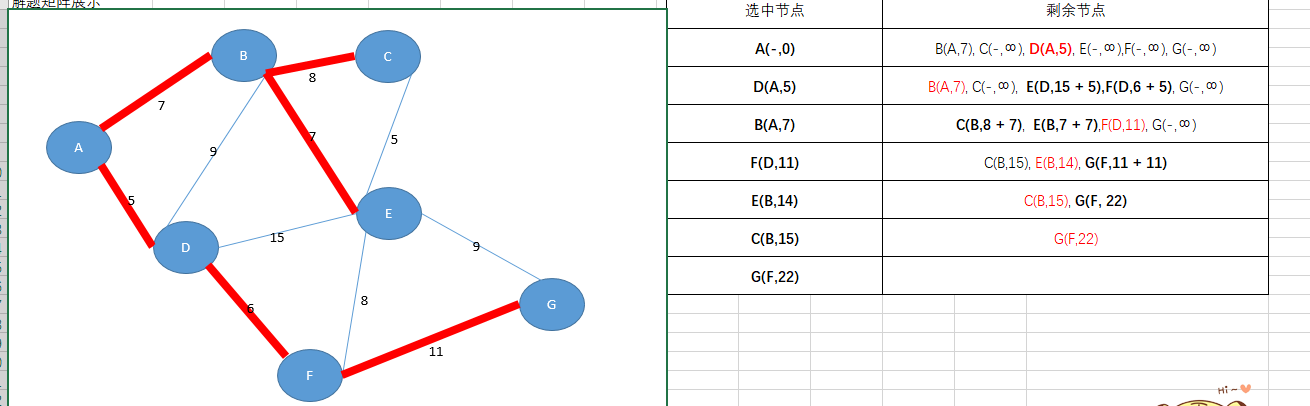
首先看看这换个数据图

邻接矩阵
dijkstra算法的寻找最短路径的核心就是对于这个节点的数据结构的设计
1、节点中保存有已经加入最短路径的集合中到当前节点的最短路径的节点
2、从起点经过或者不经过 被选中节点到当前节点的最短路径
以这个思路开始,就可以根据贪心算法,获取每一步需要设置的值,每一步加入路径的节点
对于这个算法,我采用:小顶堆 + 邻接矩阵(数组)
1、邻接矩阵的初始化
package cn.xf.algorithm.ch09Greedy.vo;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
public class MGraph {
private int eleSize;
private int nums[][];
private List<KruskalBianVo> kruskalBianVos = new ArrayList<KruskalBianVo>();
public MGraph() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public MGraph(int eleSize, int[][] nums) {
this.eleSize = eleSize;
this.nums = nums;
}
public MGraph(File file) throws Exception {
if(file.exists()) {
//读取数据流,获取数据源
FileInputStream fis;
BufferedInputStream bis;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//缓冲
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
byte buffer[] = new byte[1024];
while(bis.read(buffer) != -1) {
String allData = new String(buffer);
String lines[] = allData.split("
");
int allLines = lines.length;
int allColumns = lines[0].split(" ").length;
if(allLines < allColumns) {
//如果行比较小
eleSize = allLines;
} else {
//否则以列为准
eleSize = allColumns;
}
nums = new int[eleSize][eleSize];
for(int i = 0; i < eleSize; ++i) {
//对每一行数据进行入库处理
String everyNums[] = lines[i].split(" ");
for(int j = 0; j < eleSize; ++j) {
nums[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(everyNums[j]);
}
}
}
//获取这个矩阵的所有边 kruskalBianVos
for(int i = 0; i < eleSize; ++i) {
for(int j = i + 1; j < eleSize; ++j) {
if(nums[i][j] < 999) {
KruskalBianVo kruskalBianVo = new KruskalBianVo();
kruskalBianVo.setBeginNode(i);
kruskalBianVo.setEndNode(j);
kruskalBianVo.setLength(nums[i][j]);
kruskalBianVos.add(kruskalBianVo);
}
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
System.out.println("文件不存在");
}
}
public int getEleSize() {
return eleSize;
}
public void setEleSize(int eleSize) {
this.eleSize = eleSize;
}
public int[][] getNums() {
return nums;
}
public void setNums(int[][] nums) {
this.nums = nums;
}
public List<KruskalBianVo> getKruskalBianVos() {
return kruskalBianVos;
}
public void setKruskalBianVos(List<KruskalBianVo> kruskalBianVos) {
this.kruskalBianVos = kruskalBianVos;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = MGraph.class.getResource("").getPath();
path = path.substring(0, path.indexOf("/vo"));
File f = new File(path + "/resource/test.txt");
try {
MGraph mg = new MGraph(f);
System.out.println(mg.getKruskalBianVos().size());
int rr[][] = mg.getNums();
System.out.println(rr);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2、小顶堆的结构
package cn.xf.algorithm.ch09Greedy.vo;
public interface HeapValue {
/**
