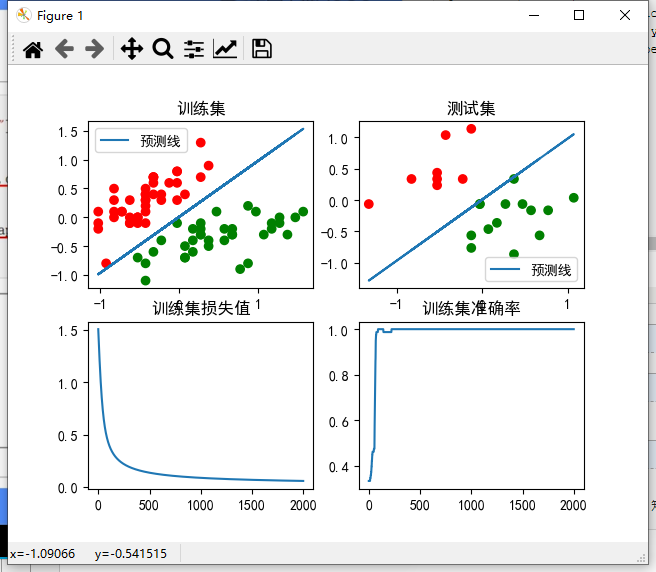
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pylab as plt import matplotlib as mpl # 读取数据集 TRIN_URL = 'http://download.tensorflow.org/data/iris_training.csv' # 数据集下载网址 df_iris = pd.read_csv('./鸢尾花数据集/iris.csv', header=0) # 读取本地csv文件数据 df_iris_test = pd.read_csv('./鸢尾花数据集/iris_test.csv', header=0) # print(df_iris) # 最后一列是分类编号 # 处理数据集 iris = np.array(df_iris) # 将数据转换成numpy数组 iris_test = np.array(df_iris_test) iris2 = iris[iris[:, -1] < 2] # 只取分类编号小于2的两类数据 iris2_test = iris_test[iris_test[:, -1] < 2] # 训练集数据处理 train_x = iris2[:, 0:2] # 只取特征的前两列 train_x = train_x - np.mean(train_x, axis=0) # 需要将样本的均值变为0 train_1 = np.ones(train_x.shape[0]).reshape(-1, 1) # 生成一个与train_x一样行数的全1矩阵 # print('train_1:',train_1) train_x = tf.concat((train_x, train_1), axis=1) # 将train_x扩充一列全1 train_x = tf.cast(train_x,tf.float32) # 测试集遵循上面训练集的操作 test_x = iris2_test[:, 0:2] test_x = test_x - np.mean(test_x, axis=0) test_1 = np.ones(test_x.shape[0]).reshape(-1, 1) test_x = tf.concat((test_x, test_1), axis=1) test_x = tf.cast(test_x,tf.float32) train_y = iris2[:, -1] # 标签 train_y = train_y.reshape(-1,1) test_y = iris2_test[:, -1] # 标签 test_y = test_y.reshape(-1,1) # print('axis = 0:',np.mean(train_x,axis=0)) # axis = 0 求一列的平均值 # print(train_y, train_y.shape) print(test_y, test_y.shape) # 设置超参 iter = 2000 learn_rate = 0.1 loss_list = [] acc_list = [] # 初始化训练参数 w = tf.Variable(np.random.randn(3,1),dtype=tf.float32) # w = tf.Variable(np.array([1.,1.,1.]).reshape(-1,1),dtype=tf.float32) for i in range(iter): with tf.GradientTape() as tape: y_p = 1 / (1 + tf.exp(-(tf.matmul(train_x, w)))) loss = tf.reduce_mean(-(train_y * tf.math.log(y_p) + (1 - train_y) * tf.math.log(1 - y_p))) dloss_dw = tape.gradient(loss, w) w.assign_sub(learn_rate * dloss_dw) loss_list.append(loss) acc = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(tf.round(y_p),train_y),dtype = tf.float32)) acc_list.append(acc) if i % 100 == 0: print('第{}次, loss:{},acc:{}'.format(i,loss,acc)) # print('y_p:{} train_y:{}'.format(y_p, train_y)) print() # 预测直线的横纵坐标处理 # 训练集 x1 = train_x[:,0] print(w[0] * 55) x2 = -(w[0] * x1 + w[2])/ w[1] # print('x2:',x2) # 测试集 x1_test = test_x[:,0] print(w[0] * 55) x2_test = -(w[0] * x1_test + w[2])/ w[1] # 画图 plt.rcParams["font.family"] = 'SimHei' # 将字体改为中文 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 设置了中文字体默认后,坐标的"-"号无法显示,设置这个参数就可以避免 # 分子图开始画图 plt.subplot(221) plt.title('训练集') cm_pt = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['red', 'green']) plt.scatter(x=train_x[:, 0], y=train_x[:, 1], c=train_y, cmap=cm_pt) plt.plot(x1,x2,label = '预测线') plt.legend() plt.subplot(222) plt.title('测试集') cm_pt = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['red', 'green']) plt.scatter(x=test_x[:, 0], y=test_x[:, 1], c=test_y, cmap=cm_pt) plt.plot(x1_test,x2_test,label = '预测线') plt.legend() plt.subplot(223) plt.title('训练集损失值') plt.plot(loss_list) plt.subplot(224) plt.title('训练集准确率') plt.plot(acc_list) plt.show()