恒等块(Identity block)
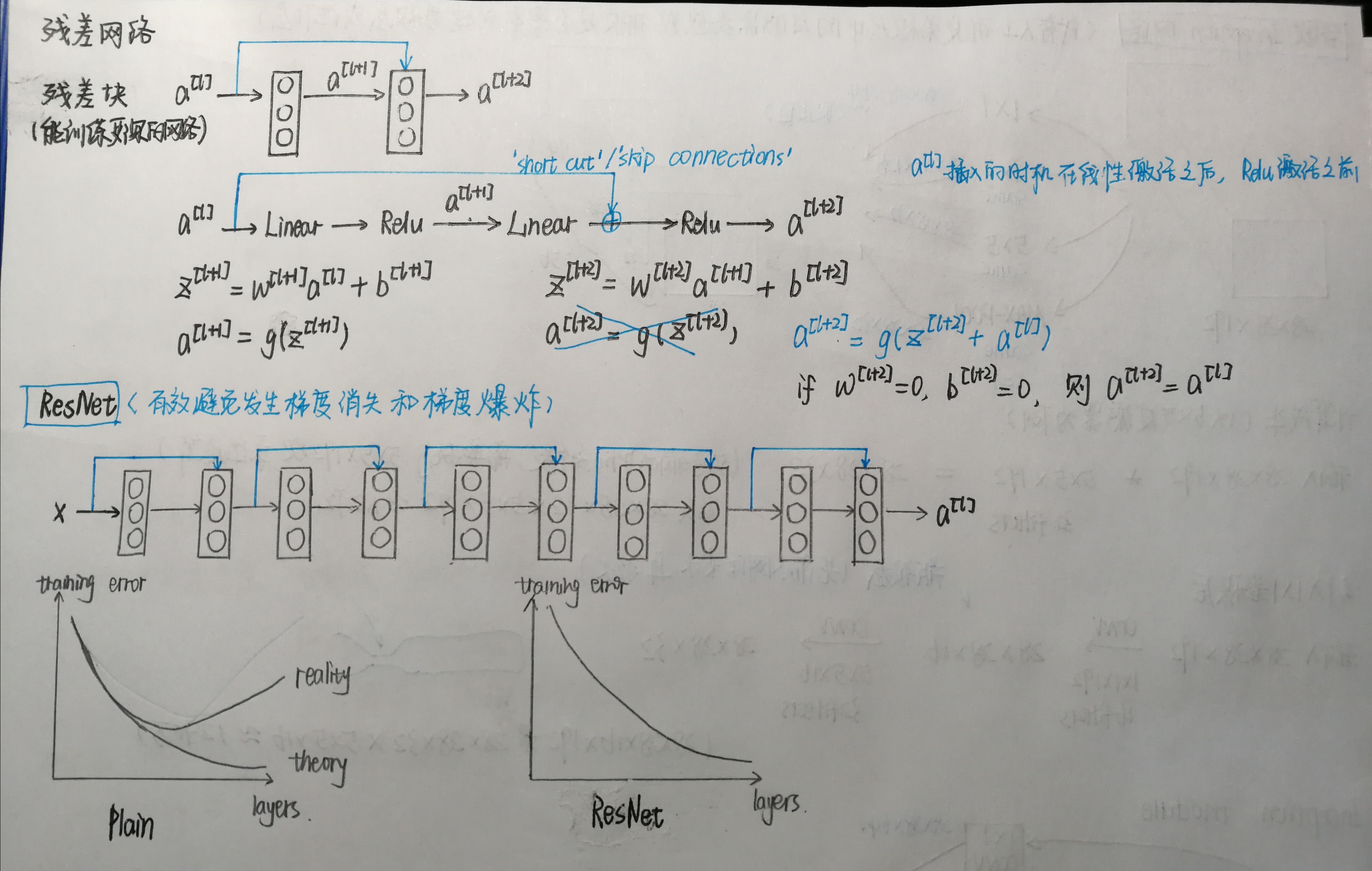
和图中不同,下例中会跳过三个隐藏层,且路径中每一步先进行卷积操作,再Batch归一化,最后进行Relu激活。
相关函数:
1 def identity_block(X, f, filters, stage, block): 2 """ 3 Implementation of the identity block as defined in Figure 3 4 5 Arguments: 6 X -- input tensor of shape (m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev) 7 f -- integer, specifying the shape of the middle CONV's window for the main path 8 filters -- python list of integers, defining the number of filters in the CONV layers of the main path 9 stage -- integer, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network 10 block -- string/character, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network 11 12 Returns: 13 X -- output of the identity block, tensor of shape (n_H, n_W, n_C) 14 """ 15 # defining name basis 16 conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch' 17 bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch' 18 19 # Retrieve Filters 20 F1, F2, F3 = filters 21 22 # Save the input value. You'll need this later to add back to the main path. 23 X_shortcut = X 24 25 # First component of main path 26 X = Conv2D(filters = F1, kernel_size = (1, 1), strides = (1,1), padding = 'valid', name = conv_name_base + '2a', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) 27 X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2a')(X) 28 X = Activation('relu')(X) 29 30 ### START CODE HERE ### 31 # Second component of main path (≈3 lines) 32 X = Conv2D(filters = F2, kernel_size = (f, f), strides = (1,1), padding = 'same', name = conv_name_base + '2b', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) 33 X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2b')(X) 34 X = Activation('relu')(X) 35 36 # Third component of main path (≈2 lines) 37 X = Conv2D(filters = F3, kernel_size = (1, 1), strides = (1,1), padding = 'valid', name = conv_name_base + '2c', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) 38 X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2c')(X) 39 40 # Final step: Add shortcut value to main path, and pass it through a RELU activation (≈2 lines) 41 X = Add()([X,X_shortcut]) 42 X = Activation("relu")(X) 43 ### END CODE HERE ### 44 45 return X
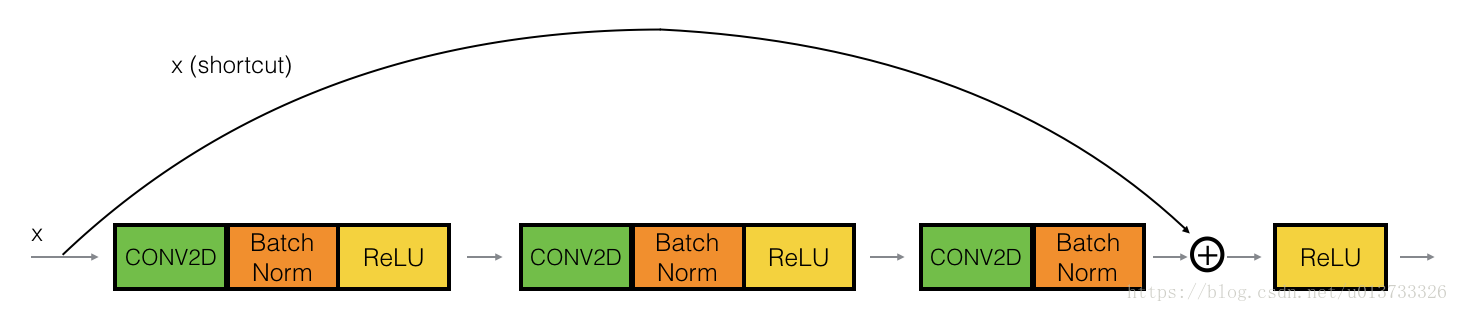
卷积块
输入与输出有不同的维度(对应于上图中的a[l]和a[l+2])