* 当前对象小于,等于比较对象的时候,返回true
* @param heapValue
* @return
*/
public abstract Boolean compareMin(HeapValue heapValue);
public abstract Object getValue();
public Object getKey();
}
package cn.xf.algorithm.ch09Greedy.util;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import cn.xf.algorithm.ch09Greedy.vo.HeapValue;
/**
* 堆构造以及排序
*
* .功能:堆的构造
* 1、堆可以定义为一颗二叉树,树的节点包含键,并且满足一下条件
* 1) 树的形状要求:这棵二叉树是基本完备的(完全二叉树),树的每一层都是满的,除了最后一层最右边的元素可能缺位
* 2) 父母优势,堆特性,每一个节点的键都要大于或者等于他子女的键(对于任何叶子我们认为这都是自动满足的)
*
* 对于堆:
* 只存在一颗n个节点的完全二叉树他的高度:取下界的 log2的n的对数
* 堆的根总是包含了堆的最大元素
* 堆的一个节点以及该节点的子孙也是一个堆
* 可以用数组的来实现堆,方法是从上到下,从左到右的方式来记录堆的元素。
*
* @author xiaof
* @version Revision 1.0.0
* @see:
* @创建日期:2017年8月25日
* @功能说明:
*
*/
public class HeapDijsstraMin {
private List<HeapValue> heap;
//构造函数
public HeapDijsstraMin() {
//创建堆
heap = new ArrayList<HeapValue>();
}
public HeapDijsstraMin(List<HeapValue> heap) {
//创建堆
this.heap = heap;
createHeadDownToUp(this.heap);
}
/**
* 从小到大的堆
* @param heap
* @return
*/
private void createHeadDownToUp(List<HeapValue> heap){
//对数组进行堆排序
if(heap == null || heap.size() <= 0)
return;
int len = heap.size();
//从树的中间开始循环
for(int i = len / 2; i > 0; --i) {
//首先预存当前进行操作的节点‘
//索引和值
int selectIndex = i - 1;
HeapValue selectValue = heap.get(selectIndex);
boolean isHeap = false; //用来判断当前节点下是否已经没有其他节点比这个节点小了,作为是否成堆的标识
while(!isHeap && 2 * (selectIndex + 1) <= len) {
//当前节点的最大的孩子节点的位置,开始默认是第一个孩子节点的位置
int childIndex = 2 * i - 1;
//判断是否存在两个孩子节点,如果存在,那么就选出最大的那个
if(2 * i < len) {
//获取比较小的那个节点作为备选替换节点
childIndex = heap.get(childIndex).compareMin(heap.get(childIndex + 1)) ? childIndex : childIndex + 1;
}
//判断当前节点是不是比下面最小的那个节点还要小 heap.get(childIndex)
if(selectValue.compareMin(heap.get(childIndex))) {
//如果比下面最大的还大,那就表明这个节点为根的子树已经是一颗树了
isHeap = true;
} else {
//如果节点不是小的,那么更换掉
heap.set(selectIndex, heap.get(childIndex));
//并交换当前遍历交换的节点
selectIndex = childIndex;
//这个节点和子节点全部遍历结束之后,交换出最初用来交换的选中节点
heap.set(selectIndex, selectValue);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 对堆的节点的单次变换
* @param i 第几个节点
*/
private void shifHeadDownToUp(int i) {
if(heap == null || heap.size() <= 0)
return;
int len = this.heap.size();
//索引i需要存在于这个节点中
if(i >= len)
return;
// 首先预存当前进行操作的节点‘
// 索引和值
int selectIndex = i - 1;
HeapValue selectValue = heap.get(selectIndex);
boolean isHeap = false; // 用来判断当前节点下是否已经没有其他节点比这个节点小了,作为是否成堆的标识
while (!isHeap && 2 * (selectIndex + 1) <= len) {
// 当前节点的最大的孩子节点的位置,开始默认是第一个孩子节点的位置
int childIndex = 2 * (selectIndex + 1) - 1;
// 判断是否存在两个孩子节点,如果存在,那么就选出最大的那个
if (2 * (selectIndex + 1) < len) {
// 获取比较小的那个节点作为备选替换节点
// childIndex = heap.get(childIndex) < heap.get(childIndex + 1) ? childIndex : childIndex + 1;
