1.描述
为系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,Facade模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用。
2.模式的使用
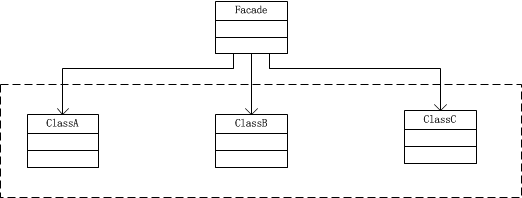
·子系统(SubSystem):子系统是若干个类的集合,这些类的实例协同合作为用户提供服务,子系统中任何类都不包含外观类的实例引用。
·外观(Facade):外观是一个类,该类包含子系统中全部或部分类的实例引用,当用户希望和子系统中的若干类打交道时,可通过外观类实现。
3.使用情景
·对一个复杂的子系统,需要为用户提供一个简单的交互操作。
·不希望用户代码和子系统中的类又耦合,以便提高子系统的独立性和可移植性。
·当整个系统需要构建一个层析结构的子系统,不希望这些子系统相互直接的交互。
4.优点
·使客户和子系统的类无耦合,并且使子系统中的类使用起来更放方便。
·外观只提供一个更简洁的界面,不影响用户直接使用子系统中的类。
·子系统中任何类的修改不影响外观类。
5.UML图
6.案例
一个文件子系统中三个类:ReadFile(读取文件内容)、AanlyzeInformation(删除用户不想要的内容)、SaveFile(存储文件),组合起来实现将一个html文件的标签全部去除并保存的功能。
1 package 外观模式; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.BufferedWriter; 5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 6 import java.io.FileReader; 7 import java.io.FileWriter; 8 import java.io.IOException; 9 import java.io.StringReader; 10 11 public class test1 { 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 Facade facade = new Facade(); 14 String regex = "<[^>]*>"; 15 String readFile = "C:/uc1.txt"; 16 String saveFile = "C:/uc.txt"; 17 facade.doOption(readFile, regex, saveFile); 18 } 19 20 } 21 22 /* 23 * 子系统ReadFile,AnalyzeInformation,WriteFile三个类 24 */ 25 26 /* 27 * 读取文件内容 28 */ 29 class ReadFile{ 30 public String readFile(String fileName){ 31 StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer(); 32 try { 33 FileReader in = new FileReader(fileName); 34 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(in); 35 String s = null; 36 while((s = br.readLine()) != null){ 37 str.append(s); 38 str.append(" "); 39 } 40 in.close(); 41 br.close(); 42 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } catch (IOException e) { 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 } 47 return new String(str); 48 } 49 } 50 51 /* 52 * 从文本中删除用户不需要的内容 53 */ 54 class AnalyzeInformation{ 55 public String getSaveContext(String content, String deleteContent){ 56 content = content.replaceAll(deleteContent, ""); 57 return content; 58 } 59 } 60 61 /* 62 * 把文件保存起来 63 */ 64 class WriteFile{ 65 public void writeToFile(String fileName, String content){ 66 try { 67 StringReader in = new StringReader(content); 68 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(in); 69 FileWriter out = new FileWriter(fileName); 70 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(out); 71 String s = null; 72 while((s = br.readLine()) != null){ 73 bw.write(s); 74 bw.newLine(); 75 bw.flush(); 76 } 77 in.close(); 78 br.close(); 79 out.close(); 80 bw.close(); 81 } catch (IOException e) { 82 e.printStackTrace(); 83 } 84 } 85 } 86 87 /* 88 * 外观 89 */ 90 class Facade{ 91 private ReadFile readFile; 92 private AnalyzeInformation analyze; 93 private WriteFile writeFile; 94 Facade(){ 95 this.readFile = new ReadFile(); 96 this.analyze = new AnalyzeInformation(); 97 this.writeFile = new WriteFile(); 98 } 99 100 public void doOption(String readFileName, String deleteContent, String saveFileName){ 101 String content = readFile.readFile(readFileName); 102 System.out.println("读取文件:" + readFileName); 103 System.out.println(content); 104 String saveContent = analyze.getSaveContext(content, deleteContent); 105 writeFile.writeToFile(saveFileName, saveContent); 106 System.out.println("保存到:" + saveFileName); 107 System.out.println(saveContent); 108 } 109 }