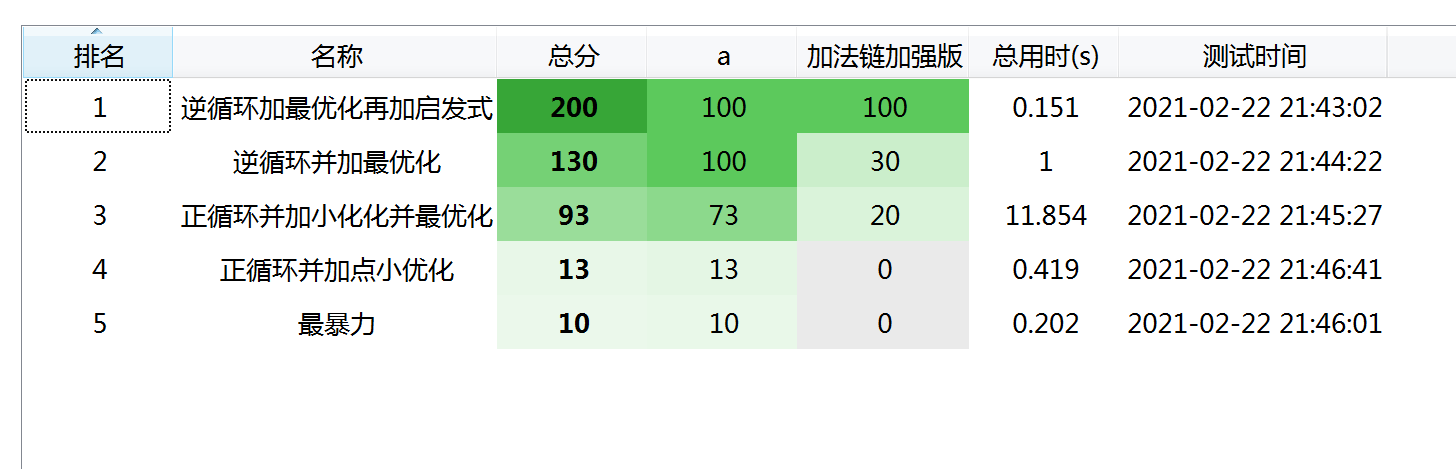
1:最暴力的程序,过前10个点
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int tag[1130],num[1130],n,ans;
int ans1[1100];
void dfs(int dep)
{
if (tag[dep-1]==n)
if (dep-1<ans)
{
ans=dep-1;
return ;
}
for(int i=1;i<=dep-1;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=dep-1;j++)
{
int temp;
temp=tag[i]+tag[j];
if (temp<=n&&temp>tag[dep-1])
{
tag[dep]=temp;
dfs(dep+1);
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
if (n<=2)
{
cout<<n<<endl;
return 0;
}
ans=1000;
tag[1]=1;
tag[2]=2;
dfs(3);
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
Sol2:对枚举优化了下,并及时进行了退出,过13个
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int tag[1130],num[1130],n,ans;
int ans1[1100];
void dfs(int dep)
{
for(int i=1;i<=dep-1;i++)
for(int j=i;j<=dep-1;j++)
{
int temp;
temp=tag[i]+tag[j];
if (temp<=n&&temp>tag[dep-1])
{
if(temp==n&&dep<ans)
{
ans=dep;return;
}
tag[dep]=temp;
dfs(dep+1);
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
if (n<=2)
{
cout<<n<<endl;
return 0;
}
ans=1000;
tag[1]=1;
tag[2]=2;
dfs(3);
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
加上最优化cut,过了72个点,所以最优化剪枝还是很用的。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int tag[1130],num[1130],n,ans;
int ans1[1100];
void dfs(int dep)
{
if (dep>ans)
return ;
for(int i=1;i<=dep-1;i++)
for(int j=i;j<=dep-1;j++)
{
int temp;
temp=tag[i]+tag[j];
if (temp<=n&&temp>tag[dep-1])
{
if(temp==n&&dep<ans)
{
ans=dep;return;
}
tag[dep]=temp;
dfs(dep+1);
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
if (n<=2)
{
cout<<n<<endl;
return 0;
}
ans=1000;
tag[1]=1;
tag[2]=2;
dfs(3);
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
接着对循环进化优化下,改成逆的,全过,用时0.985。
改成逆循环,可以很快得到一个较优解,用于今后的最优化的剪枝
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int tag[1130],num[1130],n,ans;
int ans1[1100];
void dfs(int dep)
{
if (dep>ans)
return ;
for(int i=dep-1;i>=1;i--)
for(int j=i;j>=1;j--)
{
int temp;
temp=tag[i]+tag[j];
if (temp<=n&&temp>tag[dep-1])
{
if(temp==n&&dep<ans)
{
ans=dep;return;
}
tag[dep]=temp;
dfs(dep+1);
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
if (n<=2)
{
cout<<n<<endl;
return 0;
}
ans=1000;
tag[1]=1;
tag[2]=2;
dfs(3);
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
再加上启发式,Ac,用时0.075 并且对于N<=1000,也能通过
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int tag[1100],n,ans=999999;
void dfs(int dep)
{
int temp1=tag[dep-1];
int sum=0;
while(temp1<=n)
{
temp1*=2;
sum++;
}
if(dep+sum-1>=ans)
return;
for(int i=dep-1;i>=1;i--)
for(int j=i;j>=1;j--)
{
int temp=tag[i]+tag[j];
if(temp>tag[dep-1]&&temp<=n)
{
tag[dep]=temp;
if(dep<ans&&tag[dep]==n)
{
ans=dep;
return;
}
dfs(dep+1);
}
}
}
int main()
{
ans=999999;
cin>>n;
if(n<=2)
cout<<n<<endl;
else
{
tag[1]=1;
tag[2]=2;
dfs(3);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
}