序列化是一种将对象状态转换为字节流的机制。反序列化是使用字节流在内存中重新创建实际Java对象的反向过程。此机制用于持久化对象。
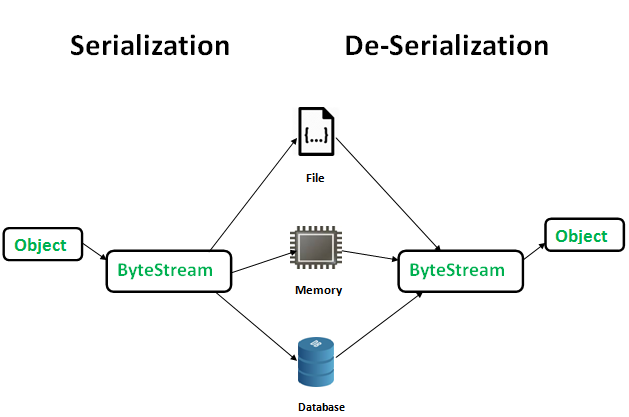
创建的字节流与平台无关。因此,在一个平台上序列化的对象可以在另一个平台上反序列化。
为了使Java对象可序列化,我们实现java.io.Serializable可序列化接口。
ObjectOutputStream类包含writeObject()序列化对象的方法。
public final void writeObject(Object obj) throws IOException
ObjectInputStream类包含readObject()用于反序列化对象的方法。
public final Object readObject() throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException
1、序列化的优点
- 保存/保持对象的状态。
- 在网络中传输一个物体。

只有那些类的对象可以序列化,这些类正在实现java.io.Serializable可序列化接口。
可序列化是标记接口(没有数据成员和方法)。它用于“标记”java类,以便这些类的对象可以获得一定的功能。标记接口的其他示例包括:Cloneable and Remote.
2、要点
1如果父类实现了可序列化接口,则子类不需要实现它,反之亦然。
2只有非静态数据成员通过序列化过程保存。
3static数据成员和transient数据成员不会通过序列化过程保存。所以,如果您不想保存非静态数据成员的值,请将其设为transient。
4反序列化对象时从不调用对象的构造函数。
5关联对象必须实现可序列化接口。
例子:
class A implements Serializable{ // B also implements Serializable // interface. B ob=new B(); }
3、SerialVersionUID(序列号)
序列化运行时将一个版本号与每个称为SerialVersionUID的可序列化类相关联,在反序列化过程中使用该序列号验证序列化对象的发送方和接收方是否为该对象加载了与序列化兼容的类。如果接收方为对象加载的类的UID与相应发送方类的UID不同,则反序列化将导致InvalidClassException. 可序列化类可以通过声明字段名来显式声明自己的UID。
它必须是static、final和long类型。
l例如:(public/private/protected/default) static final long serialVersionUID=42L;
如果可序列化类没有显式声明serialVersionUID,则序列化运行时将根据类的各个方面为该类计算默认值,如Java对象序列化规范中所述。但是,强烈建议所有可序列化类显式声明serialVersionUID值,因为它的计算对类细节高度敏感,这些细节可能因编译器实现而异,因此类中的任何更改或使用不同的id都可能影响序列化的数据。
还建议对UID使用private修饰符,因为它作为继承成员没有用处。
4、serialver(串行器)
serialver是JDK附带的工具。它用于获取Java类的serialVersionUID号。
您可以运行以下命令来获取serialVersionUID
serialver [-classpath classpath] [-show] [classname…]

例1:
// Java code for serialization and deserialization // of a Java object import java.io.*; class Demo implements java.io.Serializable { public int a; public String b; // Default constructor public Demo(int a, String b) { this.a = a; this.b = b; } } class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Demo object = new Demo(1, "geeksforgeeks"); String filename = "file.ser"; // Serialization try { //Saving of object in a file FileOutputStream file = new FileOutputStream(filename); ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(file); // Method for serialization of object out.writeObject(object); out.close(); file.close(); System.out.println("Object has been serialized"); } catch(IOException ex) { System.out.println("IOException is caught"); } Demo object1 = null; // Deserialization try { // Reading the object from a file FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(filename); ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(file); // Method for deserialization of object object1 = (Demo)in.readObject(); in.close(); file.close(); System.out.println("Object has been deserialized "); System.out.println("a = " + object1.a); System.out.println("b = " + object1.b); } catch(IOException ex) { System.out.println("IOException is caught"); } catch(ClassNotFoundException ex) { System.out.println("ClassNotFoundException is caught"); } } }
输出:
Object has been serialized Object has been deserialized a = 1 b = geeksforgeeks
例2:
// Java code for serialization and deserialization // of a Java object import java.io.*; class Emp implements Serializable { private static final long serialversionUID = 129348938L; transient int a; static int b; String name; int age; // Default constructor public Emp(String name, int age, int a, int b) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.a = a; this.b = b; } } public class SerialExample { public static void printdata(Emp object1) { System.out.println("name = " + object1.name); System.out.println("age = " + object1.age); System.out.println("a = " + object1.a); System.out.println("b = " + object1.b); } public static void main(String[] args) { Emp object = new Emp("ab", 20, 2, 1000); String filename = "shubham.txt"; // Serialization try { // Saving of object in a file FileOutputStream file = new FileOutputStream (filename); ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream (file); // Method for serialization of object out.writeObject(object); out.close(); file.close(); System.out.println("Object has been serialized " + "Data before Deserialization."); printdata(object); // value of static variable changed object.b = 2000; } catch (IOException ex) { System.out.println("IOException is caught"); } object = null; // Deserialization try { // Reading the object from a file FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream (filename); ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream (file); // Method for deserialization of object object = (Emp)in.readObject(); in.close(); file.close(); System.out.println("Object has been deserialized " + "Data after Deserialization."); printdata(object); // System.out.println("z = " + object1.z); } catch (IOException ex) { System.out.println("IOException is caught"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { System.out.println("ClassNotFoundException" + " is caught"); } } }
输出:
Object has been serialized Data before Deserialization. name = ab age = 20 a = 2 b = 1000 Object has been deserialized Data after Deserialization. name = ab age = 20 a = 0 b = 2000
输出说明:
在反序列化对象时,您已经看到a和b的值发生了更改。原因a是transient修饰 ,b是static修饰。
transient:在序列化过程中,使用transient关键字定义的变量未序列化。在反序列化期间,将使用默认值初始化此变量。(例如:Object为null,int为0)
static:使用static关键字定义的变量在序列化过程中未序列化。在反序列化期间,将使用类中定义的当前值加载此变量。