1 def convolutional_block(X, f, filters, stage, block, s = 2): 2 """ 3 Implementation of the convolutional block as defined in Figure 4 4 5 Arguments: 6 X -- input tensor of shape (m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev) 7 f -- integer, specifying the shape of the middle CONV's window for the main path 8 filters -- python list of integers, defining the number of filters in the CONV layers of the main path 9 stage -- integer, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network 10 block -- string/character, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network 11 s -- Integer, specifying the stride to be used 12 13 Returns: 14 X -- output of the convolutional block, tensor of shape (n_H, n_W, n_C) 15 """ 16 # defining name basis 17 conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch' 18 bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch' 19 20 # Retrieve Filters 21 F1, F2, F3 = filters 22 23 # Save the input value 24 X_shortcut = X 25 26 ##### MAIN PATH ##### 27 # First component of main path 28 X = Conv2D(F1, (1, 1), strides = (s,s),padding = 'valid', name = conv_name_base + '2a', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) 29 X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2a')(X) 30 X = Activation('relu')(X) 31 32 ### START CODE HERE ### 33 # Second component of main path (≈3 lines) 34 X = Conv2D(F2, (f, f), strides = (1,1), padding = 'same', name = conv_name_base + '2b', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) 35 X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2b')(X) 36 X = Activation('relu')(X) 37 38 # Third component of main path (≈2 lines) 39 X = Conv2D(F3, (1, 1), strides = (1,1), padding = 'valid', name = conv_name_base + '2c', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) 40 X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2c')(X) 41 42 ##### SHORTCUT PATH #### (≈2 lines) 43 X_shortcut=Conv2D(F3,(1,1), strides=(s,s), padding='valid', name=conv_name_base + '1', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X_shortcut) 44 X_shortcut=BatchNormalization(axis=3,name=bn_name_base + '1')(X_shortcut) 45 46 # Final step: Add shortcut value to main path, and pass it through a RELU activation (≈2 lines) 47 X = Add()([X,X_shortcut]) 48 X = Activation("relu")(X) 49 ### END CODE HERE ### 50 51 return X
构建残差网络(50层)
