一、Numpy
NumPy(Numeric Python)系统是 Python 的一种开源的数值计算扩展。这种工具可用来存储和处理大型矩阵,比 Python 自身的嵌套列表(nested list structure)结构要高效的多(该结构也可以用来表示矩阵(matrix))。据说 NumPy 将 Python 相当于变成一种免费的更强大的 MatLab 系统。
numpy 特性:开源,数据计算扩展,ndarray, 具有多维操作, 数矩阵数据类型、矢量处理,以及精密的运算库。专为进行严格的数字处理而产生。
特点:运算速度快、消耗资源少。
默认使用 Anaconda 集成包环境开发。
1、numpy 属性
几种 numpy 的属性:
-
ndim:维度
-
shape:行数和列数
-
size:元素个数
使用 numpy 首先要导入模块
1 import numpy as np #为了方便使用numpy 采用np简写
列表转化为矩阵:
array = np.array([[1,2,3],[2,3,4]]) #列表转化为矩阵 print(array) """ array([[1, 2, 3], [2, 3, 4]]) """
numpy 的几种属性:
print('number of dim:',array.ndim) # 维度 # number of dim: 2 print('shape :',array.shape) # 行数和列数 # shape : (2, 3) print('size:',array.size) # 元素个数 # size: 6
2、Numpy 的创建 array
关键字
-
array:创建数组
-
dtype:指定数据类型
-
zeros:创建数据全为0
-
ones:创建数据全为1
-
empty:创建数据接近0
-
arrange:按指定范围创建数据
-
linspace:创建线段
二、Matplotlib
Matplotlib 是 Python 的绘图库。 它可与 NumPy 一起使用,提供了一种有效的 MatLab 开源替代方案。 它也可以和图形工具包一起使用,如 PyQt 和 wxPython。
matplotlib.pyplot 模块可以画折线图,分为两个步骤,分别是 pyplot.plot() 和 pyplot.show() ,前者负责画图,后者将画好的图展示出来。
基本使用:
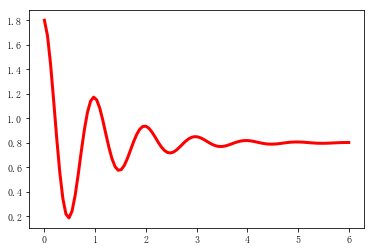
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x=np.linspace(0,6,100) y=np.cos(2*np.pi*x)*np.exp(-x)+0.8 plt.plot(x,y,'k',color='r',linewidth=3,linestyle="-") plt.show()
效果如图:
三、雷达图绘制
代码如下:
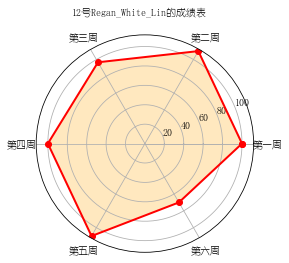
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib matplotlib.rcParams['font.family']='YouYuan' matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['YouYuan'] labels=np.array(['第一周','第二周','第三周','第四周','第五周','第六周']) nAttr=6 data=np.array([100,100,96.7,100,110,70]) angles=np.linspace(0,2*np.pi,nAttr,endpoint=False) data=np.concatenate((data,[data[0]])) angles=np.concatenate((angles,[angles[0]])) fig=plt.figure(facecolor="white") plt.subplot(111,polar=True) plt.plot(angles,data,'bo-',color='red',linewidth=2) plt.fill(angles,data,facecolor='orange',alpha=0.25) plt.thetagrids(angles*180/np.pi,labels) plt.figtext(0.5,0.95,'12号Regan_White_Lin的成绩表',ha='center') plt.grid(True) plt.savefig('pic.JPG') plt.show()
效果图如下:
四.散点图绘画
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt if __name__ == '__main__': print ("--------------散点图--------------") x = np.arange(50) print ("x") y = x + 5* np.random.rand(50) plt.scatter(x, y) plt.show()
运行结果:

五.自定义手绘风
import numpy as np
vec_az=np.pi/4.
depth=10.
im=Image.open("HIT2.jpg").convert('L')
a=np.asarray(im).astype('float')
grad=np.gradient(a)
grad_x,grad_y=grad
grad_x=grad_x*depth/100.
grad_y=grad_y*depth/100.
dx=np.cos(vec_el)*np.cos(vec_az)
dy=np.cos(vec_el)*np.sin(vec_az)
dz=np.sin(vec_el)
A=np.sqrt(grad_x**2+grad_y**2+1.)
uni_x=grad_x/A
uni_y=grad_y/A
uni_z=1./A
a2=255*(dx*uni_x+dy*uni_y+dz*uni_z)
a2=a2.clip(0,255)
im2=Image.fromarray(a2.astype('uint8'))
im2.save('hit2-SH.jpg')
ils/82344288
原图:

手绘效果图:
