概述
- 也叫快照(SnapShot)
- 属于行为类设计模式
- 允许在不暴露对象实现细节的情况下保存和恢复对象之前的状态
- 软件构建过程中,某些对象的状态在转换过程中,可能由于某种需要,要求程序能回溯到对象之前处于某个点时的状态,如果使用一些公有接口来让其他对象得到对象的状态,便会暴露对象的细节实现
- 如何实现对象状态的良好保存与恢复,但同时又不会因此而破坏对象本身的封装性
- 在不破坏封装性的前提下,捕捉一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之外保存这个状态,这样以后就可以将该对象恢复到原先保存的状态
- 备忘录(Memento)存储原发器(Originator)对象的内部状态,在需要时恢复原发器状态
- Memento模式的核心是信息隐藏,即Originator需要向外接隐藏信息,保持其封装性,但同时又需要将状态保持到外界(Memento)
- 由于现代语言(Java,C#)运行时,都具有相当的序列化支持,因此往往用效率较高,又较容易正确实现的序列化方案来实现Memento模式
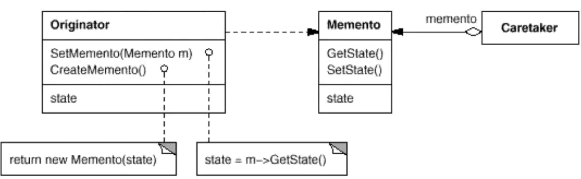
结构1

- 原发器类:用于获取状态,生成备忘录对象(快照),并在需要时通过快照恢复状态
- 备忘录类:用于保存状态,通常将备忘录设为不可变的,同通过构造函数一次性传递数据
- 负责人类:仅知道“何时”及“为何”捕捉原发器的状态,以及何时恢复状态,通过备忘录栈记录原发器的历史状态,当原发器要追溯历史状态时,负责人获取栈顶备忘录,传递给原发器的恢复方法
- 备忘录类嵌套在原发器类中,原发器就可以访问备忘录的成员变量和方法
结构2

- 允许存在多种不同类型的原发器和备忘录,每种原发器都和其响应的备忘录类进行交互
- 负责人被禁止修改在备忘录中的状态,恢复方法被定义在了备忘录类中
- 每个备忘录与创建了自身的原发器连接,原发器将自己及状态传递给备忘录的构造函数
场景
- 开发一款文字编辑器应用,让用户可以撤销施加在文本上的任何操作。可让程序在执行前记录所有的对象状态,并将其保存下来,当用户以后撤销某个操作时,程序将从历史记录中获取最近的快照,然后恢复所有对象的状态
联系
- 同时使用命令模式和备忘录模式实现撤销,命令用于对目标对象执行各种不同的操作,备忘录用于保存命令执行前对象的状态
- 同时使用备忘模式和迭代器模式获取当前迭代器的状态,并在需要时进行回滚
- 对象状态比较简单时,原型模式可以作为备忘录的一个简化版本
示例1
memento.cpp

1 class Memento 2 { 3 string state; 4 //.. 5 public: 6 Memento(const string & s) : state(s) {} 7 string getState() const { return state; } 8 void setState(const string & s) { state = s; } 9 }; 10 11 class Originator 12 { 13 string state; 14 //.... 15 public: 16 Originator() {} 17 Memento createMomento() { 18 Memento m(state); 19 return m; 20 } 21 void setMomento(const Memento & m) { 22 state = m.getState(); 23 } 24 }; 25 26 int main() 27 { 28 Originator orginator; 29 30 //捕获对象状态,存储到备忘录 31 Memento mem = orginator.createMomento(); 32 33 //... 改变orginator状态 34 35 //从备忘录中恢复 36 orginator.setMomento(memento); 37 38 }
示例2


