STL中的迭代器总是出现各种问题,这个是我在打表达式求值时碰到的...
综合网上的答案,一般来说有两种情况:
第一:访问了非法位置。
一般来说可能在queue为空时取front(),rear(),或者用list时误访最后一个结点,再或是在stack为空时进行了top(),pop()操作等。
一般来说用一下方法解决即可:
(1)在访问链表元素时判断当前迭代器是否指向链表尾
1 list<Boom*>::iterator ite=m_listBoom.begin(); 2 while(ite!=m_listBoom.end()) 3 { 4 (*ite)->BoomShow(hdc); 5 if(ite==m_listBoom.end()) 6 { 7 return ; 8 } 9 ite++; 10 }
这是一段想对图片进行展示的代码,正常情况下红字部分我们是没有必要加的,但当你多次运行该程序时很可能会报错,错误为:list iterator not dereferencable
原因就是误访了尾节点。
(2)栈:
以下是表达式求值的部分代码(把中缀转后缀部分)
我在注释出刚开始是把!s1.empty()的判断放在后面的,于是就不停的报错...是不是很熟悉?
原因其实很简单,我们都知道在top(),pop()操作之前都要先判断栈是否为空
而又因为&&的短路原则,如果栈为空,则&&前面的表达式值为0,不会走后面对top()进行操作的代码,避免了错误
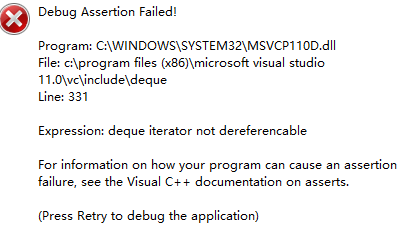
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string.h> 3 #include<stack> 4 using namespace std; 5 stack<char>s1; 6 stack<int>s2; 7 char str[105]; 8 int num[11]; 9 int prior(char c) 10 { 11 if(c==')'||c=='(') return 1; 12 else if(c=='+'||c=='-') return 2; 13 else if(c=='*'||c=='/') return 3; 14 } 15 void getLast(int n) 16 { 17 int i=0; 18 char tmp; 19 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 20 { 21 if(str[i]>='0'&&str[i]<='9') 22 { 23 s2.push(str[i]); 24 if(str[i+1]>='0'&&str[i+1]<='9') 25 { 26 27 } 28 else 29 { 30 s2.push('#'); 31 } 32 } 33 else 34 { 35 if(s1.empty()||prior(str[i])>prior(s1.top())||str[i]=='('/*||!s1.empty()*/) 36 { 37 s1.push(str[i]); 38 } 39 else if(!s1.empty()&&str[i]==')') 40 { 41 while(!s1.empty()&&(s1.top())!='(') 42 { 43 tmp=s1.top(); 44 s2.push(tmp); 45 s1.pop(); 46 } 47 s1.pop(); 48 } 49 else 50 { 51 while(!s1.empty()&&(prior(str[i])<=prior(s1.top())))//注意短路原则,要先判断是否为空为空自然不走后面的代码 52 { //如果把判断是否为空放优先级判断之后,就会出现栈为空却 53 tmp=s1.top(); //试图进行top(),pop()操作的情况 54 s1.pop(); //会出现错误deque iterator not dereferencable 55 s2.push(tmp); //!所以要把s1.empty的判断放前面 56 } 57 s1.push(str[i]); 58 59 } 60 } 61 } 62 while(!s1.empty()) 63 { 64 tmp=s1.top(); 65 s1.pop(); 66 s2.push(tmp); 67 } 68 } 69 int cal(int n) 70 { 71 return 0; 72 } 73 int main() 74 { 75 int n,i; 78 scanf("%s",&str); 79 80 n=strlen(str); 81 char tmp; 82 getLast(n); 83 while(!s2.empty()) 84 { 85 tmp=s2.top(); 86 s2.pop(); 87 printf("%c",tmp); 88 } 89 return 0; 90 }
第二:多线程编程
在多线程编程里面,这种问题也出现的比较多。
两个线程同时访问同一个容器,也会导致出现这种情况。
解决办法:关键代码段。
不建议用互斥内核对象是因为关键代码段是用户层的,调用很快,互斥内核对象调用需要从用户态转入内核态!时间很长!
参考资料:http://blog.csdn.net/midle110/article/details/823858