一、 异常概述:
1. 异常体系结构图:
java.lang.Throwable
|-----java.lang.Error:一般不编写针对性的代码进行处理。
|-----java.lang.Exception:可以进行异常的处理
|------编译时异常(checked)
|-----IOException
|-----FileNotFoundException
|-----ClassNotFoundException
|------运行时异常(unchecked,RuntimeException)
|-----NullPointerException
|-----ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
|-----ClassCastException
|-----NumberFormatException
|-----InputMismatchException
|-----ArithmeticException
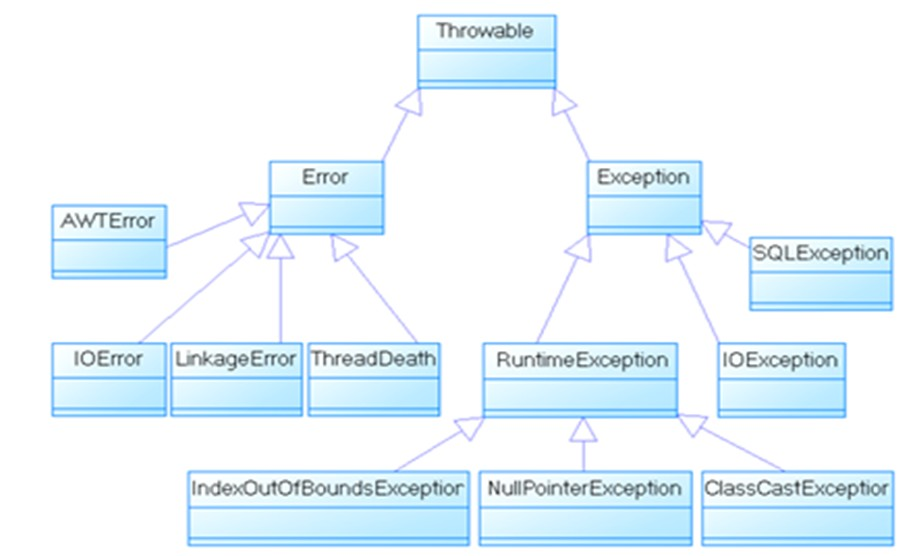
2. 异常的分类:
- 运行时异常:是指编译器不要求强制处置的异常。一般是指编程时的逻辑错误,是程序员应该积极避免其出现的异常。java.lang.RuntimeException类及它的子类都是运行时异常
- 编译时异常:是指编译器要求必须处置的异常。即程序在运行时由于外界因素造成的一般性异常。编译器要求Java程序必须捕获或声明所有编译时异常。
3. 常见异常的举例:
1 class demo1{//常见异常举例 2 //空指针异常 NullPointerException 3 @Test 4 public void test1(){ 5 int[] arr = null; 6 arr[4] = 0; 7 } 8 9 //数组角标越界异常 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 10 @Test 11 public void test2(){ 12 int[] arr = new int[4]; 13 arr[4] = 0; 14 } 15 16 //字符串角标越界异常 StringIndexOutOfBoundsException 17 @Test 18 public void test3(){ 19 String s = "abc"; 20 System.out.println(s.charAt(3)); 21 } 22 23 //ClassCastException 24 @Test 25 public void test4(){ 26 Object obj = new Date(); 27 String str = (String)obj; 28 } 29 30 //NumberFormatException 31 @Test 32 public void test5(){ 33 String str = "12ac"; 34 int num = Integer.parseInt(str); 35 } 36 37 //ArithmeticException 38 @Test 39 public void test6(){ 40 int a = 10; 41 int b = 0; 42 int c = a/b; 43 } 44 }
二、 异常处理机制:
1. try-catch-finally:
1 try{ 2 ...... //可能产生异常的代码 3 }catch( ExceptionName1 e ){ 4 ...... //当产生ExceptionName1型异常时的处置措施 5 }catch( ExceptionName2 e ){ 6 ...... //当产生ExceptionName2型异常时的处置措施 7 }finally{ 8 ...... 9 //无论是否发生异常,都无条件执行的语句 10 }
1 //1.2 异常的处理 *******try-catch-finally******* 2 @Test 3 public void test5(){ 4 String str = "12ac"; 5 try { //抛 6 int num = Integer.parseInt(str); 7 System.out.println("Hello 1"); 8 }catch (NumberFormatException e){ //抓 9 e.printStackTrace(); 10 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); 11 }catch (Exception e){ //此时不执行,因为在上面已经抓到了 12 System.out.println("Hello 2"); 13 }finally { 14 System.out.println("Hello 3"); // 在前面的return执行前一定会执行这个语句 15 // return 4; // 由于在前面的return执行前一定会执行finally, 16 // 因此会执行finally里面的return 17 } 18 }
Java 7开始,一个catch块可以捕获多个异常,多种异常之间使用 | 来隔开。另外,通常情况下,不要在finally块中使用return或throw等导致方法终止的语句,否则将会导致try、catch块中的return语句失效,如:
1 try{ 2 return true; 3 }finally{ 4 return false; 5 }
2. throws:如果一个方法(中的语句执行时)可能生成某种异常,但是并不能确定如何处理这种异常,则此方法应显示地声明抛出异常,表明该方法将不对这些异常进行处理,而由该方法的调用者负责处理。在方法声明中用throws语句可以声明抛出异常的列表,throws后面的异常类型可以是方法中产生的异常类型,也可以是它的父类 。
1 //1.2 异常的处理 ******* throws ******* 2 @Test 3 public void method3(){ //在这里进行处理 4 try { //下面扔上来了几个异常,就要catch几个异常 5 method2(); 6 }catch (IOException e){ 7 e.printStackTrace(); 8 } 9 } 10 11 public void method2()throws IOException { //继续向上扔 12 method1(); 13 } 14 15 public void method1() throws IOException { //向上扔 16 File file = new File("hello.txt"); 17 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); 18 int data = fis.read(); 19 while(data != -1){ 20 System.out.println((char)data); 21 data = fis.read(); 22 } 23 fis.close(); 24 }
3. 异常对象的产生方式:
- 系统自动生成
- 手动生成一个异常对象,如:
1 class Student{ 2 private int id; 3 4 public void regist(int id) throws Exception { 5 if(id>0) 6 this.id = id; 7 else 8 // throw new RuntimeException("您输入的数据非法!");//此时无须处,因为是运行时异常 9 throw new Exception("您输入的数据非法");//此时须throws,并且需要try-catch 10 } 11 } 12 13 public StudentTest{ 14 public static void main(String[] args){ 15 Student s=new Student(); 16 try{ 17 s.regist(-1); 18 }catch(Exception e){ 19 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); 20 } 21 } 22 }
4. 用户自定义异常类:
- 需要继承现有的异常类:RuntimeException、Exception
- 提供全局变量:serialVersionUID
- 提供重载构造器
1 class MyException extends RuntimeException{ 2 static final long serialVersionUID = -7034897190745766939L; 3 public MyException() { 4 5 } 6 public MyException(String msg) { 7 super(msg); 8 } 9 } 10 11 class MyExceptionTest{ 12 private int num; 13 public void myfun(int num){ 14 if (num>0) 15 this.num = num; 16 else 17 throw new MyException("输入值非法!"); 18 } 19 } 20 21 public class Test{ 22 public static void main(String[] args) { 23 MyExceptionTest test = new MyExceptionTest(); 24 test.myfun(-1); 25 } 26 }
【注意】throw和throws的对比:
