1、路由基础
(1)安装 vue-router:
cnpm install vue-router --save
(2)如果在一个模块化工程中使用它,必须要通过 Vue.use() 初始化路由插件:
import Vue from 'vue' import VueRouter from 'vue-router' Vue.use(VueRouter)
(3)创建路由格式:
const router = new VueRouter({ routes:[ { path: "/learn", // 访问路由的路径 name: "Learn", // 路由名称 component: Learn // 对应组件 } ] })
(4)给出路由显示位置:
<div id="app"> <!-- 路由出口 --> <!-- 路由匹配到的组件将渲染在这里 --> <router-view></router-view> </div>
(5)使用示例:
首先在 src 目录下创建一个 router 文件夹,同时在该文件夹下创建一个 index.js 文件,目录结构如下:
index.js 文件内容:
import Vue from 'vue' import VueRouter from 'vue-router' import Learn from '@/components/Learn' import HelloWord from '@/components/HelloWorld' // 初始化 VueRouter 插件 Vue.use(VueRouter) // 创建路由 export default new VueRouter({ routes: [ { path: '/learn', name: 'Learn', component: Learn }, { path: '/hello', name: 'Hello', component: HelloWord } ] })
然后创建 Learn.vue,HelloWorld.vue 两个文件,目录结构如下:

HelloWorld.vue 文件内容:
<template>
<div class="container">
<p>This is HelloWorld</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
data () {
return {
}
}
}
</script>
Learn.vue 文件内容:
<template>
<div class="container">
<p>This is learn</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Learn",
data() {
return {
};
}
};
</script>
App.vue 文件内容:
<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="./assets/logo.png">
<p>
<!-- 使用声明式导航 router-link 组件来导航. -->
<!-- 通过传入 `to` 属性指定链接. -->
<!-- <router-link> 默认会被渲染成一个 `<a>` 标签 -->
<router-link to="/hello">go to hello</router-link>
<router-link to="/learn">go to learn</router-link>
</p>
<!-- 路由显示位置 -->
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
data() {
return {
}
}
};
</script>
main.js 文件内容:
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' // 引入路由对象 import router from './router' Vue.config.productionTip = false /* eslint-disable no-new */ new Vue({ el: '#app', render: h => h(App), router // 注入路由对象 })

如上,当点击不同链接时,红色框会显示指定路径所对应的组件内容。
2、传递参数
声明式导航(<router-link>)传参
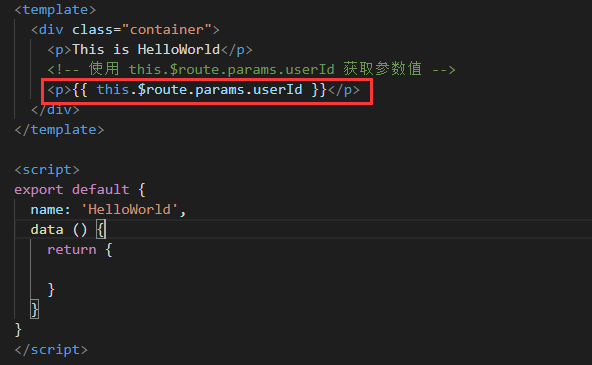
HelloWorld.vue :
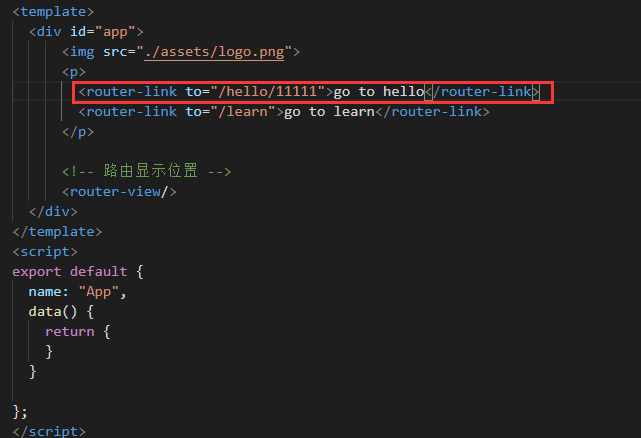
App.vue:
页面效果:

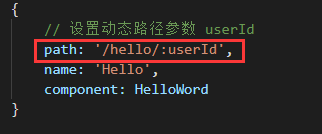
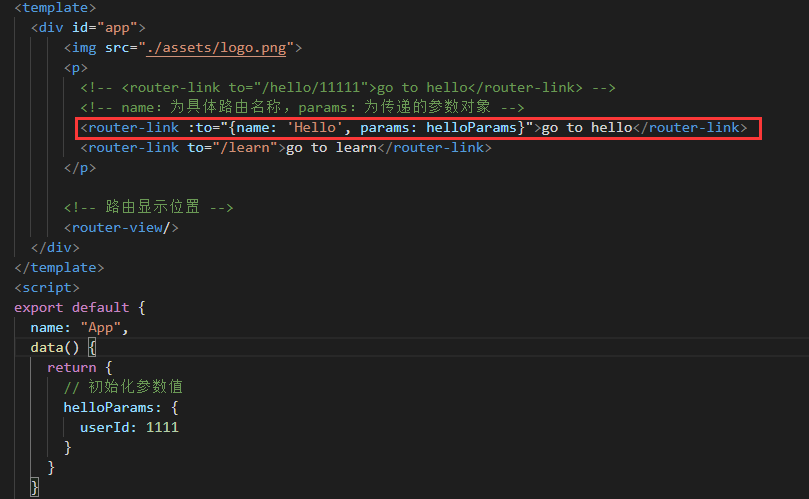
(2)声明式导航(使用命名路由,对象参数):
App.vue :
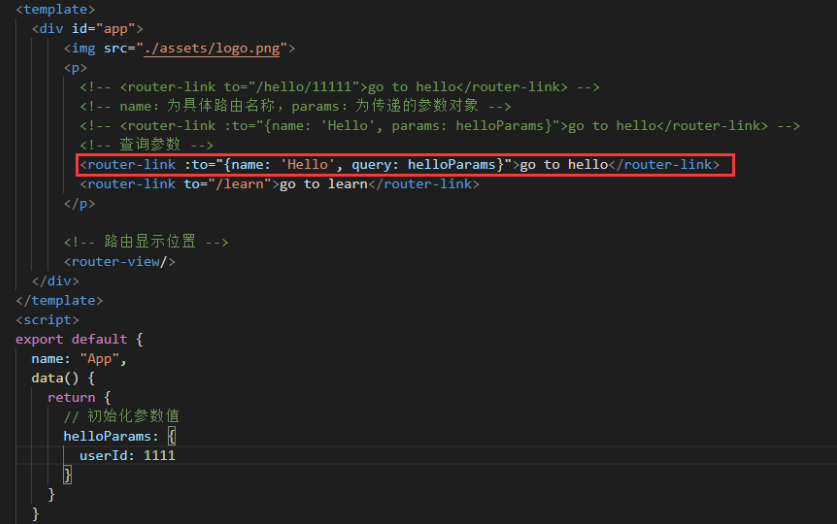
(3)声明式导航(使用命名路由,查询参数):
查询参数就是在路由地址后面带上参数,与传统的 url 参数一致,会变成 /hello?userId=1111
App.vue :
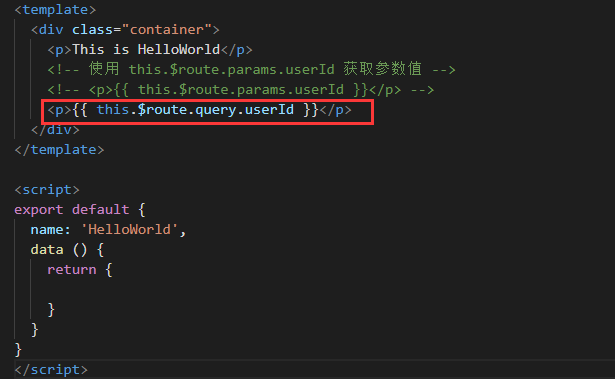
HelloWorld.vue:
页面效果:

(4)编程式导航(与声明式导航一样,只是写法不同,实际开发中以这种方式为主):
// 字符串 this.$router.push('/hello') // 对象 this.$router.push({ path: '/hello' }) // 对象 + 路径字符串参数 const userId = '1111' this.$router.push({ path: '/hello/${userId}' }) // -> /hello/1111 // 命名的路由 this.$router.push({ name: 'Hello', params: { userId: '1111' }}) // 带查询参数,变成 /hello?userId=1111 this.$router.push({ path: '/hello', query: { userId: '1111' }})
3、嵌套路由
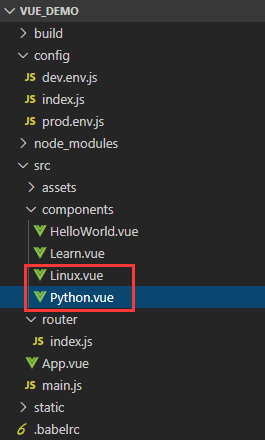
(1)在 components 目录下,创建 Python.vue、Linux.vue 两个文件:
Python.vue:
<template>
<div class="python">
<p>学习Python</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Python',
data() {
return {
}
}
}
</script>
Linux.vue:
<template>
<div class="linux">
<p>学习Linux</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Linux',
data() {
return {
}
}
}
</script>
router/index.js:
import Vue from 'vue' import VueRouter from 'vue-router' import Learn from '@/components/Learn' import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld' /* 导入子组件 */ import Python from '@/components/Python' import Linux from '@/components/Linux' // 初始化 VueRouter 插件 Vue.use(VueRouter) // 创建路由 export default new VueRouter({ routes: [ { path: '/learn', name: 'Learn', component: Learn, // 使用 children 定义子组件 children: [ { // 以"/"开头的嵌套路径会被当作根路径,所以子路由上不用加"/; // 在生成路由时,主路由上的path会被自动添加到子路由之前, // 所以子路由上的path不用在重新声明主路由上的path了。 // Python 会被渲染在 Learn 的 <router-view> 中 path: 'python', name: 'Python', component: Python }, { // Linux 会被渲染在 Learn 的 <router-view> 中 path: 'linux', name: 'Linux', component: Linux } ] }, { path: '/hello', name: 'Hello', component: HelloWorld } ] })
Learn.vue:
<template>
<div class="container">
<p>This is learn</p>
<router-link to="/learn/python">learn python</router-link>
<router-link to="/learn/linux">learn linux</router-link>
<!-- Learn 的子组件会被渲染在 <router-view> 中 -->
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Learn",
data() {
return {
};
}
};
</script>
App.vue:
<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="./assets/logo.png" />
<div>
<router-link to="/learn">go to learn</router-link>
</div>
<router-view />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
data() {
return {
};
}
};
</script>
页面效果:

4、路由杂项
(1)404 Not Found路由:
router/index.js :
// 访问根路径时,匹配到 Learn 组件 { path: '/', component: Learn }, // * 号为通用匹配,即匹配所有路径,通常用于客户端 404 错误 { path: '*', component: NotFound }
// 给出一个路由 { path: '/user-*' } this.$router.push('/user-admin') this.$route.params.pathMatch // 'admin' // 给出一个路由 { path: '*' } this.$router.push('/non-existing') this.$route.params.pathMatch // '/non-existing'
(2)history 模式:
const router = new VueRouter({ mode: 'history', routes: [...] })
当你使用 history 模式时,URL 就像正常的 url,例如 http://yoursite.com/user/id,也好看!
所以呢,你要在服务端增加一个覆盖所有情况的候选资源:如果 URL 匹配不到任何静态资源,则应该返回同一个 index.html 页面,这个页面就是你 app 依赖的页面。
比如 Nginx 配置:
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
}
参考:
《Vue.js 实战》