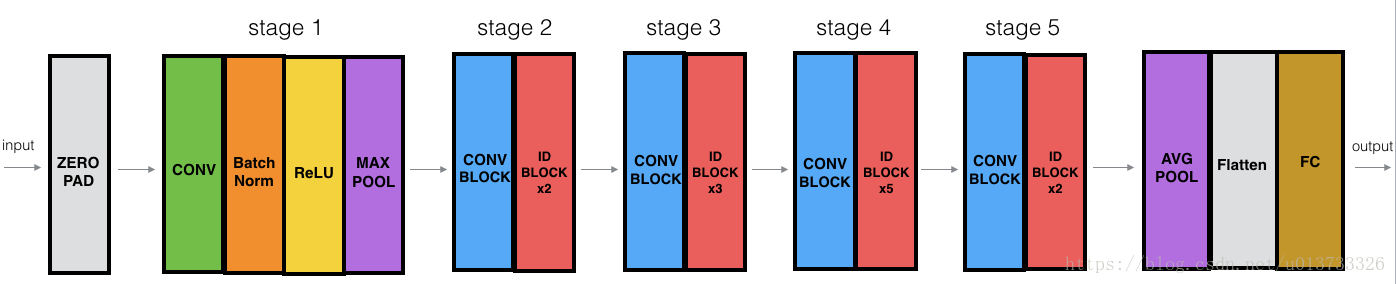
1 def ResNet50(input_shape = (64, 64, 3), classes = 6): 2 """ 3 Implementation of the popular ResNet50 the following architecture: 4 CONV2D -> BATCHNORM -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*2 -> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*3 5 -> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*5 -> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*2 -> AVGPOOL -> TOPLAYER 6 7 Arguments: 8 input_shape -- shape of the images of the dataset 9 classes -- integer, number of classes 10 11 Returns: 12 model -- a Model() instance in Keras 13 """ 14 # Define the input as a tensor with shape input_shape 15 X_input = Input(input_shape) 16 17 # Zero-Padding 18 X = ZeroPadding2D((3, 3))(X_input) 19 20 # Stage 1 21 X = Conv2D(64, (7, 7), strides = (2, 2), name = 'conv1', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) 22 X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = 'bn_conv1')(X) 23 X = Activation('relu')(X) 24 X = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(X) 25 26 # Stage 2 27 X = convolutional_block(X, f = 3, filters = [64, 64, 256], stage = 2, block='a', s = 1) 28 X = identity_block(X, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='b') 29 X = identity_block(X, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='c') 30 31 ### START CODE HERE ### 32 33 # Stage 3 (≈4 lines) 34 X = convolutional_block(X, f = 3, filters = [128, 128, 512], stage = 3, block='a', s = 2) 35 X = identity_block(X, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='b') 36 X = identity_block(X, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='c') 37 X = identity_block(X, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='d') 38 39 # Stage 4 (≈6 lines) 40 X = convolutional_block(X, f = 3, filters = [256, 256, 1024], stage = 4, block='a', s = 3) 41 X = identity_block(X, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='b') 42 X = identity_block(X, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='c') 43 X = identity_block(X, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='d') 44 X = identity_block(X, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='e') 45 X = identity_block(X, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='f') 46 47 # Stage 5 (≈3 lines) 48 X = convolutional_block(X, f = 3, filters = [512, 512, 2048], stage = 5, block='a', s = 4) 49 X = identity_block(X, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='b') 50 X = identity_block(X, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='c') 51 52 # AVGPOOL (≈1 line). Use "X = AveragePooling2D(...)