childIndex = heap.get(childIndex).compareMin(heap.get(childIndex + 1)) ? childIndex : childIndex + 1;
}
// 判断当前节点是不是比下面最小的那个节点还要小
if (selectValue.compareMin(heap.get(childIndex))) {
// 如果比下面最大的还大,那就表明这个节点为根的子树已经是一颗树了
isHeap = true;
} else {
// 如果节点不是小的,那么更换掉
heap.set(selectIndex, heap.get(childIndex));
// 并交换当前遍历交换的节点
selectIndex = childIndex;
// 这个节点和子节点全部遍历结束之后,交换出最初用来交换的选中节点
heap.set(selectIndex, selectValue);
}
}
}
//向堆添加元素
public void add(HeapValue element) {
// int oldLen = heap.size();
heap.add(element);
//然后从加入的位置的父节点开始,从下向上所有父节点,全部变换一次
for(int i = heap.size() / 2; i > 0; i = i / 2) {
this.shifHeadDownToUp(i);
}
}
/**
* 移除堆中一个指定元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
// public int remove(int index) {
// int result = heap.get(index - 1);
// //思路是吧剩下的最后一个元素作为参照元素,填充进去
// int lastValue = heap.get(heap.size() - 1);
// heap.set(index - 1, lastValue);
// heap.remove(heap.size() - 1);
// //然后从下向上,吧这个节点对应的位置的数据进行递归
// for(int i = index; i > 0; i = i / 2) {
// this.shifHeadDownToUp(i);
// }
// return result;
// }
public int remove(Object key) {
int index = getKeyIndex(key);
//遍历这个key
if(index == -1) {
return -1;
}
//思路是吧剩下的最后一个元素作为参照元素,填充进去
HeapValue lastValue = heap.get(heap.size() - 1);
heap.set(index, lastValue);
heap.remove(heap.size() - 1);
//然后从下向上,吧这个节点对应的位置的数据进行递归
for(int i = index + 1; i > 0; i = i / 2) {
this.shifHeadDownToUp(i);
}
return index;
}
private int getKeyIndex (Object keyName) {
int index = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < heap.size(); ++i) {
if(keyName.equals(heap.get(i).getKey())) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
return index;
}
private HeapValue getKeyValue (Object keyName) {
int index = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < heap.size(); ++i) {
if(keyName.equals(heap.get(i).getKey())) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
return heap.get(index);
}
/**
* 默认删除根节点
* @return
*/
public HeapValue remove() {
HeapValue result = heap.get(0);
//思路是吧剩下的最后一个元素作为参照元素,填充进去
HeapValue lastValue = heap.get(heap.size() - 1);
heap.set(0, lastValue);
heap.remove(heap.size() - 1);
//然后从下向上,吧这个节点对应的位置的数据进行递归
for(int i = 1; i > 0; i = i / 2) {
this.shifHeadDownToUp(i);
}
return result;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String result = "";
for(int i = 0; i < heap.size(); ++i) {
HeapValue hv = heap.get(i);
result += hv.getValue().toString() +" ";
// System.out.print(hv.getValue().toString() + " ");
}
return result;
}
public int size() {
return heap.size();
}
public HeapValue getIndex(int i) {
return heap.get(i);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
3、标识各个节点的数据结构
package cn.xf.algorithm.ch09Greedy.vo;
/**
*
* 存放节点信息
* .
