocations(String... configLocations);
@Nullable
String[] getConfigLocations();
}
可以看到使用这个类能指定上下文配置加载的位置
3、AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext
implements ConfigurableWebApplicationContext, ThemeSource {
.......
}
首先可以看到这个类继承了AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext,代表它需要从指定的位置加载配置,其次它首先了ConfigurableWebApplicationContext,所以它具有web容器的属性。
4、XmlWebApplicationContext
public class XmlWebApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext {
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION = "/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml";
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_PREFIX = "/WEB-INF/";
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_SUFFIX = ".xml";
// .......
@Override
protected String[] getDefaultConfigLocations() {
if (getNamespace() != null) {
return new String[] {DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_PREFIX + getNamespace() + DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_SUFFIX};
}
else {
return new String[] {DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION};
}
}
}
进一步指定了配置文件的加载形式
- 需要加载XML类型配置
- 对于根容器,加载路径为
/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml - 对于子容器,加载路径为
/WEB-INF/+'namespace'+.xml,比如常用的dispatchServlet.xml
5、AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
指定了以注解的方式配置web容器
6、GenericWebApplicationContext
类比GenericApplicationContext,没有指定配置相关的任何东西,全手动
总结
从上面我们可以看到,整个一套体系下来不可谓不庞大,Spring在单一职责可以说做到了极致。不论是按功能分,比如HierarchicalBeanFactory,ListableBeanFactory,AutowireCapableBeanFactory就是按照不同功能拆分,或者是按照功能实现的层级划分,比如上面说到的配置文件的加载机制。对类之间的关系进行明确的分层,代表了整个体系会具备非常强大的扩展性,我们可以在每一步进行自己的扩展。这是让Spring能组件化开发,可插拔,变得如此优秀、普适的重要原因
到此,关于ApplicationContext相关的内容终于也可以告一段落了,代表着IOC已经结束了,粗略看了下官网,接下来还剩数据绑定,数据校验,类型转换以及AOP,任重而道远,加油吧!~