C++Primer第五版习题解答---第一章
ps:答案是个人在学习过程中书写,可能存在错漏之处,仅作参考。
作者:cosefy
Date: 2022/1/7
第一章:开始
练习1.3
#include<iostream>
int main() {
std::cout << "hello, world" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
练习1.4:
#include<iostream>
int main()
{
int v1 = 0, v2 = 0;
std::cout << "please input two numbers: " << std::endl;
std::cin >> v1 >> v2;
std::cout << "The product of " << v1 << " and " << v2 << " is: " << v1 * v2 << std::endl;
return 0;
}
练习1.5:
#include<iostream>
int main()
{
int v1 = 0, v2 = 0;
std::cout << "please input two numbers: " << std::endl;
std::cin >> v1 >> v2;
std::cout << "The product of ";
std::cout << v1;
std::cout << " and ";
std::cout << v2;
std::cout << " is: ";
std::cout << v1 * v2;
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
练习1.6:
结果如下图所示,存在报错,显然格式不合法。
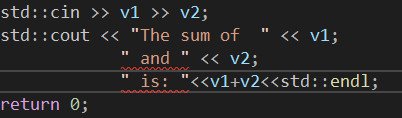
错误原因:输出流表示的格式不正确。
修改格式为:
std::cout << "The sum of " << v1;
std::cout<< "and " << v2;
std::cout<<"is: "<<v1+v2<<std::endl;
运行结果:
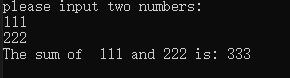
练习1.7:
不正确的嵌套程序:
#include<iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout<<"hello,C++" << std::endl;
/*
*int v1 = 0;
*/*std::cin >> v1 * /
*/
return 0;
}
错误信息:

练习1.8:
部分代码如下:
std::cout << "/*";
std::cout << "
";
std::cout << "*/";
std::cout << "
";
//std::cout << /*"*/"*/;
std::cout <</*"*/"/*"/*"*/;
运行结果:

代码中只有被注释的该行的输出会发生错误,错误原因是界定符不可以嵌套。
练习1.9:
#include<iostream>
int main()
{
//编写程序,使用while循环将50-100的整数相加
int val = 50, sum = 0;
while (val <= 100)
{
sum += val;
++val;
}
std::cout << "Sum of 50 to 100 inclusive is: " << sum << std::endl;
return 0;
}
练习1.10:
#include<iostream>
int main()
{
//使用递减运算符(--),实现按递减顺序输出10-0之间的整数
int val = 10;
while (val >= 0)
{
std::cout << val << " ";
--val;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
练习1.11:
#include<iostream>
int main()
{
//用户输入两个整数,打印出俩整数范围内所有整数
std::cout << "please input two numbers: " << std::endl;
int a = 0, b = 0;
std::cin >> a >> b;
if (a <= b)
{
int temp = b;
b = a;
a = temp;
}
while (b <= a)
{
std::cout << b << " ";
b++;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
练习1.12:
for循环使得i从-100增加到100,同时每次循环里,会执行 sum+=i代码
易知,最终sum=0。
练习1.13:
#include<iostream>
int main()
{
//练习9
int sum1 = 0;
for (int val = 50; val <= 100; val++)
sum1 += val;
std::cout << "The sum is: " << sum1 << std::endl;
//练习10
for (int i = 10; i >= 0; i--)
std::cout << i << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
//练习11
std::cout << "please input two numbers: " << std::endl;
int a = 0, b = 0;
std::cin >> a >> b;
if (a <= b)
{
int temp = b;
b = a;
a = temp;
}
for (; b <= a; b++)
std::cout << b << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
练习1.14:
比较for循环和while循环的优缺点:
1.在for循环中,循环控制变量的初始化和修改都放在语句头部分,形式较简洁,且特别适用于循环次数已知的情况。
2.在while循环中,循环控制变量的初始化一般放在while语句之前,循环控制变量的修改一般放在循环体中,形式上不如for语句简洁,但它比较适用于循环次数不易预知的情况(用某一条件控制循环)。
3.两种形式各有优点,但它们在功能上是等价的,可以相互转换。
练习1.15:
#include<iostream>
int main()
{
//语法错误syntax error:例如
/*
1,单行命令结尾忘记写分号
2,字符串输出忘记加双引号
3,main的参数列表忘记了
4,大括号,破折号,引号等没有对等好
*/
//类型错误type error:
/*
例如,定义的是int型变量,却传入了一个字符型数据
*/
//声明错误declaration error
/*
应用未声明的变量: 如用cin忘记添加std::或者用变量i却没有定义
*/
}
练习1.16:
#include<iostream>
int main()
{
//从cin读取一组数,求和
std::cout << "请输入一组数: " << std::endl;
int value, sum=0;
while (std::cin >> value)//windows系统中文件结束符是Ctrl+Z,然后回车键。
sum += value;
std::cout << "The sum is: " << sum << std::endl;
return 0;
}
此例中while循环结束的标志是:
1,遇到文件结束符
2,遇到一个无效的输入,比如非整数。
练习1.17:
如果输入值都相等,结果只输出一句语句来显示该值出现了多少次。
如果输入值都不相等,则每个值结束输入都会打印出该值出现了一次。
练习1.18:
输入相等的值:

输入不等的值:
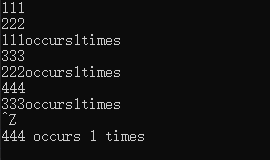
练习1.19:
上面写的原程序已经做过两次输入数的大小判断处理。
练习1.20:
#include<iostream>
#include"Sales_item.h"
int main()
{
Sales_item book;
std::cin >> book;
std::cout << "The record: " << book << std::endl;
return 0;
}
练习1.21:
#include<iostream>
#include"Sales_item.h"
int main()
{
Sales_item item1,item2;
std::cin >>item1>>item2;
if(item1.isbn() == item2.isbn())
{
std::cout << "The record: " << item1 + item2 << std::endl;
return 0;
}
else
{
std::cout << "Error:different ISBN" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
}
练习1.22:
#include<iostream>
#include"Sales_item.h"
int main()
{
Sales_item item,result;
if (std::cin >> result)
{
while (std::cin >> item)
{
if (result.isbn() == item.isbn())
result += item;
else
{
std::cout << "Error:different ISBN" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
}
std::cout << "The final record: " << result << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}