*
* @author xiaof
* @version Revision 1.0.0
* @see:
* @创建日期:2017年8月30日
* @功能说明:
*
*/
public class DijkstraElementVo implements HeapValue {
private String elementName; //节点名字
private DijkstraElementVo preDijkstraElementVo; //最短路径的上一个节点
private int minLength; //当前节点的从开始起点到当前节点的最短路径
public String getElementName() {
return elementName;
}
public void setElementName(String elementName) {
this.elementName = elementName;
}
public DijkstraElementVo getPreDijkstraElementVo() {
return preDijkstraElementVo;
}
public void setPreDijkstraElementVo(DijkstraElementVo preDijkstraElementVo) {
this.preDijkstraElementVo = preDijkstraElementVo;
}
public int getMinLength() {
return minLength;
}
public void setMinLength(int minLength) {
this.minLength = minLength;
}
@Override
public Boolean compareMin(HeapValue heapValue) {
int value = (Integer) heapValue.getValue();
Boolean result = false;
if(this.minLength <= value)
result = true;
return result;
}
@Override
public Object getValue() {
return minLength;
}
@Override
public Object getKey() {
return elementName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
//a[b,lenght]
String preName = "null";
if(preDijkstraElementVo != null) {
// preName = preDijkstraElementVo.getElementName();
preName = preDijkstraElementVo == null ? "null" : preDijkstraElementVo.getElementName();
}
return elementName + "[" + preName + ", " + minLength + "]";
// return elementName + "[" + preDijkstraElementVo != null ? "null" : preDijkstraElementVo.getElementName() + ", " + minLength + "]";
}
}
4、算法的核心实现
package cn.xf.algorithm.ch09Greedy.dijkstra;
import cn.xf.algorithm.ch09Greedy.util.HeapDijsstraMin;
import cn.xf.algorithm.ch09Greedy.vo.DijkstraElementVo;
import cn.xf.algorithm.ch09Greedy.vo.HeapValue;
import cn.xf.algorithm.ch09Greedy.vo.MGraph;
/**
* 单起点最短路径的dijkstra算法
* 功能:输入:具非负权重加权连通图G = <V, E> 以及它的顶点s
* 输出:对于V中每个顶点v来说,从s到v的最短路径的长度dv
* 以及路径上的倒数第二个顶点pv
* @author xiaofeng
* @date 2017年8月31日
* @fileName DijkstraAlgorithm.java
*
*/
public class DijkstraAlgorithm {
/**
*
* @param mg 图邻接矩阵
* @param start 初始起点
*/
public void dijkstra(MGraph mg, DijkstraElementVo start) {
if(mg == null)
return;
//获取邻接矩阵
int juzhen[][] = mg.getNums();
//先初始化小顶堆的所有节点
