1.字符类型char
- char是基本的数据类型
- char:保存一个字符,如英文字符、中文字符。
- Java使用unicode表示字符,可以将char赋值给int类型,查看字符对应的unicode编码。
- 使用16进制的unicode编码定义字符
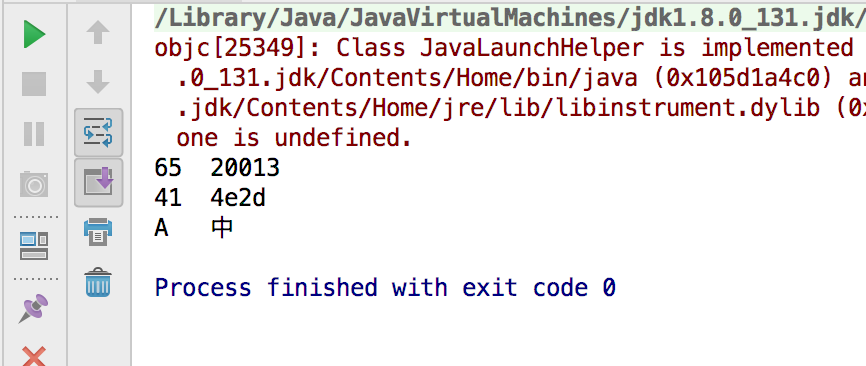
char c1 = 'A';
char c2 = '中';
int n1 = c1;//65
int n2 = c2;//20013
System.out.println(n1+" "+n2);
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(n1)+" "+Integer.toHexString(n2));
//注意是16进制
char c3 = 'u0041';
char c4 = 'u4e2d';
System.out.println(c3+" "+c4);
2.字符串类型
2.1字符串定义
定义字符串:String name;
- 字符串类型是引用类型
- 字符串类型用双引号表示,但内容不包括双引号
- 转译字符
- 常见转译字符: "
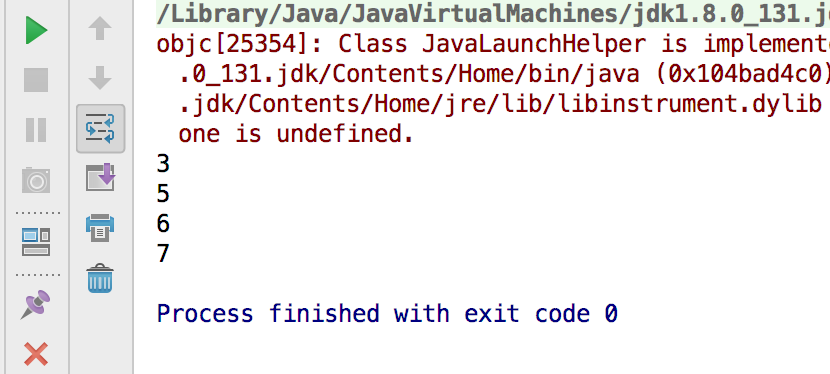
String s1 = "ABC";//3
String s2 = "中文str";//5
String s3 = "Hello
";//6
String s4 = ""Hello"";//7
System.out.println(s1.length());
System.out.println(s2.length());
System.out.println(s3.length());
System.out.println(s4.length());
2.2字符串操作
- 字符串连接用+
- 可以连接字符串和其他数据类型字符串
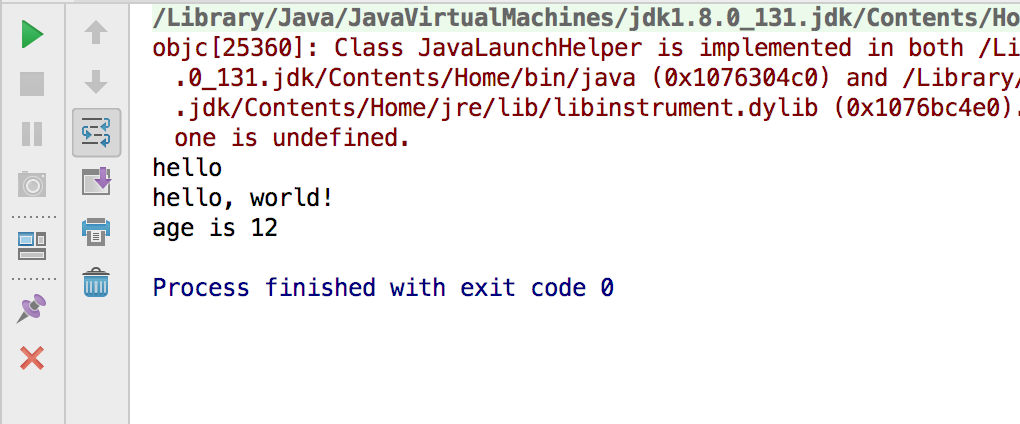
String s= "hello";
System.out.println(s);
String h = "hello, "+ "world!";
System.out.println(h);
String a = "age is "+ 12;
System.out.println(a);
2.3字符串是引用类型
- 字符串不是基本类型
- 字符串是引用类型
- 字符串不可变
引用类型是变量指向某个对象,而不是持有某个对象。
'''#java
String s= "hello";
String t = s;
s = "world!";
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(t);
Intellij单步执行
<img src="https://img2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1418970/201901/1418970-20190109213211216-752206661.jpg" width="500" />
# 3.空值
所有的引用类型都可以指向空值null,即不指向任何对象。
空字符串和空值不一样
```#java
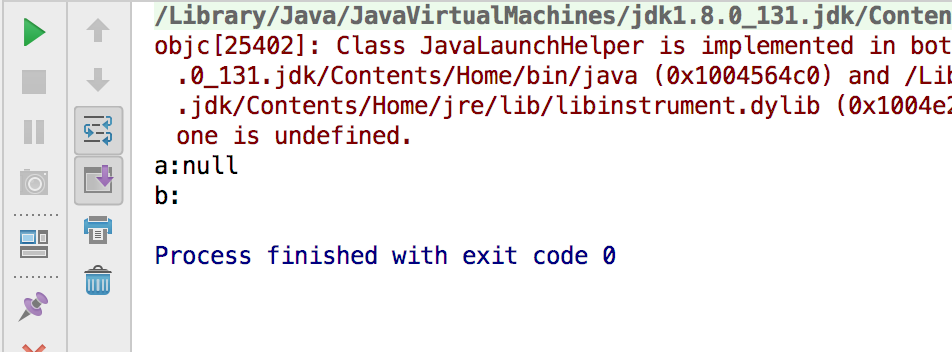
String a = null;
String b = "";
System.out.println("a:"+a);
System.out.println("b:"+b);
4.总结:
- 区分字符类型(基本类型)和字符串类型(引用类型)
- 基本类型的变量是持有某个数值
- 引用类型的变量是指向某个数值
- 引用类型的变量可以是null
- 区分空值(null)和空字符串("")