1 // 原发器中包含了一些可能会随时间变化的重要数据。它还定义了在备忘录中保存 2 // 自身状态的方法,以及从备忘录中恢复状态的方法。 3 class Editor is 4 private field text, curX, curY, selectionWidth 5 6 method setText(text) is 7 this.text = text 8 9 method setCursor(x, y) is 10 this.curX = curX 11 this.curY = curY 12 13 method setSelectionWidth(width) is 14 this.selectionWidth = width 15 16 // 在备忘录中保存当前的状态。 17 method createSnapshot():Snapshot is 18 // 备忘录是不可变的对象;因此原发器会将自身状态作为参数传递给备忘 19 // 录的构造函数。 20 return new Snapshot(this, text, curX, curY, selectionWidth) 21 22 // 备忘录类保存有编辑器的过往状态。 23 class Snapshot is 24 private field editor: Editor 25 private field text, curX, curY, selectionWidth 26 27 constructor Snapshot(editor, text, curX, curY, selectionWidth) is 28 this.editor = editor 29 this.text = text 30 this.curX = curX 31 this.curY = curY 32 this.selectionWidth = selectionWidth 33 34 // 在某一时刻,编辑器之前的状态可以使用备忘录对象来恢复。 35 method restore() is 36 editor.setText(text) 37 editor.setCursor(curX, curY) 38 editor.setSelectionWidth(selectionWidth) 39 40 // 命令对象可作为负责人。在这种情况下,命令会在修改原发器状态之前获取一个 41 // 备忘录。当需要撤销时,它会从备忘录中恢复原发器的状态。 42 class Command is 43 private field backup: Snapshot 44 45 method makeBackup() is 46 backup = editor.createSnapshot() 47 48 method undo() is 49 if (backup != null) 50 backup.restore() 51 // ...
示例3

1 #include <string> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <ctime> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 class Memento{ 8 public: 9 virtual string GetName() const = 0; 10 virtual string date() const = 0; 11 virtual string state() const = 0; 12 }; 13 14 class ConcreteMemento:public Memento{ 15 private: 16 string state_; 17 string date_; 18 public: 19 ConcreteMemento(string state):state_(state){ 20 this->state_ = state; 21 time_t now = time(0); 22 this->date_ = ctime(&now); 23 } 24 string state() const override{ 25 return this->state_; 26 } 27 string GetName() const override{ 28 return this->date_ + "/(" + this->state_.substr(0,9)+"...)"; 29 } 30 string date() const override{ 31 return this->date_; 32 } 33 }; 34 35 class Originator{ 36 private: 37 string state_; 38 string GenereateRandomString(int length = 10){ 39 const char alphanum[] = 40 "0123456789" 41 "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ" 42 "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"; 43 int stringLength = sizeof(alphanum) - 1; 44 45 string random_string; 46 for(int i = 0; i < length; i ++){ 47 random_string += alphanum[rand()%stringLength]; 48 } 49 return random_string; 50 } 51 public: 52 Originator(string state):state_(state){ 53 cout << "Originator: My initial state is: " << this->state_ << " "; 54 } 55 56 void DoSomething(){ 57 cout << "Originator: I'm doing something important. "; 58 this->state_ = this->GenereateRandomString(30); 59 cout << "Originator: and my state has changed to: " << this->state_ << " "; 60 } 61 62 Memento *Save(){ 63 return new ConcreteMemento(this->state_); 64 } 65 66 void Restore(Memento *memento){ 67 this->state_ = memento->state(); 68 cout << "Originator: My state has changed to: " << this->state_ << " "; 69 } 70 }; 71 72 class Caretaker{ 73 private: 74 vector<Memento *> mementos_; 75 Originator *originator_; 76 public: 77 Caretaker(Originator *originator):originator_(originator){ 78 this->originator_ = originator; 79 } 80 81 void Backup(){ 82 cout << " Caretaker: Saving Originator's state... "; 83 this->mementos_.push_back(this->originator_->Save()); 84 } 85 void Undo(){ 86 if(!this->mementos_.size()){ 87 return; 88 } 89 Memento *memento = this->mementos_.back(); 90 this->mementos_.pop_back(); 91 cout << "Caretaker: Restoring state to: " << memento->GetName() << " "; 92 try{ 93 this->originator_->Restore(memento); 94 }catch(...){ 95 this->Undo(); 96 } 97 } 98 void ShowHistory() const{ 99 cout << "Caretaker: Here's the list of mementos: "; 100 for(Memento *memento : this->mementos_){ 101 cout << memento->GetName() << " "; 102 } 103 } 104 }; 105 106 void ClientCode(){ 107 Originator *originator = new Originator("Super-duper-super-puper-super."); 108 Caretaker *caretaker = new Caretaker(originator); 109 caretaker->Backup(); 110 originator->DoSomething(); 111 caretaker->Backup(); 112 originator->DoSomething(); 113 caretaker->Backup(); 114 originator->DoSomething(); 115 cout << " "; 116 caretaker->ShowHistory(); 117 cout << " Client: Now, let's rollback! "; 118 caretaker->Undo(); 119 cout << " Client: Once more! "; 120 caretaker->Undo(); 121 delete originator; 122 delete caretaker; 123 } 124 125 int main(){ 126 srand(static_cast<unsigned int>(time(NULL))); 127 ClientCode(); 128 return 0; 129 }

参考