(X)" 53 X = AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(2,2),padding="same")(X) 54 ### END CODE HERE ### 55 56 # output layer 57 X = Flatten()(X) 58 X = Dense(classes, activation='softmax', name='fc' + str(classes), kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) 59 60 # Create model 61 model = Model(inputs = X_input, outputs = X, name='ResNet50') 62 63 return model
加载数据
1 X_train_orig, Y_train_orig, X_test_orig, Y_test_orig, classes = load_dataset() 2 3 # Normalize image vectors 4 X_train = X_train_orig/255. #(1080,64,64,3) 5 X_test = X_test_orig/255. #(120,64,64,3) 6 7 # Convert training and test labels to one hot matrices 8 Y_train = convert_to_one_hot(Y_train_orig, 6).T #(1080,6) 9 Y_test = convert_to_one_hot(Y_test_orig, 6).T #(120,6)
训练、评估模型
1 model = ResNet50(input_shape = (64, 64, 3), classes = 6) 2 model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) 3 model.fit(X_train, Y_train, epochs = 2, batch_size = 32) 4 5 preds = model.evaluate(X_test, Y_test) 6 print ("Loss = " + str(preds[0])) 7 print ("Test Accuracy = " + str(preds[1]))
Epoch 1/2
1080/1080 [==============================] - 236s - loss: 3.0773 - acc: 0.4037
Epoch 2/2
1080/1080 [==============================] - 228s - loss: 1.5003 - acc: 0.6028
120/120 [==============================] - 6s
Loss = 2.42033188343
Test Accuracy = 0.166666668653
用已经训练好的RESNET50模型评估
1 import keras 2 keras.backend.clear_session() 3 model = load_model('ResNet50.h5',compile=False) 4 model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) 5 preds = model.evaluate(X_test, Y_test) 6 print ("Loss = " + str(preds[0])) 7 print ("Test Accuracy = " + str(preds[1]))
120/120 [==============================] - 7s
Loss = 0.108543064694
Test Accuracy = 0.966666662693
Tip:此处采坑TypeError: Cannot interpret feed_dict key as Tensor: Tensor Tensor("Placeholder_121:0", shape=(1, 1, 128, 512), dtype=float32) is not an element of this graph.
原因:第二次调用model的时候,model底层tensorflow的session中还有数据。
解决:在调用model之前执行keras.backend.clear_session()