HeapDijsstraMin heapDijsstraMin = new HeapDijsstraMin();
for(int i = 0; i < mg.getEleSize(); ++i) {
DijkstraElementVo dijkstraElementVo = new DijkstraElementVo();
char cur = (char) ('A' + i);
dijkstraElementVo.setElementName(String.valueOf(cur));
//路径长度,初始都为无穷大,用999来虚拟
dijkstraElementVo.setMinLength(999);
//路径的上一个节点
dijkstraElementVo.setPreDijkstraElementVo(null);
heapDijsstraMin.add(dijkstraElementVo);
}
//更新初始节点,就是先删除,然后新增进去
heapDijsstraMin.remove(start.getKey());
start.setMinLength(0);
start.setPreDijkstraElementVo(null);
heapDijsstraMin.add(start);
//输出验证一波
// System.out.print(start.toString() + "=>");
//依次遍历所有的节点,并更新对应的节点在堆中的数据
int selected[] = new int[mg.getEleSize()];
while(heapDijsstraMin.size() > 0) {
//当堆中还有节点没有被选中
HeapValue dijkstraHeapValue = (DijkstraElementVo) heapDijsstraMin.remove();
System.out.print(dijkstraHeapValue.toString() + "=>");
//遍历剩下所有,节点,并逐个更新一遍所有的数据
for(int i= 0; i < heapDijsstraMin.size(); ++i) {
//比较当前对象的最短路径,如果比用当前的这个节点到对应的节点的路径长,那么就更新为当前的最短路径
//说白了,就是把当前节点加入路径 中之后,后面节点可以通过这个节点或者不用这个节点和起点的最短距离
String curName = (String) dijkstraHeapValue.getKey();
int cur = curName.toCharArray()[0] - 'A';
int curValue = Integer.valueOf(String.valueOf(dijkstraHeapValue.getValue()));
//获取下一个对象的节点
HeapValue dijkstraHeapValueNext = heapDijsstraMin.getIndex(i);
String nextName = (String) dijkstraHeapValueNext.getKey();
int next = nextName.toCharArray()[0] - 'A';
int nextValue = Integer.valueOf(String.valueOf(dijkstraHeapValueNext.getValue()));
if(curValue + juzhen[cur][next] < nextValue) {
//如果是通过新节点的路径比通过原来的路径小,那么更新路径
DijkstraElementVo dijkstraElementVoNew = new DijkstraElementVo();
dijkstraElementVoNew.setElementName(nextName);
dijkstraElementVoNew.setMinLength(curValue + juzhen[cur][next]);
dijkstraElementVoNew.setPreDijkstraElementVo((DijkstraElementVo) dijkstraHeapValue);
//先移除这个节点,然后新增
heapDijsstraMin.remove(dijkstraHeapValueNext.getKey());
heapDijsstraMin.add(dijkstraElementVoNew);
} //判断是否更新
}
}
}
}
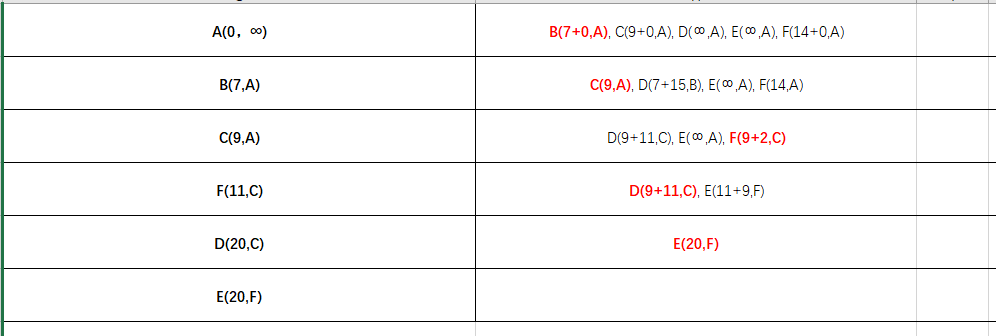
5、结果显示
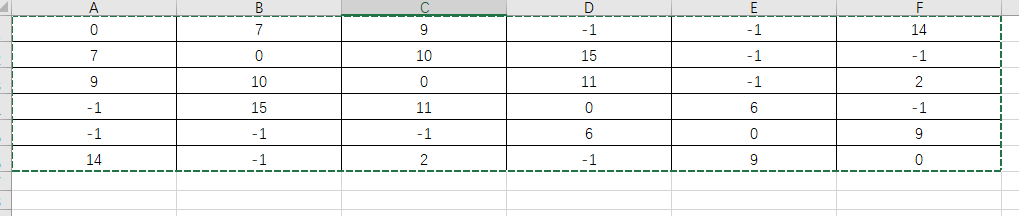
矩阵数据来源:
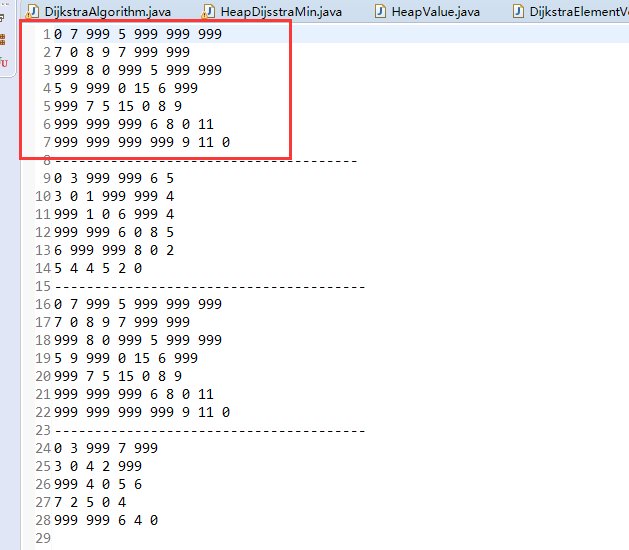
999代表不可到达

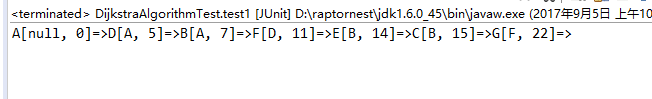
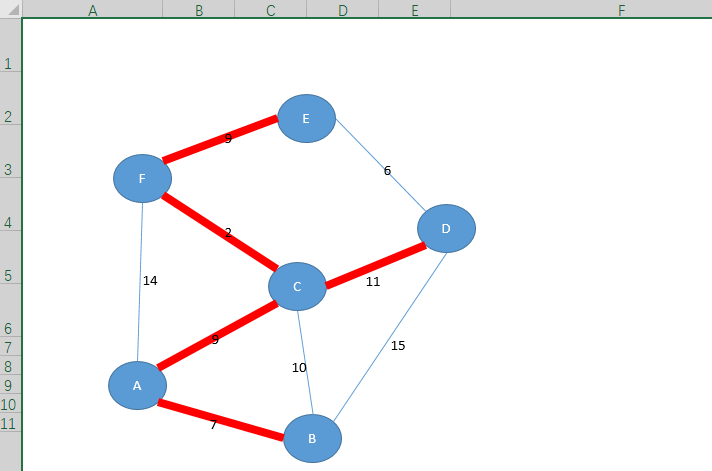
这个题的图解